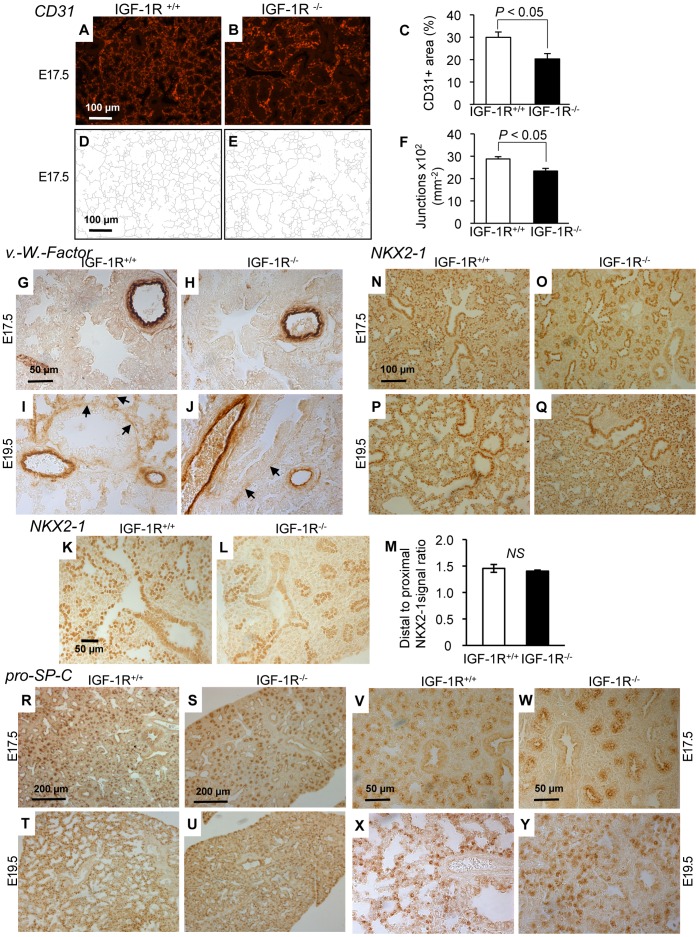
Figure 5. Immunohistochemistry of lung differentiation markers.
A and B, Representative tissue sections from IGF-1R+/+ and IGF-1R−/− embryos at stage E17.5 showing CD31-immunoreactivity specific for capillary endothelia. C, Morphometric comparison of CD31 signal between genotypes (n = 5 per group; two-tailed t-test). D–F, Capillary complexity was estimated calculating the density of capillary junctions from CD31 IHC. G–J, Sections from IGF-1R+/+ and IGF-1R−/− embryos at E17.5 and E19.5 show IHC of blood vessel-specific von Willebrand protein. Arrows (I, J) point to small blood vessels developing in saccular walls. Large blood vessels were similarly marked in all specimen. K–M, Representative lung histology from IGF-1R+/+ and IGF-1R−/− embryos at E17.5. NKX2-1 distal-to-proximal IHC signal ratio was measured in 6 IGF-1R+/+ and 5 IGF-1R−/− embryos. NS, not significant; Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney U test. N-Q, Epithelial cell-specific NKX2-1 transcription factor was detected in IGF-1R+/+ and IGF-1R−/− embryos at E17.5 and E19.5. R–Y, IHC of type 2-specific pro-SP-C at low (R-U) and high magnification (V-Y). Interestingly, for NKX2-1 and pro-SP-C, the IHC pattern of IGF-1R−/− lungs at E19.5 resembles controls at E17.5 (panel N versus Q, R versus U, and V versus Y), suggesting an approximately 2-day developmental delay in IGF-1R−/− end-gestational lungs.