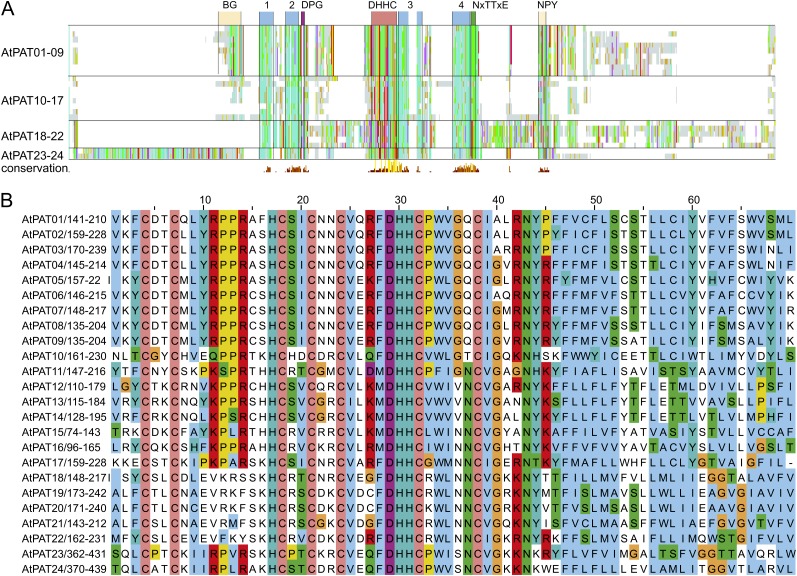
Figure 2.
Alignment of Arabidopsis PAT proteins. A, Alignment overview of Arabidopsis PAT proteins. Light-gray lines/bars indicate the respective position of amino acid. Conserved amino acids were decorated using the ClustalX color code. In addition, coloring was performed group-wise (AtPATs 1–9, 10–17, 18–22, and 23–24) to identify conserved blocks within subgroups. Below, the histogram displays the degree of conservation (large yellow bar represents conserved amino acids). Only the central DHHC-CRD is highly conserved in all proteins. Upstream and downstream hydrophobic stretches are indicated as blue boxes (1–4), as well as the position of short, conserved peptide sequences (DPG in purple and NxTTxE in green), which follow the second and fourth hydrophobic stretch. AtPATs 1 to 9 contain a conserved N-terminal region that contains several basic and Gly residues (BG). A less conserved region was discovered in the C-terminal region, which in most proteins consists of the amino acid sequence NPYxxGxxxN. B, Alignment of the central DHHC-CRD domain. Coloring of conserved amino acids was performed according to the ClustalX specifications. Coloring was applied to all proteins as one group. Cys residues (orange) are invariant amino acids, as well as the central DHHC peptide. The DHHC peptide is followed by a hydrophobic stretch of amino acids. Further upstream, a [KR]PPR peptide is nearly conserved in all Arabidopsis PATs but missing in the PAT group 18–22. Number range after the protein name and diagonal slash (e.g. 141–210 in AtPAT01) give the amino acid positions within the protein. Numbers above the alignment give the position of an amino acid within the alignment. [See online article for color version of this figure.]