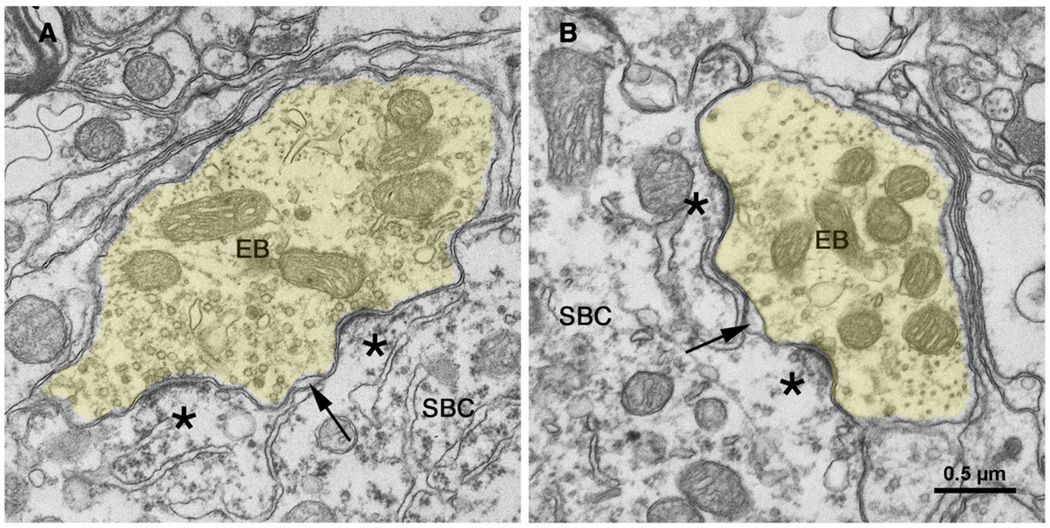
Figure 11.
Electron micrographs through synapses of endbulbs (EB) from cats with normal hearing [135]. The endbulb (yellow) forms synapses opposite dome-shaped postsynaptic densities (*) and round synaptic vesicles accumulate along the presynaptic membrane. Cisternae (arrow) form between the membrane of the endbulb and that of the postsynaptic spherical bushy cell (SBC); these intermembraneous channels may serve as “gutters” to facilitate transmitter diffusion away from the synapse. Scale bar equals 0.5 µm. [135] (O'Neil, JN, Limb, CJ, Baker, CA, et al. Bilateral effects of unilateral cochlear implantation in congenitally deaf cats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010;518: 2382–2404, with permission.)