Abstract
Eukaryotic flagella and cilia have attracted the attention of many researchers over the last century, since they are highly arranged organelles and show sophisticated bending movements. Two important cytoskeletal and motor proteins, tubulin and dynein, were first found and described in flagella and cilia. Half a century has passed since the discovery of these two proteins, and much information has been accumulated on their molecular structures and their roles in the mechanism of microtubule sliding, as well as on the architecture, the mechanism of bending movement and the regulation and signal transduction in flagella and cilia. Historical background and the recent advance in this field are described.
Keywords: tubulin, dynein, flagella, cilia, sperm motility, microtubule
Historical background
A half century ago, the actomyosin (actin-myosin) system was considered responsible for all forms of motility shown by eukaryotes, including muscle contraction, amoeboid movement, cytoplasmic streaming, cell division, flagellar and ciliary movement, and axonal flow, and there was no knowledge of any other systems involved in these functions. In 1945 Engelhardt described a myosin-like ATPase protein, named “spermosin,” from bull sperm flagella,1,* although his group had failed to obtain actin. In the years following this report, many researchers examined the presence of myosin and actin in flagella and cilia. Active ATPase activity was indeed observed in these materials, although the ATPase properties of isolated flagella from marine spermatozoa were somewhat different from those of muscle myosin.3,4) Nobody, however, had succeeded in isolating actin, myosin or actomyosin from flagella or cilia or even in extracting the ATPase protein from these materials until the early 1960s. As for the detailed ultrastructure of flagella and cilia, the present image of a so-called “9+2” structure of the flagellar and ciliary axoneme was first revealed in 1959 by Afzelius, who described “arms” and “spokes” attaching to the outer doublet microtubules and also proposed a numbering system for the outer doublets5) (See Fig. 1 6)).
Figure 1.
Schematic cross-sections of flagellum and cilium in protists and lower plants (left) and in choanoflagellates and animals (right), modified from Ref. 6.
There was a breakthrough in this field in 1963, when Gibbons isolated the ATPase protein from Tetrahymena cilia after removal of the ciliary membrane and indicated that the protein constitutes the arms.7) Since the ATPase showed properties different from myosin and more like the properties of isolated sperm flagella, he gave the name “dynein” to this new protein.8) In subsequent studies, the notion that dynein made up the arms was confirmed by using an anti-dynein antibody which inhibited its ATPase activity as well as the reactivation of demembranated sperm models and microtubule sliding.9,10) It was found that dynein molecule, especially from the outer arms, of protists consists of three heavy chains with three corresponding “heads”,11) while that of animals consists of only two heavy chains with two corresponding heads,12) together with several intermediate chains and light chains. As will be described presently, the inner arms are not identical with the outer arms as postulated earlier and consist of various dynein molecules with one or two heads. The amino acid sequence of the dynein heavy chain was first determined by Ogawa and by Gibbons’ group independently with the β-chain of the outer arm dynein from sea urchin.13,14)
Then a question arose as to which protein would be the counterpart of dynein in the way that actin was the counterpart to myosin in muscle. Among the components of the axoneme “9+2” microtubules would be a plausible candidate for the structure corresponding to actin filaments in muscle. After various analyses and a comparison between actin and the main constituent of microtubules, Mohri concluded that the sought protein should be a novel protein and named it “tubulin” in 1968.15–17) The tubulin molecule is a heterodimer of α- and β-tubulin, binds to GTP or GDP and is post-translationally modified by phosphorylation, tyrosination, acetylation, glycosylation, glycylation, etc. (See Ref. 18). Because it binds to colchicine and other antimitotic drugs, it was once called colchicine-binding protein.19) Reconstitution of microtubules from tubulin dimers was accomplished by Weisenberg in 1972,20) which facilitated the purification and further analyses of this protein. The whole sequences of α- and β-tubulin were decoded in 1981.21,22) Thus in flagella and cilia, the pair of dynein, a motor protein, and tubulin, a rail or cytoskeletal protein, replaces the pair of myosin and actin in muscle and other motile systems. Later still another motor protein, “kinesin,” was found to be involved in microtubule-dependent motility.23)
Concerning the mechanism of flagellar and ciliary movement, the idea that it was accomplished by sliding of the outer doublet microtubules with the aid of the arms had already been suggested when the ultrastructures of flagella and cilia were first revealed.5) The experimental evidence was obtained by electron microscopical observation of the tips of the mussel gill cilia beating metachronally24) and more directly by observing the extrusion of doublet microtubules from the trypsin-treated demembranated axonemes of sea urchin spermatozoa on the addition of ATP.25) The reactivation of sperm models by ATP was first achieved by Hoffman-Berling with glycerol-extracted locust sperm in 1955.26) Subsequently, the replacement of glycerol with Triton X-100 greatly facilitated the reactivation of flagellar and ciliary models.27,28) A local application of ATP to the demembranated sea urchin sperm by iontophoresis revealed that local active sliding of outer doublets could be converted into bending.29) In addition, a useful motility assay was introduced by observing the sliding of microtubules on dynein molecules absorbed on a glass surface, as in the case of kinesin or heavy meromyosin.30)
Flagellar and ciliary components
As described in the previous section, the sperm model demembranated with Triton X-100 reproduced normal flagellar bend propagation, indicating that the cytoskeletal element in flagella, the axonemes (Fig. 1), is responsible for the elemental property of flagellar motility. The motive force of flagellar motility is exerted by axonemal dyneins, which are phylogenetically distinct from cytoplasmic dyneins. Studies on the molecular structure of outer arm dynein have been more advanced than those on the inner arm dynein because the former can be easily purified from the axonemes31) and is present as a single molecular species in flagella and cilia. The molecular structures of outer arm dyneins have been extensively studied using sperm flagella from marine invertebrates, because in these flagella the outer arm dynein is selectively extracted from the axonemes by a high salt solution and can be purified simply by sucrose density gradient centrifugation.31,32) On the other hand, dyneins from flagella and cilia in several protists, such as Chlamydomonas, Tetrahymena and Paramecium, have also been used. In particular, studies on dyneins, as well as other axonemal components, have been extensively carried out using Chlamydomonas flagella,33) because several mutants of this species lacking axonemal components have become available.34,35) Here we comparatively describe the molecular structures of dyneins and other axonemal components in flagella from sperm and Chlamydomonas.
Dyneins.
