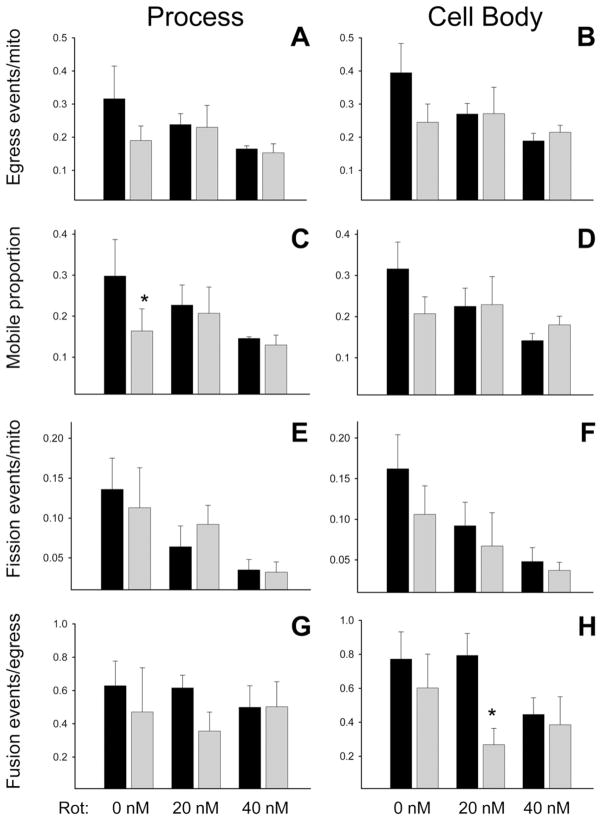
Fig. 5.
In the presence of contact co-cultured neurons, astrocytic DJ-1 knock-down reduced mitochondrial motility in untreated astrocyte processes and mitochondrial fusion in rotenone-treated astrocyte cell bodies. Control (black bars) and DJ-1 knock-down (gray bars) astrocytes were co-transfected with mtDsRed2 and mtPAGFP, and then treated for 24 h with 0, 20, or 40 nM rotenone. Astrocyte mitochondrial egress events (A–B), mobile proportions (C–D), fission events (E–F), and fusion events (G–H) were calculated in cellular processes (A, C, E, G) and cell bodies (B, D, F, H). Asterisks (*) represent P<0.05 for same-treatment comparisons made between control and DJ-1 knock-down astrocytes by paired t-tests. Mean±SE shown, n=6. (A) In astrocyte processes, DJ-1 knock-down caused a trend towards reduced mitochondrial egress only in untreated cells. (B) In astrocyte cell bodies, a similar pattern was seen. (C) In astrocyte processes, DJ-1 knock-down reduced the mitochondrial mobile proportion only in untreated cells. (D–G) DJ-1 knock-down did not affect the mitochondrial mobile proportion in astrocyte cell bodies (D), mitochondrial fission in astrocyte processes (E) or cell bodies (F), or mitochondrial fusion in astrocyte processes (G). (H) In astrocyte cell bodies, DJ-1 knock-down reduced mitochondrial fusion in cells treated with 20 nM rotenone, but the effect at 40 nM was obscured by a similar reduction in fusion induced by rotenone.