Figure 1.
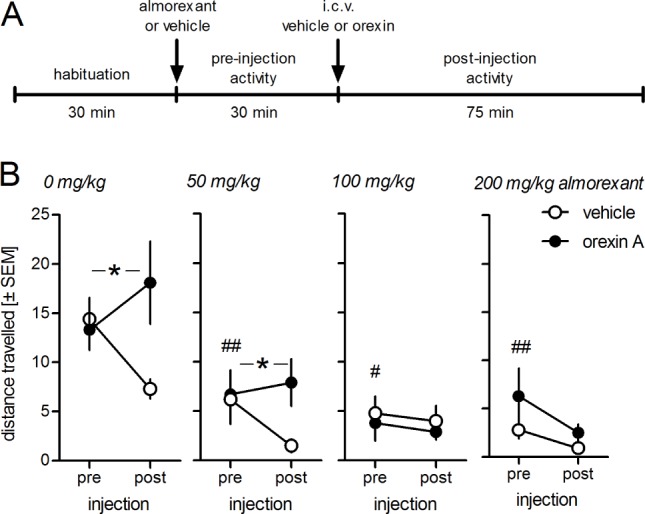
Almorexant blocks orexin-induced locomotion in C57BL/6 mice. A, Design of experiment. Each mouse was tested once and received either vehicle (0 mg/kg almorexant) or a given dose of almorexant prior to recording 30 min of baseline activity (N = 10-12/group). After recording baseline activity half the mice received 3 μg orexin A intracerebroventricular (icv) or an equal volume of vehicle and activity was recorded for a further 75 min. B, Data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of the total distance traveled in the 30 min prior to icv injection of 3 μg orexin (pre) and for 75 min after icv injections (post). Almorexant at doses from 50 mg/kg by mouth significantly reduced baseline locomotor activity and abolished the stimulatory effect of orexin at 100 and 200 mg/kg. *P < 0.05 interaction icv injection × time, i.e. stimulatory effect of orexin; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, baseline activity with almorexant versus baseline activity with vehicle pretreatment.