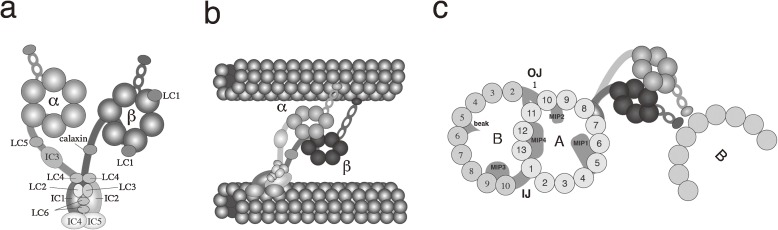
The dynein arms are observed as projections from A-tubules of outer doublet microtubules. Based on their positions, they are called outer and inner arms. The outer arms are considered to be single molecular species arranged on each doublet microtubule with 24 nm intervals, whereas the inner arms contain multiple molecular species. The outer arm dynein of metazoan sperm is comprised of two heavy chains (HC; α, β, ∼500 kDa), three to five intermediate chains (IC; 60–120 kDa), and six light chains (LC; 8–30 kDa)36,37) (Fig. 2a). Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein contains three heavy chains (α, β, γ), two intermediate chains (WD-repeat) and ten light chains.38) Dynein heavy chains are members of the ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA) superfamily. Each of the six AAA domains constitutes a subdomain in the head part of dynein, forming a ring-like structure of the dynein head (Fig. 2a). The coiled-coil domain present between the fourth and fifth AAA motif forms a small stalk with a globular domain that acts as the ATP-sensitive microtubule-binding site (MTBD).39) Recent advances in cryoEM and tomographic observation have shown that multiple AAA ring heads are stacked atop each other and the plane of each ring runs through the axis of the adjacent B-tubule (Fig. 2b and 2c).40,41) Attempts have been made to detect the conformational changes of dynein during the mechano-chemical cycle by using biochemical methods. A study using the limited proteolytic digestion detected large conformational changes of outer arm dynein in the presence of ADP/Vi in sea urchin sperm flagella. The changes are seen not only in the vicinity of the primary ATP hydrolysis site (AAA1) but also throughout all the regions of the dynein heavy chain, including the C-terminal region.42–44) Advances in electron microscopy have allowed visualization of the conformational changes in multiple head rings and in the relative position of the head and stem.45,46) It is known that each heavy chain of the outer arm dynein exhibits a distinct ATPase activity and distinct microtubule-sliding activity in both sea urchin sperm flagella12,47,48) and Tetrahymena cilia.49,50) However, the physiological importance of the multiple heavy chains in outer arm dyneins is still unclear.
Figure 2.
Structure and in situ configuration of outer arm dynein. (a) Schematic subunit structure of outer arm dynein from Ciona sperm flagella. The structure is divided into three parts; head, stalk and stem. Outer arm dynein is composed of two heavy chains (α and β), five intermediate chains (ICs) and six light chains (LCs). (b) Longitudinal configuration of outer arm dynein bound to doublet microtubules. (c) Structure of the outer doublet microtubule and in situ configuration of outer arm dynein. The outer and inner junction (OJ and IJ) connect the A- and B-tubules. Microtubule inner proteins (MIP) and the “beak” structure are associated with the internal wall of the A- or B-tubule. Note that the Ciona α or β heavy chain corresponds to the sea urchin β or α and Chlamydomonas β/α or γ, respectively.
The outer arm dynein contains two ICs with WD repeats, which are involved in protein–protein interaction and may play a key role in the assembly and binding of dynein on the A-tubule. An IC with thioredoxin and nucleoside diphosphate kinase (TNDK-IC) motifs is present in metazoan sperm, but not in Chlamydomonas flagella.32,51) The structure for the assembly and anchoring of outer arm dynein to the doublet microtubules at regular intervals (24 nm) is called the outer dynein arm docking complex (ODA-DC).52) This complex is composed of three polypeptides (DC1-DC3).53–55) DC1 and DC2 are coiled-coil proteins, and likely serve in scaling regular intervals for dyneins. DC3 has four EF-hand motifs that may bind Ca2+ and thereby play roles in the regulation of outer arm dynein. In tunicate Ciona, salmonid fish and molluscs, outer arm dynein contains two or three other ICs. These additional ICs are shown to be coiled-coil proteins with sequence similarities to Chlamydomonas DC2.56,57)
Outer arm dynein LCs are thought to be involved in the assembly and regulation of dynein motor function.57) In Ciona and sea urchin sperm, six distinct proteins have been identified as outer arm dynein LCs. Two of these molecules show homology to t-complex testis-expressed proteins (Tctex1 and Tctex2), which are involved in transmission ratio distortion in mice.58,59) Although the Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein contains Ca2+-binding LC4, no Ca2+ binding protein has been identified as a subunit of outer arm dynein in metazoa. A 25-kDa protein with sequence similarity to the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) has recently been identified in association with the Ciona outer arm dynein and designated calaxin. Calaxin has orthologs in metazoan species, including mice and human, and is thought to participate in the regulation of flagellar wave asymmetry.60)
Inner arm dyneins include multiple molecular species with one or two heavy chains. In Chlamydomonas they contain at least seven species (named a–g dyneins).61) The f inner arm dynein (also called I1) contains IC140, IC138, and IC97, the 14-kDa Tctex1 LC, and an 8-kDa LC.62,63) Another type of inner arm dynein also contains p28, actin, centrin, and Tctex1 and a few unidentified proteins as LCs. Chlamydomonas IC138 is phosphorylated/dephosphorylated through a kinase/phosphatase system present in the radial spoke and central pair in response to changes in motility.64,65) A homolog of IC140 (Ci-IC116) was identified in Ciona sperm flagella. Ci-IC116 is dephosphorylated at activation of sperm motility.66)
Tubulins and microtubules.
Microtubules are tubular cytoskeletal elements polymerized from α- and β-tubulin heterodimers. The doublet microtubule is a microtubule form uniquely seen in flagella and cilia. Although the mechanism for the formation of doublet microtubules is still unclear, their structural and biochemical characteristics have been partly clarified. The doublet consists of A- and B-tubules: the A-tubules contain 13 tubulin protofilaments (A1–A13) and the B-tubules are incomplete tubules of 10 protofilaments (B1–B10).67) Several structures were observed inside the A- and B-tubules. Extraction of doublet microtubules with the detergent Sarkosyl solubilizes tubulins and results in the isolation of remnant filamentous structures called “ribbons”. One of the protein components of ribbons, tektins, were first isolated from the flagella of sea urchin sperm.68) Other components of ribbons include some Ca2+-binding proteins.69) Cryo-electron microscopy observation has recently revealed the detailed structure of doublet microtubules. The B-tubules contain the inner junction and the outer junction between the A- and B-tubules.70) Microtubule inner proteins (MIPs) are observed on the inside of the A- and B-tubules. According to a recent observation, MIP1, MIP2 and MIP4 are associated with the A-tubules, and MIP3 is associated with the B-tubules, with a certain longitudinal periodicity. A projection called a “beak” structure is observed within the B-tubules of Chlamydomonas doublet microtubules 1, 5 and 6 (Fig. 2c).71)
The presence of multiple molecular species of both α- and β-tubulin was first demonstrated in marine sperm flagella.72) The heterogeneity of α- and β-tubulin is important for the construction and function of outer doublet microtubules in the axonemes. It first arose from multiple genes of α- and β-tubulin. Vertebrate genomes encode six to seven genes for both α- and β-tubulin.73) Second, axonemal tubulins undergo several types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation of α-tubulin and polyglutamylation and polyglycylation of both α- and β-tubulin.74,75) Recent research on the tubulin tyrosine ligase like (TTLL) family of proteins has revealed their significant role in the assembly and regulation of axonemes.76) For example, knockdown of TTLL3 tubulin glycin ligase results in shortening of cilia in Tetrahymena.77) Knockout of TTLL1 (PGs3) results in a shortening of and asymmetry abnormalities of mouse airway cilia.78)
Radial spokes, central pair and other axonemal structures.
