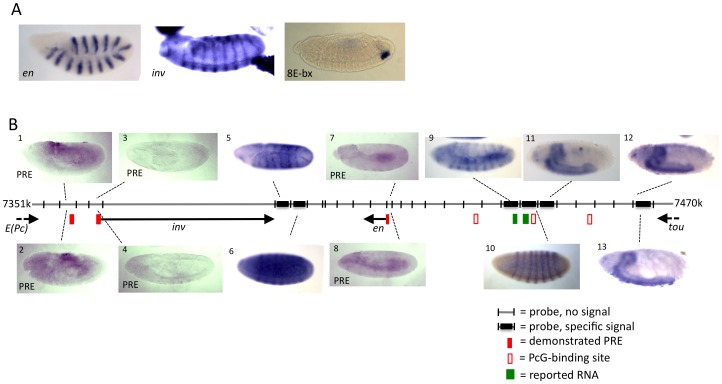
Figure 1. Whole mount embryo in situ hybridization reveals that ncRNAs are not detectable at the known en and inv PREs.
Grey Line indicates genomic DNA, with the coordinates listed at both ends (genome version R5.1). DIG-labeled RNA probes were generated to cover the entire region shown, on both strands. (A) Positive controls showing robust signal from en and inv probes, and from a probe against miR-iab-8, a miRNA in the BX-C [30]. (B) Selected in situ results from inv-en region. Panels 1–4 and 7, 8 show non-specific background staining using probes to detect RNAs transcribed in the regions of the inv and en PREs. Several probes yielded specific signals. Panels 5 and 9 show an en-like pattern at stage 9, panels 6 and 10 show a pair-rule pattern at stage 5, and panels 11–13 show late CNS staining at stage 16. Embryos located above the genomic DNA line were hybridized with antisense probes (with respect to inv), embryos located below the line were hybridized with sense probes (with respect to inv). Filled red boxes are the locations of PREs (as evidence by PcG binding and by PRE activity in transgenes). PcG protein binding sites, depicted with open red box, are where Pho was reported to bind in ChIP/chip studies in larvae and embryos [39]. Green boxes indicate the locations of regions reported to be transcribed [31], [32].