Figure 4. Areas in the human brain involved in updating model-free and model-based value functions (Behrens et al. 2008).
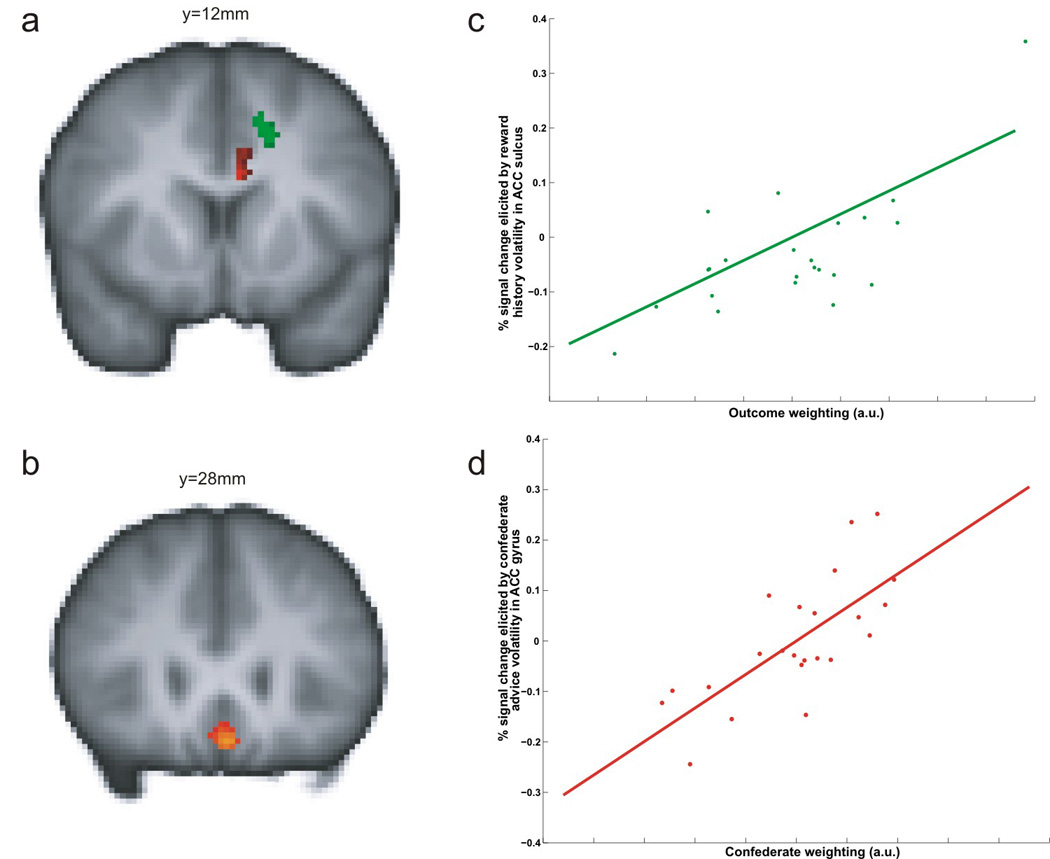
(a) Regions in which the activity is correlated with the volatility in estimating the value functions based on reward history (green) and social information (red). (b) Activity in the ventromedital prefrontal cortex was correlated with the value functions regardless of whether they were estimated from reward history or social information. (c) Subjects more strongly influenced by reward history (ordinate) tended to show greater signal change in the anterior cingulate cortex in association with reward history (abscissa; green region in a). (d) Subjects more strongly influenced by social information (ordinate) showed greater signal changes in the anterior cingulate cortex in association with social information (abnscissa; red region in a).