Radial spokes (RS) and the central pair (CP) are the structures inside the outer rows of doublet microtubules and appear to modulate dynein activities. Several lines of evidence indicate that the CP/RS system is not principally required for flagellar bend formation and propagation. Rather, CP/RS are involved in the signaling for controlling the properties of bend and for modifying motility in response to specific signals.79,80) The regulation of dynein arms by CP/RS involves protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. Approximately 23 proteins (1–350 kDa) comprise RS in Chlamydomonas flagella. These proteins contain those for Ca2+/CaM-dependent or cAMP-dependent signaling pathway, such as a protein with the A-kinase anchor protein (AKAP) domain PRS3.80) Similarly to RS, CP also contains domains for molecular assembly and signaling, including CaM, CaM-binding protein Pcdp1, AKAP-binding protein AAT-1, and a protein with the adenylate kinase domain Cpc1.81)
The dynein regulatory complex (DRC) is the structure at the junction between the radial spokes and inner arm dynein. DRC is thought to be important in anchoring inner arm dynein and for connecting the inner arms to the radial spokes. Seven polypeptides (29–192 kDa) have been proposed as DRC components in Chlamydomonas,82) but neither molecular characterization nor the presence of homologs in metazoan sperm have been reported.
Nexin links or interdoublet links contribute to the elastic resistance involved in the conversion of microtubule sliding into axonemal bending. It has been proposed that the interdoublet link is the major part of the DRC.83) Actually, recent analysis by electron tomography revealed that one end of the Chlamydomonas interdoublet link formed a bifurcated attachment to the B tubule; the other was attached to the A tubule close to the base of DRC. Link structures are also present between outer arms and between outer- and inner-arm dyneins.84) These link structures suggest a mechanism for coordinating inner and outer dynein arm activities.
Sliding of outer doublet microtubules
The idea of the sliding of outer doublet microtubules was first proposed by Afzelius5) based on the analogy of the arms projecting from the doublet microtubules with the cross-bridges between the myofilaments of the muscle cells. This idea was experimentally tested and it was confirmed that the microtubules themselves did not shorten during beating, and thus that sliding of the outer doublet microtubules occurred.24,85) Extrusion of the doublet microtubules from sea urchin sperm axonemes was demonstrated using segments of the sperm axoneme that were treated with trypsin and then exposed to ATP.25) Using this method, the sliding direction of the doublet microtubules was determined; that is, the dynein arms on tubule A of a doublet microtubule push the B tubule of the adjacent doublet microtubule toward the tip of the cilium.86) However, the opposite direction of sliding was later proposed in sea urchin spermatozoa at low levels of calcium/calmodulin87) and in mammalian spermatozoa.88)
The sliding of doublet microtubules was influenced by various factors, including the number of dynein arms on the doublet microtubule, ATP, Ca2+ and cAMP. When the dynein arms were removed from the axoneme, the velocity of the microtubule sliding was proportional to the total number of dynein arms present.89–91) The sliding velocity was also directly related to MgATP2−,90–92) and its maximum value was approximately 14 µm/sec. The force produced by sliding was measured and found to be approximately 1 pN per dynein arm.93) However, the force developed by sliding did not change with the sliding velocity.94) This insensitivity of force to the sliding velocity was previously pointed out by Hiramoto,95) and its load dependency was explained by the relation of the sliding velocity largely to stiffness of the sperm flagella, e.g., those having different diameters.96,97) Ca2+ decreased the sliding velocity.98,99) Furthermore, Ca2+ affected the pattern of sliding of the doublet microtubules extruding from the axoneme; that is, at low Ca2+ concentrations, most of the axonemes separated into individual doublet microtubules, but at high Ca2+ concentrations, most of them separated into two microtubule bundles.87,99) The former pattern has never been seen before.100) The Ca2+ sensitivity is removed by trypsin treatment from the basic sliding machinery in Paramecium axonemes.101) The effect of pH, inhibitory agents and cAMP on the microtubule sliding has been investigated using mammalian spermatozoa.102–104) Strangely enough, the outer doublet microtubules activated by Ca2+ were different between the sea urchin and mammalian spermatozoa105) because the doublet microtubules of 6–7, 7–8 and 8–9 were activated by Ca2+ in the sea urchin99) while those of 2–3, 3–4 and 4–5 were slid by Ca2+ in rat spermatozoa.102) It should be noted here that the principal bend defined by Woolley106) in hamster sperm flagella corresponds to the reverse bend in sea urchin and starfish sperm flagella and vice versa.105,107) The conversion of sliding of the doublet microtubules to bending was demonstrated if there was some resistance to the microtubule sliding.29) This sliding-to-bending conversion due to resistance has been confirmed using a fluorescent reagent that inhibits the microtubule sliding.108)
Regulation of microtubule sliding during flagellar and ciliary beating
The sliding between the outer doublet microtubules of the axoneme must be modulated to generate the various patterns of the flagellar and ciliary beating. To clarify this regulatory mechanism, several approaches have been taken, including the computer simulation of the beating pattern in order to test the hypothesis of the regulatory mechanism and estimation of microtubule sliding from the flagellar and ciliary beating. By reconstructing the beating pattern of Paramecium cilium using a computer, Sugino and Naitoh109) estimated the behavior of the microtubule sliding; that is, the sliding between the doublets 1, 2, 3, and 4 on one side of the cilium is active during the effective stroke while the activity switches to the doublets 6, 7, 8, and 9 on the other side during the recovery stroke. Furthermore, various hypotheses to explain the planar beating of sperm flagella have been tested by computer simulation, including the “curvature control” hypothesis, “geometric clutch” hypothesis, and “sliding control” hypothesis.110,111) However, none of these hypotheses has been widely accepted,111,112) possibly because the flagellar beating of spermatozoa is fundamentally three-dimensional (see below).
