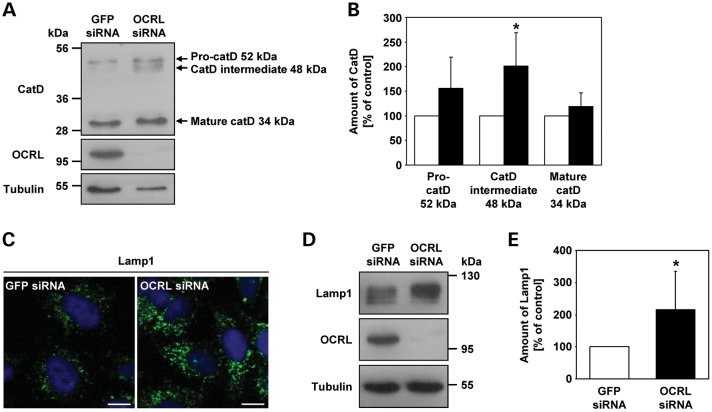
Figure 12.
Depletion of OCRL results in increased amounts of the cathepsin D intermediate form and the lysosomal protein Lamp1. (A) RNAi-treated HeLa cells were harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-cathepsin D (catD) antibody (representative immunoblot—top panel). OCRL depletion was monitored by immunoblotting with an anti-OCRL antibody (middle panel), and an anti-tubulin antibody was used as loading control (lower panel). (B) Amounts of pro-cathepsin D (52 kDa), cathepsin D intermediate (48 kDa) and mature cathepsin D (34 kDa) were determined by scanning densitometry and normalization to tubulin. The amount of each cathepsin D form in OCRL-depleted cells is expressed as percentage of control cells (white square GFP siRNA, black square OCRL siRNA). Each bar is the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. *P = 0.024 (two-tailed Student's t-test). (C) HeLa cells were treated with OCRL- or GFP-specific siRNA, fixed and analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cells were stained with an anti-Lamp1 antibody, followed by an AlexaFluor488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). The nucleus was visualized with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) RNAi-treated HeLa cells were harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-Lamp1 antibody (representative immunoblot—top panel). Depletion of OCRL was monitored by immunoblotting with an anti-OCRL antibody (middle panel), and an anti-tubulin antibody was used as loading control (lower panel). (E) The Lamp1 amount was determined by scanning densitometry and normalization to tubulin. The amount of Lamp1 in OCRL-depleted cells is expressed as percentage of control cells. Each bar is the mean ± SD of seven independent experiments. *P = 0.025 (two-tailed Student's t-test).