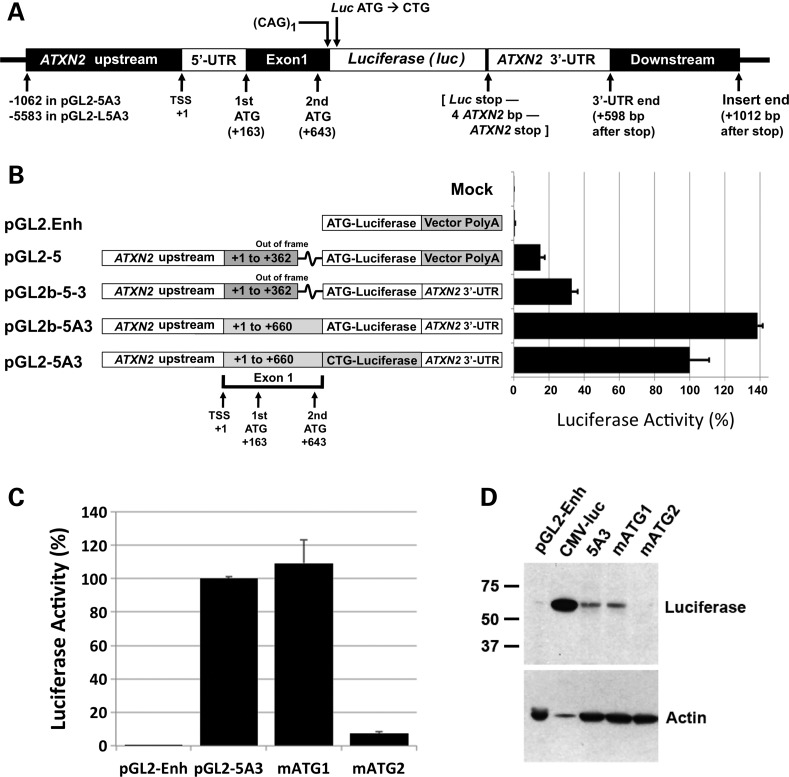
Figure 1.
Cloning of pGL2-5A3 and evaluation of start codons. (A) Features of pGL2-5A3, the principal clone from which most other constructs in the study were made. pGL2-5A3 includes −1062 to +660 of the ATXN2 gene ending on the first CAG of the CAG tract followed by an XhoI restriction site. The luciferase start codon was mutated to CTG, encoding leucine, so to fuse the ataxin-2 fragment with luciferase. Downstream of the luciferase stop codon is an AgeI restriction site followed by 1019 bp of ATXN2 3′-UTR and downstream sequence (+4098 to +5116). ATXN2 bp positions are relative to the TSS except as indicated in the figure. (B) Representation of the cloning process from top to bottom, comparing pGL2-5A3 to three of its ‘ancestral’ plasmids and the vector from which they were made, pGL2.Enhancer (pGL2.Enh). Colored boxes indicate differences among the cloned regions. Note that addition of the ‘A’ fragment of ATXN2 exon 1 in pGL2b-5A3 placed the longer exon 1 fragment in frame with luciferase. On the right are the results of assays showing how expression of luciferase differed among these plasmids. Shown are the mean ± SD of RLUfirefly/RLURenilla values from three independent transfections each read in triplicate, expressed as a percentage. (C) Relative use of the two start codons in ATXN2. Luciferase assays were conducted to compare expression from pGL2-5A3 with two plasmids where either of the two start codons were mutated to CTG, pGL2-5A3(mATG1) and pGL2-5A3(mATG2). Mutation of the second start codon resulted in nearly complete loss of ATXN2-luc expression, while mutation of the first start codon resulted in no expression change. The data shown are for HEK293 cells. The experiment conducted in SH-SY5Y cells showed a nearly identical result. (D) Western blot analysis with anti-luciferase antibody of proteins expressed from pGL2-5A3, pGL2-5A3(mATG1) and pGL2-5A3(mATG2) in HEK293 revealed ATXN2-luc proteins of the size predicted for the usage of the second start codon. Note that lane 2 was purposefully underloaded.