Hiramoto and Baba113) developed a method for quantitatively evaluating the tangential angle (which is also referred to as the shear angle or bend angle) at any point on the flagellum from a photograph of the flagellar wave, and found that this angle of the flagellum at any distance from the base is expressed by a sine function of time plus a constant. To explain this fact, they proposed a model in which the active force required to generate sliding is propagated along and around the flagellar axoneme. This model has been strongly supported by experimental evidence obtained from the analyses of the rotational movements of spermatozoa.114,115) Furthermore, the helical waves were converted from the planar waves in the tunicate and sea urchin sperm flagella under certain high viscosity conditions.116,117) These findings suggest that the flagellar beating of the tunicate and sea urchin spermatozoa is fundamentally three-dimensional due to the intrinsic asymmetrical geometry of the sperm axoneme, and that the almost planar beating usually observed in these sperm flagella results from the additional regulation.117) One of the most plausible candidates for this role is the central complex, because the absence of this structure from the axoneme is associated with helical beating118) and the stiffness of sea urchin sperm flagella significantly differs between the direction parallel to the beating plane and that perpendicular to it.119,120)
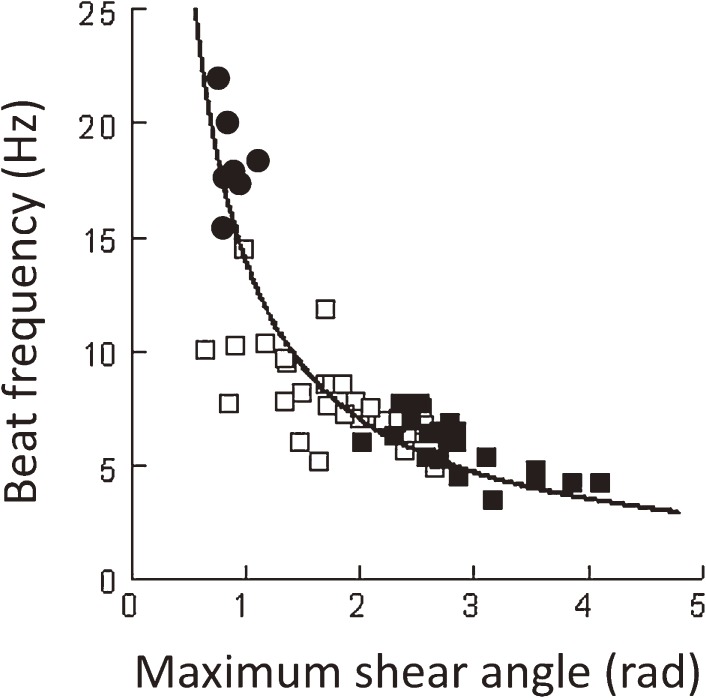
A digital image analysis, with accuracy enhanced by Bohboh software,121,122) of the flagellar beating of hyperactivated mammalian spermatozoa, which are characterized by large bends at the midpiece and slow beating, revealed that the sliding velocity remained constant before and after hyperactivation, although it varied with the stiffness of the sperm flagella in several species.96,97) This fact suggests that the mechanisms regulating the beat frequency and flagellar waveform are tightly dependent on each other. The sliding velocity is kept constant, since it is proportional to the product of the beat frequency and tangential angle.123) In a wide range of working seen before and after hyperactivation, the beating mode switches from a constant-sliding-extent mode, in which the frequency varies to a greater degree, to a constant-frequency mode, in which the sliding extent (maximum shear angle) varies widely (Fig. 3).87,123)
Figure 3.
Relationship between beat frequency and maximum shear angle. The flagellar beating of activated (●), transient (□) and hyperactivated (■) golden hamster spermatozoa is shown. The line is a least squares regression line, given by f = 14/θmax, where f is the beat frequency and θmax is the maximum shear angle. Since the sliding velocity is proportional to f·θmax, this equation clearly shows the constant rate of microtubule sliding before and after hyperactivation.
Initiation and activation of movement
Spermatozoa remain immotile or virtually immotile in the testis, undiluted semen or the male reproductive tract. They initiate flagellar movement at spawning or ejaculation into an aquatic environment such as seawater, fresh water or the seminal plasma and the fluid of the female reproductive tract. Furthermore, for instance in mammals, they are activated to show progressive forward movement and then are hyperactivated to exhibit vigorous whiplash-like movement in the female reproductive tract. In addition, spermatozoa of many species, including plants such as ferns and mosses, show chemotactic behavior in response to a specific substance from the egg or its surroundings. Thus spermatozoa are one of the best materials to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the initiation and such modifications of flagellar movement.
Initiation of flagellar movement has been studied with various spermatozoa that are immotile in the testis, such as those in marine invertebrates and fishes, or in the cauda epididymis, as in mammals before ejaculation. Various factors induce their motility among different animals, although there would be common cascade(s) which lead to final activation of the tubulin-dynein system.124–126)
Dilution of sea urchin semen (“dry sperm”) with seawater evokes the initial burst of sperm respiration and vigorous flagellar movement. Since CO2 inhibits both respiration and motility of the spermatozoa,127) it is plausible that release from the high PCO2 in the testis or in dry sperm by dilution with seawater causes an increase in intracellular pH (pHi) which in turn activates dynein ATPase activity.128) In fact, a temporary decrease in the content of ATP as well as that of phosphagen has been observed immediately after dilution.129) The initial high respiration rate would be needed for recovering high-energy phosphate compounds by oxidative phosphorylation. The phosphocreatine shuttle is considered to supply ATP produced in mitochondria situated at the proximal end of the flagellum to its distal end.130) In flatfish species, CO2 clearly shows a strong inhibitory effect on sperm motility. This inhibition is reversible and can be reproduced with demembranated sperm by bicarbonate ion. Inhibition by CO2 is mediated by a carbonic anhydrase, which catalizes the conversion between CO2 and bicarbonate.131) An increase in pHi is also caused by the efflux of H+ through a Na+/H+ exchange, resulting in the activation of dyneins.132) Full activation of dyneins appears to require cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of specific proteins at the initiation and activation of sperm motility.133)
In teleost fishes, Morisawa’s group found that high osmotic pressure for marine teleost sperm and, conversely, low osmotic pressure for fresh water teleost sperm induce the initiation of flagellar motility, while lowering of the high K+ concentration in the seminal plasma initiates the motility of salmonid fishes.126,134,135) In salmonid fishes, the efflux of K+ induces hyperpolarization of the plasma membrane, which would increase intracellular Ca2+ from both the intracellular Ca2+ store and the environment. Since cAMP is required for the initiation of motility of the demembranated spermatozoa, increased Ca2+ would activate adenyl cyclase, resulting in an increase of cAMP, which in turn would activate A kinase (PKA).124) PKA then activates a tyrosine kinase (PTK) which phosphorylates the tyrosine residue of a 15K protein (the motility initiating phosphoprotein (MOPP)). MOPP resides in the basal region of the flagellum and is involved in the initial formation of the flagellar wave.122) It is also known that at the motility initiation of salmon, a Tctex2-related light chain of the outer arm dynein is phosphorylated by PKA, and PKA is regulated by proteasomes localizing near the outer arms.59,136) PKA also shows a similar localization.137) Herring sperm are activated by a herring sperm activating peptide (HSAP) through proryl endopeptidase.126) In the cases of other teleosts, changes in external osmolality induce Ca2+ influx by opening of the Ca2+ channel or the release of Ca2+ from the intracellular storage and trigger a Ca2+-dependent, cAMP-independent signal cascade leading to the activation of the flagellar axonemes.138)
Recently, K+-independent and osmolality-dependent activation was reported in salmonid fish spermatozoa.139,140) Since the motility initiation is tightly associated with the transient increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentration, it is plausible that a Ca2+-dependent mechanism might be common to the motility activation in teleost sperm.
