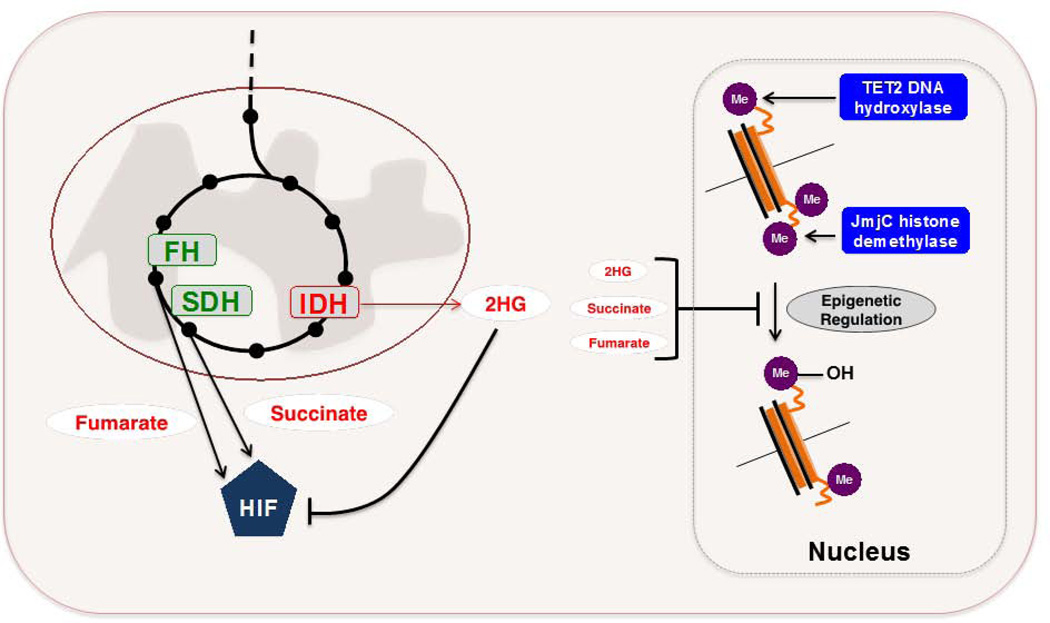
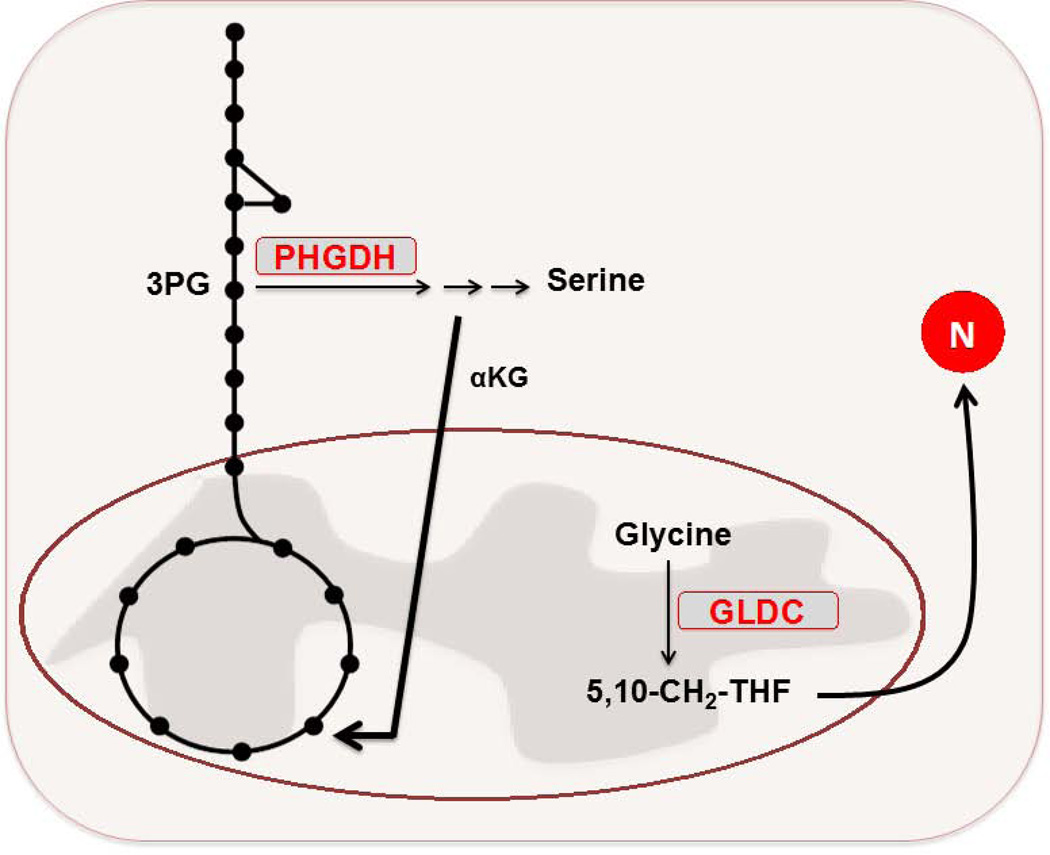
FIGURE 4. Metabolic enzymes as oncogenes or tumor suppressors.
A. SDH and FH can genetically behave as tumor suppressors in specific cancers. The accumulation of succinate or fumarate that arises owing to inactivating mutations in SDH or FH potentiates aberrant stabilization of HIF1 through competitive inhibition of PHDs. IDH mutants arise in a fraction of gliomas, acute myeloid leukemias, and chondrosarcomas. These mutants acquire a neomorphic enzymatic activity that enables the conversion of αKG to 2HG, which can impair normal epigenetic regulation through competitive inhibition of various αKG-dependent dioxygenases, including TET2 DNA hydroxylases and JmjC histone demethylases. Recent evidence suggests that 2HG can also promote HIF1 degradation, and that both succinate and fumarate accumulation may also inhibit various αKG-dependent dioxygenases. Further investigation into the pathophysiological role of 2HG may reveal a context-dependence to its functional role.
SDH – succinate dehydrogenase. FH – fumarate hydratase. HIF – hypoxia-inducible factor. PHD – prolyl hydroxylase. αKG – α – ketoglutarate. 2HG – 2-hydroxyglutarate.
B. PHGDH is elevated in a fraction of malignant breast and melanoma cells. This elevation promotes flux of glucose into the serine biosynthesis pathway. Suppression of PHGDH in those cell lines that had elevated expression of the enzyme caused a strong decrease in cell proliferation and serine synthesis. Moreover, it was revealed that the serine pathway was responsible for nearly 50% of the net conversion of glutamate to αKG for glutamine-driven anaplerosis in these PHGDH-overexpressing cells. GLDC is overexpressed in the TIC population of NSCLC cells. Suppression of GLDC effectively reduced proliferation in the TICs. Among the alterations driven by enhanced GLDC expression in these cells was an increase in pyrimidine biosynthesis, which made these cells particularly sensitive to treatment with low doses of the antimetabolite methotrexate.
PHGDH – 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. GLDC – glycine decarboxylase. NSCLC – non-small cell lung cancer. TIC – tumor-initiating cell.