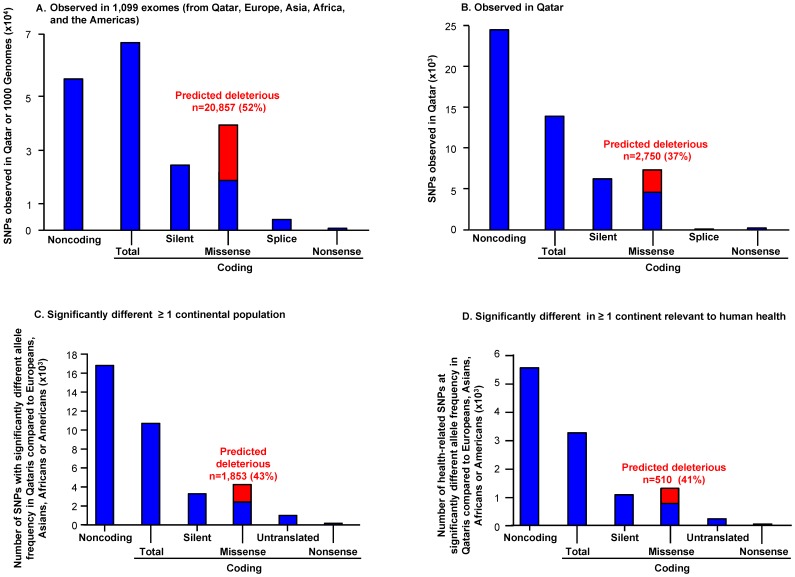
Figure 1. Functional classification of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites in seven Qatari exomes.
Genotypes for 126,924 SNPs in target exons ±500 bp were confidently called as ref/ref, ref/alt or alt/alt (where ref = GRCh37 reference allele and alt = non-reference allele) using GATK [33] and classified using databases of SNP function (NCBI dbSNP build 134, SIFT online webserver [34], and GATK VariantAnnotator function [33]. Shown are bar plots of: A. SNPs observed in ≥1 of 1,099 exomes [QE7 and 1000 G]; B. SNPs identified in ≥1 of 14 QE7 alleles; C. SNPs significantly higher or lower in QE7 vs at least one population; and D. Subset of significantly higher or lower SNPs in genes with a health-related role (OMIM [12], HGMD [37], PharmGKB [38] or HUGE [39]). In the four plots, the x-axis lists the functional categories (noncoding, coding, silent, missense, splice, nonsense) and the y-axis the number of SNPs. There were 20,857 (52%) missense SNPs predicted deleterious by SIFT [34] or PolyPhen2 [35] polymorphic in 1,099 exomes (QE7 and 1000 G), a subset 2,750 polymorphic in QE7 with ≥1 of 14 alleles (Table 1). There were 1,853 significantly higher or lower missense SNPs predicted deleterious by SIFT [34] or PolyPhen2 [35] polymorphic in 1,099 exomes (QE7+1000 G), and a subset of 510 relevant to health; see Table 2). Red = predicted deleterious SNPs.