In mammals, it has been shown that cAMP is an indispensable factor for the initiation of sperm motility.141–143) HCO3− in the seminal plasma stimulates both adenylyl cyclase (soluble adenylyl cyclase) and sperm motility and has been postulated to be a factor inducing the motility.144,145) Although the roles of both soluble and transmembrane adenylyl cyclases in the activation of sperm motility are controversial, it seems that two types of adenylyl cyclases play distinct roles in the motility activation or chemotaxis.146) A major soluble 55–56K protein in mammalian sperm phosphorylated by PKA at the initiation of motility was named axokinin and identified as the type II regulatory subunit of PKA (RII).141) ATP synthase and pyruvate dehydrogenase are also included in the proteins phosphorylated at the initiation or activation of motility. As PKA is a serine/threonine kinase, most of the proteins are phosphorylated at serine/threonine residues.
In general, at the initiation and activation of sperm motility, the proteins constituting the motile apparatus and those involved with the production of ATP are the main targets of phosphorylation. Although not yet thoroughly examined, dynein heavy chains are also reported to be phosphorylated.147,148) A proteomic approach has identified proteins that are phosphorylated/dephosphorylated upon the activation of sperm motility in Ciona66) and mammals.149) These proteins include not only axonemal proteins but also proteins, such as VCP97 and 14-3-3 proteins, that are potentially important for signal transduction from the plasma membrane to activate axonemes.
Modulation of movement as responces to stimuli
Upon stimulation, such as by chemicals, lights, gravity or mechanical force, protists and sperm often show changes in swimming direction. These changes accompany the symmetry-asymmetry conversion of the flagellar or ciliary waveform. For example, sperm move to the chemoattractants released from an egg of the female genital tract.129) From a series of studies using the ascidian Ciona intestinalis, it is known that sperm changes motility in response to the gradient of chemoattractants called SAAF.126) The sperm movement directed toward the egg is achieved by transient changes of intracellular Ca2+ concentration, followed by changes in the waveform asymmetry of sperm flagella.150,151) The demembranated sperm model shows an asymmetric waveform in the presence of a higher concentration of Ca2+.152,153) The regulation of the flagellar waveform is carried out by Ca2+-binding proteins that likely regulate axonemal dynein. Calaxin binds to the dynein heavy chain in the presence of Ca2+ and therefore has been postulated to be responsible for waveform asymmetry during chemotaxis.60)
Chlamydomonas shows two behaviors in response to light: phototaxis and photophobic or avoidance response. These responses require Ca2+-mediated modulation of the flagellar waveform.154) Phototaxis of Chlamydomonas is initiated by sensing through a single eyespot. The relative position of the eyespot to two flagella is always the same, but changes of the position relative to the light cause the difference in the movement of two flagella. The difference in the flagellar movement is caused by Ca2+-dependent modulation of flagellar asymmetry and by activation of flagellar motility. It has been shown that the Ca2+-dependent regulation of the flagellar waveform is conducted by outer arm dynein.155–157) On the other hand, the activation of flagellar beating is regulated by dephosphorylation of a 138 kDa intermediate chain of inner arm dynein.64,65)
Maturation and hyperactivation of mammalian spermatozoa
In mammals, the spermatozoa are not yet fully matured either morphologically or functionally even after spermiation from the testis. They gradually acquire motility and fertilizing capacity during the transit through the epididymis. Although the flagella of early spermatids, which are not yet surrounded with a mitochondrial sheath, outer coarse fibers and a fibrous sheath, show an active wave-like motion, the spermatids differentiating to the testicular spermatozoa progressively become immotile.158) In the caput epididymis, the spermatozoa are still virtually immotile even after dilution with saline solutions, while in the cauda epididymis they are ready for active progressive movement after ejaculation. In this case, vigorous motility requires extracellular factors such as Ca2+ and bicarbonate.159)
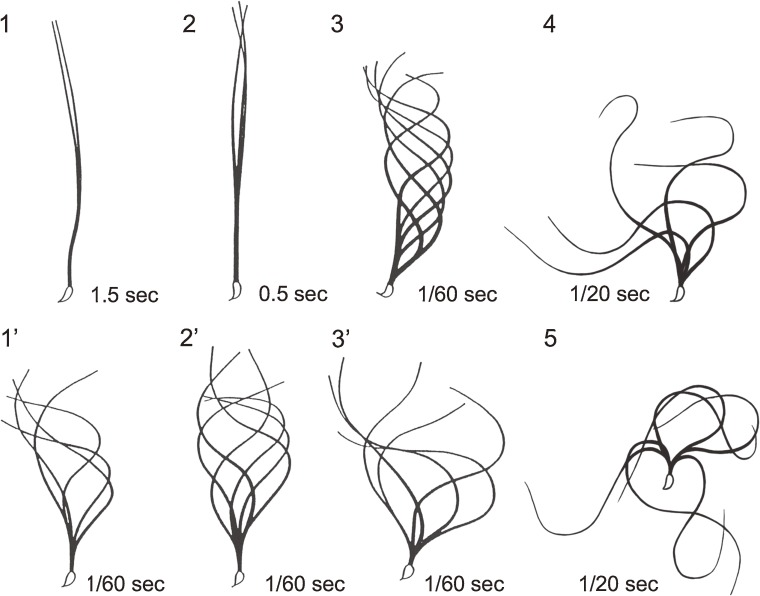
Furthermore, mammalian sperm are “capacitated” in the female reproductive tract before fertilizing the egg successfully. The capacitated spermatozoa exhibit a very vigorous movement called “hyperactivation” as well as the acrosome reaction, although capacitation and hyperactivation could occur independently from each other. Hyperactivation is characterized by high amplitude and asymmetrical flagellar bending (see Fig. 4) and is required for passing through the cumulus and zona pellucida and for release of sperm from the oviductal storage reservoir, both of which are prerequisite for fertilization in vivo.160–162) In the hyperactivated and acrosome-reacted spermatozoa, a further increase in the curvature of bends, especially at the proximal midpiece, and reduction in beat frequency are observed.163)
Figure 4.
Maturation and capacitation of mammalian spermatozoa. The flagellar movement of intact (1–3) and demembranated and ATP-reactivated (1′–3′) testicular, caput epididymal and cauda epididymal golden hamster spermatozoa are shown, respectively. Panels 4 and 5 represent the intact hyperactivated and the intact hyperactivated and acrosome-reacted spermatozoa, respectively. The time indicates the intervals between successive tracings.
