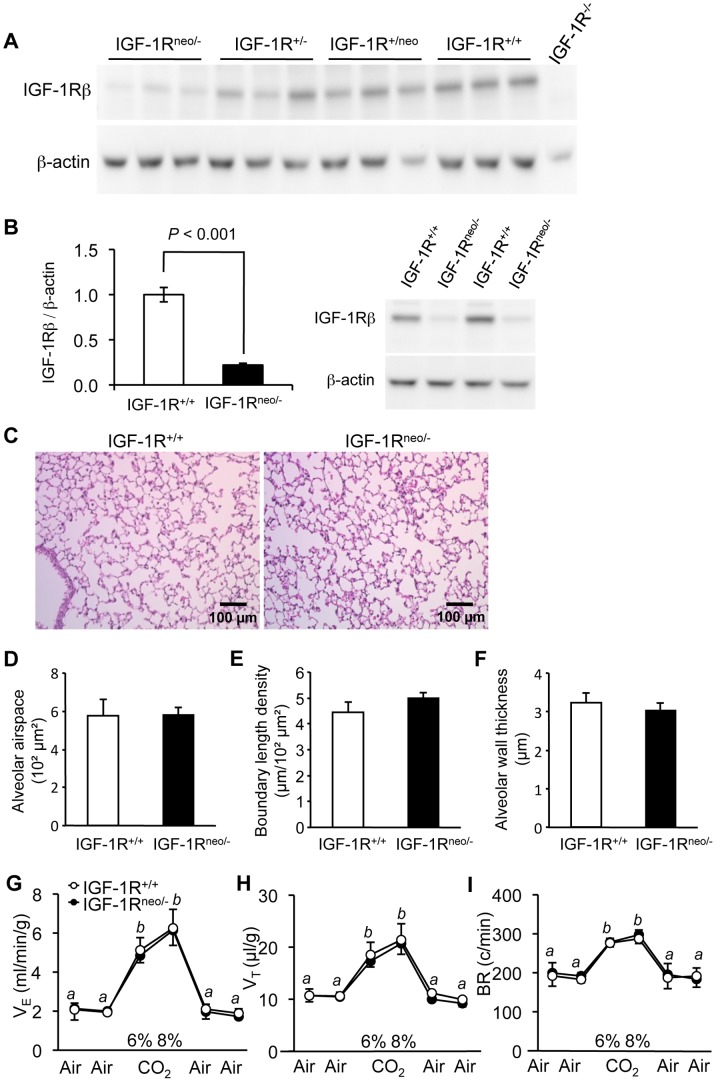
Figure 1. IGF-1R protein levels, lung histology and respiratory function in adult IGF-1Rneo/− mice. A.
, Western immunoblot of IGF-1R in lung from mice with distinct combinations of mutant IGF-1R alleles. Total proteins were extracted from lung tissue from IGF-1Rneo/−, IGF-1R+/−, IGF-1R+/neo and IGF-1R+/+ mice (n = 3 for each genotype), and IGF-1R−/− embryo (negative control), and were probed with anti-IGF-1Rβ (upper panel) or anti-β-actin antibodies (lower panel). IGF-1Rneo/− mice have 22% of receptor levels present in IGF-1R+/+ mice (quantified in B), IGF-1R+/− have 50%, IGF-1R+/neo mice are between 70 and 80%, and IGF-1R−/− mice lack IGF-1R completely. B, IGF-1R abundance determined in lung tissue. Bar graph shows IGF-1R levels relative to β-actin from 5 IGF-1R+/+ and 6 IGF-1Rneo/− individuals (Error bars SEM; Student’s t-test). Image shows 4 representative lanes from western immunoblot. C, Hematoxylin-eosin stained lung sections from IGF-1R+/+ and IGF-1Rneo/− males. D, Alveolar airspace, E, alveolar boundary length density, F, alveolar wall thickness, in IGF-1R+/+ (n = 4) and IGF-1Rneo/− mice (n = 4). Error bars indicate SEM; Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney U test. G-I, Respiratory function in adult IGF-1Rneo/− mice. Mice were challenged with 6% and 8% CO2. G, Minute ventilation (VE), H, tidal volume (VT), and I, respiratory frequency (BR) were measured in 6 individuals per group. Differences between room air and hypercapnia were significant, but no significant differences were found between genotypes. Values labeled b were different from a (P<0.005); Error bars indicate SEM; Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney U test.