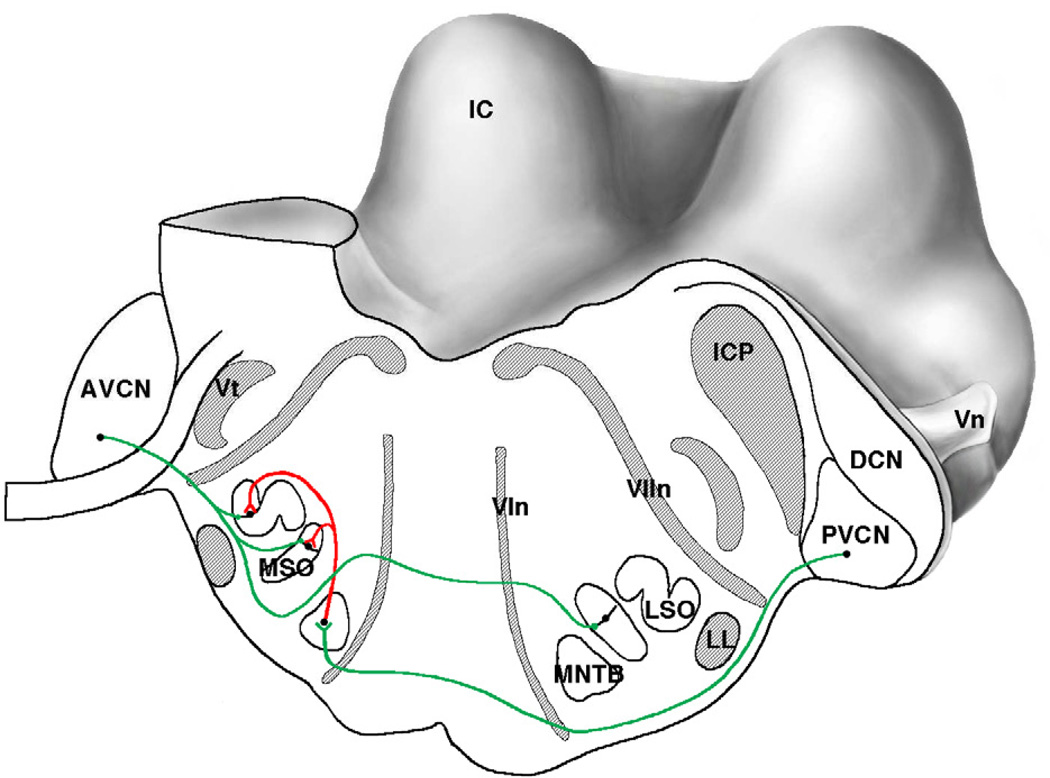
Figure 13.
Caudal-lateral view of the cat brain stem where the cut surface passes through the superior olivary complex. The cut is angled so that it also passes through different parts of the cochlear nucleus on the left and right. The excitatory path from the spherical bushy cells of the left anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) initiates processing of interaural timing differences in the medial superior olive (MSO) and interaural level differences in the lateral superior olive (LSO). The excitatory path from globular bushy cells of the right posteroventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN) initiates the processing of interaural level differences, and its target is the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB). The output of the MNTB is inhibitory (red) and it terminates in the MSO and LSO. Abbreviations: AVCN, anteroventral cochlear nucleus; DCN, dorsal cochlear nucleus; IC, inferior colliculus; ICP, inferior cerebellar peduncle; LL, lateral lemniscus; LSO, lateral superior olive; MNTB, medial nucleus of the trapezoid body; MSO, medial superior olive; VIn, abducens (6th) nerve root; VIIn, facial (7th) nerve root; Vn, trigeminal (5th) cranial nerve; Vt, spinal trigeminal tract. (Drawn by Catherine Connelly, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney, Australia.)