In our previous computation, the thrust and hydrodynamic power output developed by the flagellum in hyperactivated hamster sperm were twice and 2.5 times those of the flagellum in activated cauda epididymal sperm showing the progressive movement, respectively.105) Although the large thrust generated by the flagellum was considered to enable sperm to penetrate through the zona pellucida mechanically,161,164) the role of the thrust during the zona penetration is not yet definitely settled. A recent re-examination of this problem with monkey spermatozoa has revealed that there was no difference in the propulsive force, parallel to the longitudinal sperm axis, between the activated and hyperactivated sperm, but that the transverse force, perpendicular to the axis, of the hyperactivated sperm was 2.5 times the propulsive force. Because the beat frequency decreased remarkably during hyperactivation, the slowly oscillating transverse force seems to be most effective for the zona penetration.165)
To elucidate the mechanism of such modulations of movement in mammalian sperm, we demembranated hamster sperm of various stages during maturation and capacitation and examined their movement after reactivation by the addition of ATP and other factors.165,166) The results revealed that the demembranated models of testicular and caput epididymal sperm showed a movement almost identical with that of intact cauda epididymal and ejaculated spermatozoa, indicating that the motile apparatus, the tubulin-dynein system, is already assembled in the former, while the movement of the models of cauda epididymal or ejaculated sperm was quite similar to that of hyperactivated spermatozoa (Fig. 4).
The flagellar movement of mammalian sperm has at least three steps, initiation, activation and hyperactivation, in contrast to the one-step activation observed in marine invertebrate and fish sperm.167) The acquisition of sperm motility during the transit through the epididymis correlates with an increase in cAMP level and pHi.168) As already mentioned, these factors together with Ca2+ are considered to evoke signal cascades which would cause the modulation of flagellar movement through phosphorylation and/or dephosphorylation of specific proteins. Such an acquisition of sperm motility as spermatozoa pass from the testis to the sperm duct was also reported in salmonid fishes along with a description of the roles played by cAMP, pH and HCO3− in this process.169)
It is known that hyperactivation is triggered by Ca2+.160,161,170) For instance, both demembranated bull and monkey sperm reactivated in the presence of low concentrations of Ca2+ begin to hyperactivate with increasing concentrations of this ion, indicating rather direct effects as the primary second messenger on the 9+2 axoneme, outer coarse fibers and fibrous sheath.171,172) High levels of cAMP in the presence of low levels of Ca2+ increase the curvature of both the principal and the reverse bend of the flagellum, while Ca2+ increases only that of the principal bend, at least in monkey sperm. Hyperactivation requires a higher level of ATP and higher pH than those required for activation.171) Although the sperm mitochondria have the ability of oxidative phosphorylation,173) glycolysis is reported to mainly supply ATP for flagellar movement in mouse sperm.174) Because of the absence of the phosphocreatine shuttle in mammalian sperm, it is postulated that glycolytic machinery would provide ATP throughout the flagellum. In addition, ATP produced by glycolysis is assumed to be essential for sperm functions, including capacitation and tyrosine phosphorylation.175,176) It has been shown that glycolytic enzymes are tightly bound to the fibrous sheath of mouse sperm.177)
It is known that increased tyrosine phosphorylation of flagellar proteins is associated with hyperactivated motility in mammalian sperm.178,179) Although the sperm PTK is not cAMP-dependent, it is regulated by PKA.170) One such tyrosine phosphoprotein is the A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP), which assembles into the fibrous sheath.180) Glycolytic enzymes such as glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are also targets of tyrosine phosphorylation at capacitation and hyperactivation.181) Successive phosphorylation of members of the MAP kinase cascade (RAF/MEK/ERK) has been reported. AKAP is situated in the region downstream of ERK.182)
Most of the experiments concerning capacitation and hyperactivation have been done in vitro and the physiological factors that trigger hyperactivation in vivo have remained to be elucidated for many years. Recently, progesterone was identified as the ligand which causes non-genomic regulation of hyperactivation.170) Progesterone enhances CatSper, a Ca2+ channel in the plasma membrane of the principal piece of the sperm flagellum, which is synergistically activated by elevation of intracellular pH.183) CatSper-deficient mouse sperm cannot exhibit hyperactivation and are infertile.162) Progesterone would also bind to its receptor on the acrosome region of the sperm head and cause mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ stores.170) In both cases the resulting increase of intracellular Ca2+ would lead to tyrosine phosphorylation of the proteins necessary for hyperactivation through CAMK and PTK. In addition, it is of interest that estrogen suppresses the hyperactivation enhanced by progesterone and tyrosine phosphorylation.184) Melatonin, which binds to its receptor on the sperm mid-piece, controls the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), including NO produced by the mitochondria. Low concentrations of ROS positively regulate hyperactivation, possibly through the MAPK cascade and tyrosine phosphorylation.182,185)
Phylogenetic considerations
Microtubule and tubulin are found in eukaryotes including protists, plants and animals, although it has been revealed that FtsZ, a homolog of tubulin, is involved in the cell division of prokaryotes.186) The same is true with flagella and cilia: these complex organelles are widely distributed among eukaryotes and would be acquired at the very early phase of their evolution.
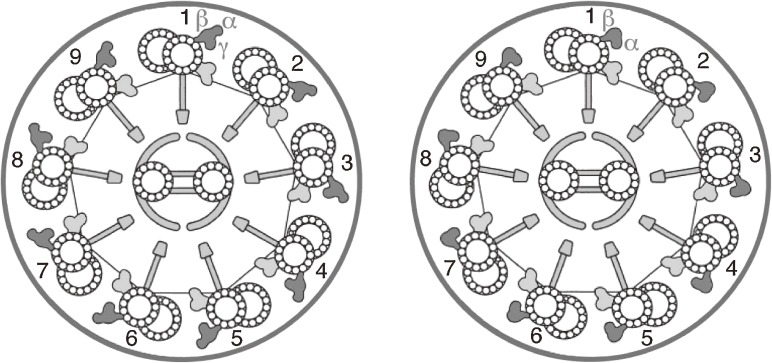
As mentioned above, the outer arm dynein molecule consists of three heavy chains (three-headed) in protists such as Tetrahymena and Chlamydomonas, while that of animals such as sea urchins, fish and mammals consists of only two heavy chains (two-headed). All these animals, however, belong to Deuterostomia. It was found that the outer arm dynein purified biochemically from oyster, as a representative of Protostomia,187) and that of sea anemone (Cnidaria)6) situated at the root of two main branches of the phylogenetic tree also consist of two heavy chains. Furthermore, the analysis of a Chlamydomonas mutant lacking one of the heavy chains of the dynein has made it possible to identify the number of heavy chains by observing the cross-sections of flagella or cilia electron-microscopically188) (see also Fig. 1). By this means it was revealed that all the flagella and cilia in animals including sponges, Mesozoa and choanoflagellates showed the two-headed outer arm profile.189) On the other hand, the above-named protists as well as Paramecium and green algae such as Bryopsis had the three-headed profile.
