Figure 1.
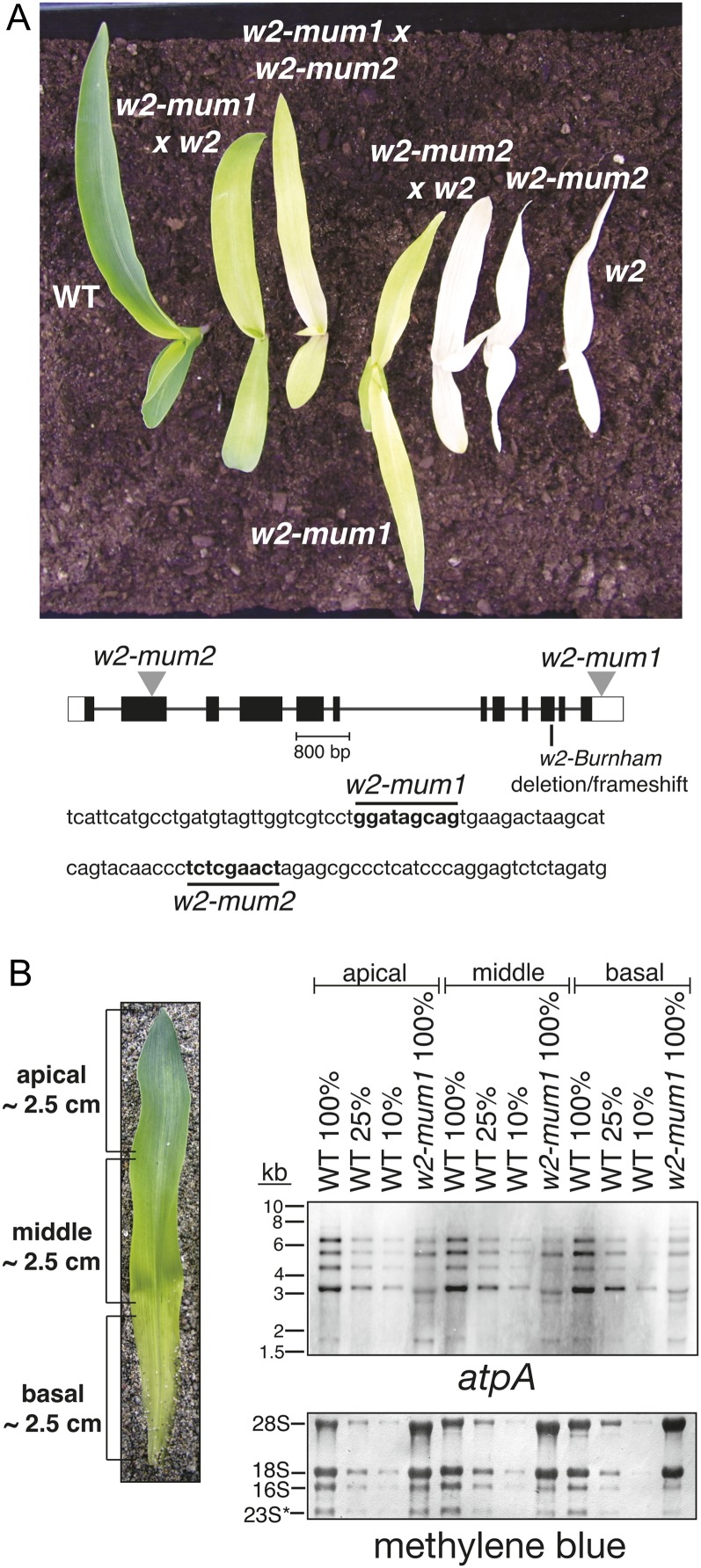
Overview of w2 mutant alleles. A, Seedling phenotype of w2 mutants. Plants of the indicated genotype were grown for 8 d under day/night cycles as described in “Materials and Methods.” Seedlings at this stage, in which the third leaf is emerging from the whorl, were used for all experiments in this study. The w2-Burnham allele is labeled w2 here and throughout. The heteroallelic progeny of complementation crosses are indicated by the two parental alleles. The position of each mutation within the GRMZM2G480171 gene model is diagrammed below. Unshaded rectangles represent transcribed, untranslated regions. The sequences flanking the Mu insertions sites are shown, with the nine base pair target duplication marked in boldface. B, Reduced abundance of chloroplast atpA mRNA in w2-mum1 homozygotes. Four micrograms of RNA purified from each of three sections of the second seedling leaf (left) was analyzed by RNA gel-blot hybridization using an atpA specific probe. A dilution series of the wild type sample was included to aid in quantification. The methylene blue-stained blot below shows the abundance of rRNAs in each sample. 28S and 18S are cytosolic rRNAs; 16S is plastid 16S rRNA, and 23S* is a cleavage product of plastid 23S rRNA.