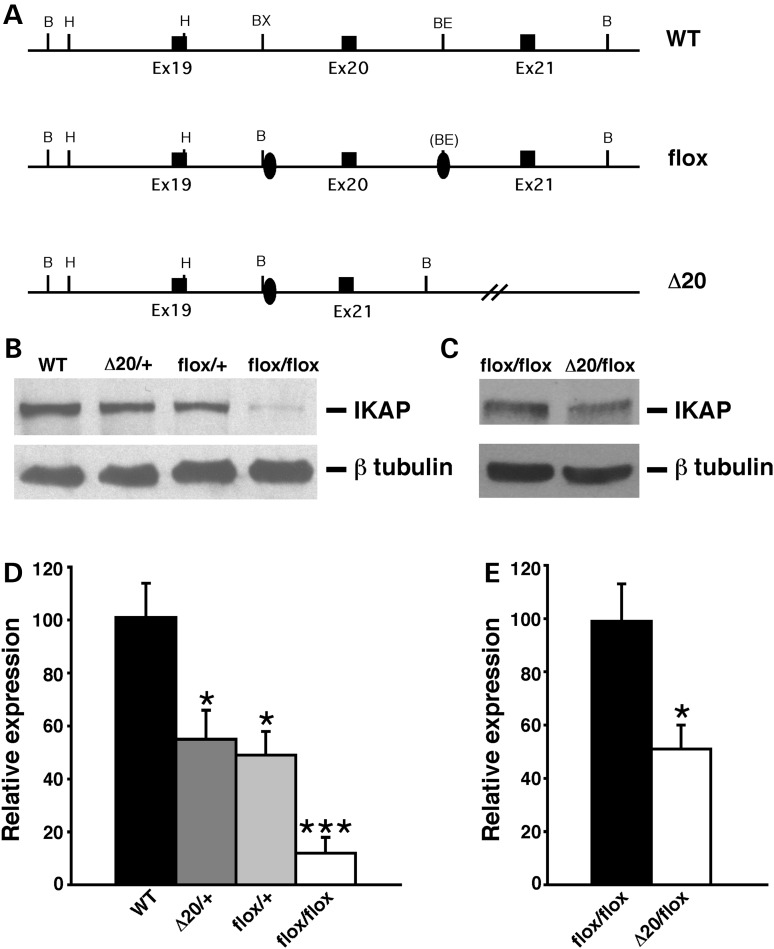
Figure 1.
Generation and molecular characterization of FD mouse models. (A) Schematic representation of the wild-type allele (WT), Ikbkapflox allele (flox) and Ikbkap allele lacking exon 20 (Δ20). Exons are represented by black rectangles, and the loxP sites by black ovals. Restriction sites shown on the schematic are: Bam HI (B), HindIII (H), BstXI (BX) and BstEII (BE). (B) Western analyses of total protein lysates from the forebrain of 11-month-old WT, IkbkapΔ20/+, Ikbkapflox/+ and Ikbkapflox/flox mice. The upper panel shows the detection of IKAP with the polyclonal anti-IKAP antibody (AnaSpec), and the lower panel shows anti-β-tubulin staining for loading control. Note that the IKAP protein level is severely reduced in Ikbkapflox/flox brain. (C) Western analyses of total protein lysates from the whole brain of E16.5 Ikbkapflox/flox and IkbkapΔ20/flox embryos. The upper panel shows the detection of IKAP with the polyclonal anti-IKAP antibody (AnaSpec), and the lower panel shows anti-β-tubulin staining for loading control. Note that in the IkbkapΔ20/flox brain IKAP protein expression is reduced compared with the Ikbkapflox/flox brain. (D and E) Quantitative analyses of IKAP expression levels in mouse brains of different genotypes. (D) IKAP expression levels were normalized over tubulin levels and are expressed as percentage of WT. (E) IKAP expression levels were normalized over tubulin levels and are expressed as percentages of Ikbkapflox/flox. Data are represented as mean ± SD; n = 3 experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.