The sea urchin sperm α heavy chain (OAD α family) and β heavy chain (OAD β family) correspond to the Chlamydomonas γ heavy chain (ODAγ) and α heavy chain (ODAα), respectively, while Chlamydomonas α and β (ODAβ) arose from a single gene by duplication at a certain point of evolution (both belong to the OAD β family). Such duplication also occurred in Tetrahymena and Paramecium, etc.190) An amitochondriate protist, Lambl flagellate (Giardia intestinalis), had once been considered to be the most primitive eukaryote because mitochondria seem to be included in proto-eukaryotic cells through endosymbiotic event. Examination of the outer arms of this species indicated the two-headed structure which was supported by an image analysis. Among the Giardia genome, however, there is a short ORF corresponding to the Chlamydomonas β gene in addition to the genes corresponding to α and γ. As in the case of mitochondria which had once been acquired but then had secondarily been lost, one of the once duplicated genes of the outer arm dynein would be degenerated into a pseudogene owing to parasitism in Giardia.191)
Loss of all or some of the dynein family members, including outer arm, inner arm and cytoplasmic dyneins, is a feature of the dynein history in eukaryotes.190) In fact, the flagella of moss and fern spermatozoids as well as the cilia of Ginkgo sperm (See Ref. 192) lack the outer arm dyneins both morphologically and genomically. Even among animals Caenorhabdatis elegans does not have any arm dyneins, leaving only cytoplasmic dyneins. A recent survey of axonemal proteins in plant genomes revealed that the genes for axonemal dyneins, radial spoke proteins and central pair proteins have been completely lost, although a set of flagellar proteins is conserved and expressed in pollen cells, suggesting their role in the formation of male gametes.193)
As far as the outer arm dynein is concerned, the dimeric, two-headed form found in Opisthokonta, including animals, choanoflagellates and fungi, would be the prototype. On the other hand, in another group consisting of kingdoms such as Archaeplastida, including plants and Chlamydomonas, and Alveolata, including Tetrahymena and Paramecium, the duplication of the OADβ family gene took place at a certain point of evolution and brought about the three-headed outer arms. The findings in Giardia would support the idea that Excavata or more definitely Diplomonadida, including this protist, would not be a primitive eukaryote but would also belong to the latter group corresponding to the bikonts. In other words, only Opisthokonta kept the prototype of the outer arm dynein after its establishment in the ancestral eukaryote, while in another group or other kingdoms the duplication of the OADβ family gene occurred once in a common ancestor or took place in various kingdoms in parallel.190)
Perspectives
Axonemes in flagella and cilia are supramolecular complex with ∼250 proteins, which are arranged so as to exert bending motion by dyneins and microtubules. Recent studies with cryoelectron tomography explore fine substructures and conformational changes of dyneins and axonemes. These lines of studies, as well as analyses by X-ray diffraction and nuclear magnetic resonance, are expected to join single molecular imaging technique and reveal structure-function relationship in dyneins and between dynein and tubulin. Ultimately it might become possible to answer the questions why dyneins are so big, why tubulins undergo a variety of post-translational modifications and why multiple dynein heavy chains are needed for flagellar and ciliary motility. Furthermore, discovery of small inhibitors for dynein or tubulin based on these structural studies would accelerate the researches not only on diverse function of cilia but also on drug discovery in the medical therapy against human ciliopathies. Challenging studies are expected to be carried out in the near future on in vitro assembly of doublet microtubules and the axonemes, which would lead to artificial ‘cilia implantation’ to a cell. In addition, the detailed mechanism underlying the initiation of flagellar and ciliary wave at their base should be explored.
Recent findings that primary cilia participate in various critical signaling pathways such as those conducted by Sonic hedgehog and Wnt elicit a general function of cilia in signaling for proliferation and differentiation of cells and the morphogenesis in the establishment of body plans.194) The importance of cilia is emphasized in some hypotheses proposed for driving force of metazoan or vertebrate body plan.195) However, the roles of cilia as ‘cell antenna’ in multicellular organisms are not surprising because the properties of flagella and cilia that change the motility in response to physical or chemical stimuli are already acquired in protists. In fact, motile protists or sperm (free cells released from multicellular organisms) achieved peculiar innovation in the diversification of flagellar and ciliary structures and functions. Because flagella and cilia have been conserved to adapt in aquatic environments during evolution, the diversification in these structures and regulation might give an important insight for the adaptation of organisms to several environments. In the near future, we anticipate studies on the regulation of sperm motility in several organisms with different fertilization environments, structures of multicilia or macrocilia seen in several protists and metazoa, and degenerated structures of cilia seen in some sensory organs in metazoa.
Although the question why flagella and cilia as well as centrioles represent nine-fold radial symmetry is still unanswered, it is considered that ancient axonemes already showed motile 9+2 structures and their variants in structures and motility are evolved during evolution.196) The 9+2 structures are generally seen in protists and also conserved well in metazoa. Then, two general questions become emerged; what is the origin of flagella and cilia and how they are diverged. The endosymbiont hypothesis was previously proposed,197) but basic cytoskeletal structure of the possible symbiont is far from eukaryotic axonemes. Recent knowledge on the connection of cilia with the regulation of cell cycle and intracellular vesicular transport supports autogenous emergence of cilia through functional transition of microtubule and motor proteins.198) Further investigation on the diversity of flagella and cilia in the future using well-known species or those newly found, such as loss of motile cilia in plants or a certain group of protostomes and compound cilia or macrocilia in metazoa, should shed new light on the biology of dynein and tubulin.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Makoto Okuno and Masakatsu Fujinoki for their helpful suggestion on the motility of mammalian spermatozoa. We are much indebted to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT), the Lalor Foundation, the Population Council, the Ford Foundation and other foundations for their support. The work concerning hyperactivation of mammalian sperm was supported by a grant-in-aid from MEXT (No. 09044240).
Profile
Hideo Mohri was born in 1930. After graduating from the Zoological Institute, the Faculty of Science at the University of Tokyo in 1953, he started his academic carrier with studies on respiration of sea urchin spermatozoa at the Misaki Marine Biological Station. It was shown that sea urchin spermatozoa utilize phospholipids as the main substrate for respiration. From 1962 he spent two years at the Stazione Zoologica, Naples, the Wenner-Gren Institute, University of Stockholm and the Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole. In Stockholm he demonstrated oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria isolated from mammalian spermatozoa. After this stay abroad his interest was concentrated in “contractile proteins” in flagella and cilia at the Komaba Campus of the University of Tokyo, although he had already described ATPase activity of the flagella isolated from sea urchin spermatozoa in 1958, and in 1968 he discovered “tubulin” as the counterpart of dynein ATPase in flagellar and ciliary movement. Then up till now, various contributions were made together with his students to elucidate the mechanism of flagellar and ciliary movement. Some work was also done on male contraceptives and on separation of X- and Y-bearing spermatozoa. He promoted to Professor in 1976 and was elected Dean of the College of General Education, the University of Tokyo, in 1987. He organized “spermatologists”, investigators in sperm cell research, both in Japan and in the world. Later he much contributed to the development of reproductive biology in this country. He was awarded the Prize of the Zoological Society of Japan in 1974 and the Purple Ribbon Medal in 1996. After having served as a Vice-President of the University of the Air for three years, he was Director-General of the National Institute for Basic Biology between 1995 to 2001 and was President of the Okazaki National Research Institutes during the following two years.
