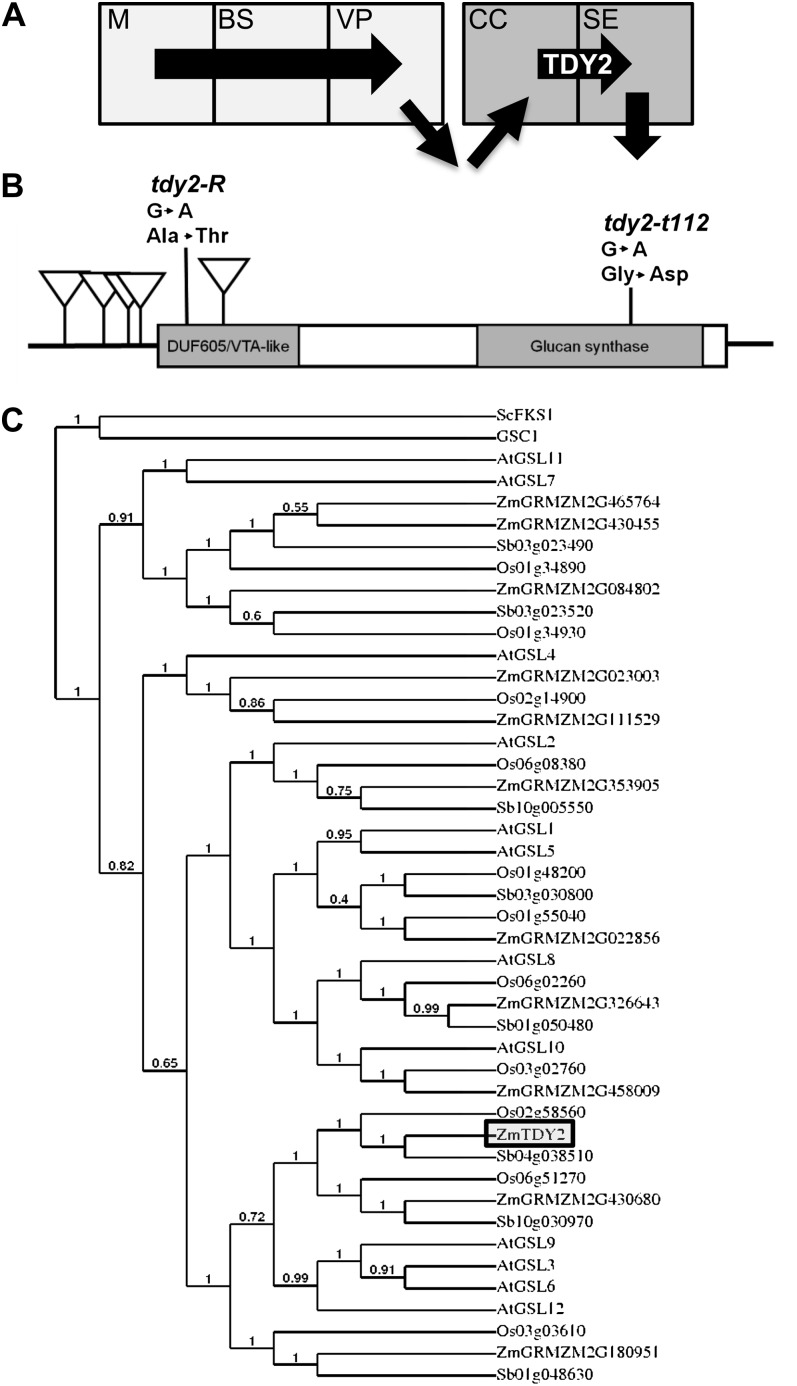
Figure 1.
Tdy2 cloning and phylogenetic analysis. A, Simplified path of Suc movement in a maize leaf (arrows). Suc is synthesized in M cells, moves into BS cells, and then into VP cells through PD. Suc is exported to the apoplast and then imported into the CC. Suc moves through the PD into the SE and then into the adjoining SE (downward arrow). TDY2 promotes Suc trafficking through the CC-SE PD. B, Schematic of the Tdy2 mRNA showing the location of seven identified mutant alleles. Mu transposon insertions are represented as downward triangles. Mutations in two EMS-derived alleles, tdy2-R and tdy2-t112, and the resulting amino acid changes are also shown. Boxes indicate protein-coding regions, and lines represent the 5′ and 3′ UTRs. Shaded boxes indicate conserved domains in the protein sequence. C, Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis of full-length callose synthase proteins. At, Arabidopsis; Os, rice; Sb, sorghum, Zm, maize. Numbers on the tree branches indicate support values as a fraction of 1. The β-1,3-glucan synthases GSC1 (XP_721429) from Candida albicans and ScFKS1 (EEU05506) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae were used as outgroups.