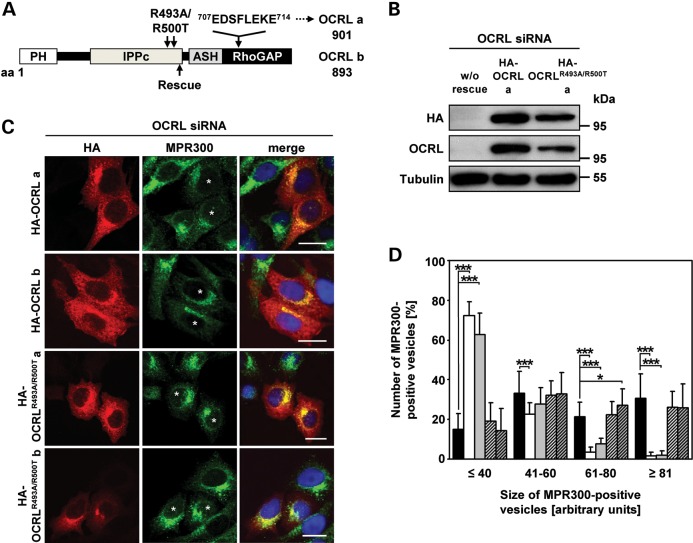
Figure 6.
The 5-phosphatase activity of OCRL is required for proper localization of MPR300. (A) Schematic view of the OCRL domain structure of isoforms a and b. The position of the siRNA-resistant rescue sequence is indicated by an arrow below the domain structure. The eight additional amino acids encoded by exon 18a in isoform a and amino acid substitutions for producing the 5-phosphatase-inactive OCRL variants are indicated above the domain structure. The first and last amino acid residues of OCRL isoforms a and b are given. PH, pleckstrin homology; IPPc, inositol polyphosphate phosphatase, catalytic; ASH, ASPM, SPD-2, hydin; RhoGAP, Rho GTPase activating protein. (B–D) HeLa cells were treated with siRNA against OCRL for 72 h, followed by transfection with siRNA-resistant constructs expressing HA-tagged wild-type OCRL isoform a or b (HA-OCRL a, HA-OCRL b) or 5-phosphatase-inactive OCRL isoform a or b (HA-OCRLR493A/R500T a, HA-OCRLR493A/R500T b), prior to cell lysis or fixation for immunofluorescence analysis. (B) After cell lysis, siRNA-resistant OCRL variants were detected by immunoblotting using an anti-HA-HRP antibody. Depletion was monitored by immunoblotting with an anti-OCRL antibody, and an anti-tubulin antibody was used as loading control. The blot shows a representative result obtained upon expression of wild-type and 5-phosphatase-deficient OCRL isoform a. The same results were obtained after expression of both OCRL isoform b variants (data not shown). (C) siRNA-resistant OCRL variants were detected by staining cells with an anti-HA antibody, followed by an AlexaFluor546-conjugated secondary antibody (red). MPR300 localization was visualized by using an anti-MPR300 antibody, followed by an AlexaFluor488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). * indicates cells transfected with an siRNA-resistant OCRL construct. The nucleus was visualized using DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 µm. (D) Quantification of MPR300-positive vesicles of various sizes was performed by the Metamorph software. To enable direct comparison, all images were taken under the same magnification and laser intensity settings. Sizes of MPR300-positive structures are given in arbitrary units (AU). The number of MPR300-positive vesicles per AU (≤40, 41–60, 61–80 and ≥81) is given as percentage of the number of vesicles counted in total. Results are from three independent experiments with a total of 20 cells per condition counted and are shown as the mean ± SD (black square OCRL siRNA, white square OCRL siRNA+HA-OCRL a, gray square OCRL siRNA+HA-OCRL b, square with cross lines OCRL siRNA+HA-OCRLR493A/R500T, a shaded square with cross lines OCRL siRNA+HA-OCRLR493A/R500T b). *P = 0.025; ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t-test).