Footnotes
The name “spermosin” is now used for a sperm acrosin-like enzyme.2)
References
- 1).Engelhardt V.A. (1946) Adenosinetriphosphatase properties of myosin. Adv. Enzymol. 6, 147–191 [Google Scholar]
- 2).Sawada H., Yokosawa H., Ishii S. (1984) Purification and characterization of two types of trypsin-like enzymes from sperm of the ascidian (Prochordata) Halocynthia roretzi. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 2900–2904 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3).Nelson L. (1955) Adenosinetriphosphatase of Mytilus spermatozoa. I. Effects of pH, calcium and magnesium, and concentration of enzyme and substrate. Biol. Bull. 109, 295–305 [Google Scholar]
- 4).Mohri H. (1958) Adenosinetriphosphatases of sea-urchin spermatozoa. J. Fac. Sci., Univ. Tokyo, IV, 8, 307–315 [Google Scholar]
- 5).Afzelius B.A. (1959) Electron microscopy of the sperm tail. Results obtained with a new fixative. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 5, 269–278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6).Mohri H., Inaba K., Kubo-Irie M., Takai H., Toyoshima Y.Y. (1999) Characterization of outer arm dynein in sea anemone, Anthopleura midori. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 44, 202–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7).Gibbons I.R. (1963) Studies on the protein components of cilia from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 50, 1002–1010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8).Gibbons I.R., Rowe A.J. (1965) Dynein: a protein with adenosinetriphosphatase activity from cilia. Science 149, 424–426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9).Ogawa K., Mohri H. (1975) Preparation of antiserum against a tryptic fragment (Fragment A) of dynein and an immunological approach to the subunit composition of dynein. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 6476–6483 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10).Ogawa K., Mohri T., Mohri H. (1977) Identification of dynein as the outer arms of sea urchin sperm axonemes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5006–5010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11).Johnson K.A., Wall J.S. (1983) Structure and molecular weight of the dynein ATPase. J. Cell Biol. 96, 669–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12).Tang W.-J.Y., Bell C.W., Sale W.S., Gibbons I.R. (1982) Structure of dynein-1 outer arm in sea urchin sperm flagella. I. Analysis by separation of subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 508–515 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13).Ogawa K. (1991) Four ATP-binding sites in the midregion of the β heavy chain of dynein. Nature 352, 643–645 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14).Gibbons I.R., Gibbons B.H., Mocz G., Asai D.J. (1991) Multiple nucleotide-binding sites in the sequence of dynein β heavy chain. Nature 352, 640–643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15).Mohri H. (1968) Amino-acid composition of “tubulin” constituting microtubules of sperm flagella. Nature 217, 1053–1054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16).Yanagisawa T., Hasegawa S., Mohri H. (1968) The bound nucleotides of the isolated microtubules of sea-urchin sperm flagella and their possible role in flagellar movement. Exp. Cell Res. 52, 86–100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17).Mohri H., Shimomura M. (1973) Comparison of tubulin and actin. J. Biochem. 74, 209–220 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18).Mohri H., Hosoya N. (1988) Two decades since the naming of tubulin—The multi-facets of tubulin—. Zool. Sci. 5, 1165–1185 [Google Scholar]
- 19).Borisy G.G., Taylor E.W. (1967) The mechanism of action of colchicine: colchicine binding to sea urchin eggs and the mitotic apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 34, 535–548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20).Weisenberg R.C. (1972) Microtubule formation in vitro in solutions containing low calcium concentrations. Science 177, 1104–1105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21).Ponstingl H., Krauhs E., Little M., Kempf T. (1981) Complete amino acid sequence of α tubulin from porcine brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2757–2761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22).Valenzuela P., Auiroga M., Zaldivar J., Rutter W.J., Kirschner M.W., Cleveland D.W. (1981) Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences encoded by α and β tubulin mRNAs. Nature 289, 650–655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23).Vale R.D., Reese T.S., Sheetz M.P. (1985) Identification of a novel force generating protein (kinesin) involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell 41, 39–50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24).Satir P. (1965) Studies on cilia II. Examination of the distal region of the ciliary shaft and the role of the filaments in motility. J. Cell Biol. 96, 669–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25).Summers K.E., Gibbons I.R. (1971) Adenosine triphosphate-induced sliding of tubules in trypsin-treated flagella of sea urchin sperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68, 3092–3096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26).Hoffmann-Berling H. (1955) Geisselmodelle und Adenosintriphosphat (ATP). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 16, 146–154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27).Naitoh Y., Kaneko H. (1972) Reactivated Triton-extracted models of Paramecium. Modification of ciliary movement by calcium ions. Science 176, 523–524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28).Gibbons B.H., Gibbons I.R. (1972) Flagellar movement and adenosine triphosphatase activity in sea urchin sperm extracted with Triton X-100. J. Cell Biol. 54, 75–97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29).Shingyoji C., Murakami A., Takahashi K. (1977) Local reactivation of Triton-extracted flagella by iontophoretic application of ATP. Nature 265, 269–270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30).Vale R.D., Toyoshima Y.Y. (1988) Rotation and translocation of microtubules in vitro induced by dynein from Tetrahymena cilia. Cell 52, 459–469 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31).Gibbons I.R., Fronk E. (1972) Some properties of bound and soluble dynein from sea urchin sperm flagella. J. Cell Biol. 54, 365–381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32).Padma P., Hozumi A., Ogawa K., Inaba K. (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a thioredoxin/nucleoside diphosphate kinase related dynein intermediate chain from the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis. Gene 275, 177–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33).Pfister K.K., Fay R.B., Witman G.B. (1982) Purification and polypeptide composition of dynein ATPases from Chlamydomonas flagella. Cell Motil. 2, 525–547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34).Kamiya R. (1988) Mutations at twelve independent loci result in absence of outer dynein arms in Chylamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Cell Biol. 107, 2253–2258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35).Piperno G., Huang B., Ramanis Z., Luck D.J. (1981) Radial spokes of Chlamydomonas flagella: polypeptide composition and phosphorylation of stalk components. J. Cell Biol. 88, 73–79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36).Gibbons I.R. (1981) Cilia and flagella of eukaryotes. J. Cell Biol. 91, 107s–124s [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37).Inaba K. (2007) Molecular basis of sperm flagellar axonemes: structural and evolutionary aspects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1101, 506–526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38).DiBella L.M., King S.M. (2001) Dynein motors of the Chlamydomonas flagellum. Int. Rev. Cytol. 210, 227–268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39).Gee M.A., Heuser J.E., Vallee R.B. (1997) An extended microtubule-binding structure within the dynein motor domain. Nature 390, 636–639 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40).Nicastro D., Schwartz C., Pierson J., Gaudette R., Porter M.E., McIntosh J.R. (2006) The molecular architecture of axonemes revealed by cryoelectron tomography. Science 313, 944–948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41).Ishikawa T., Sakakibara H., Oiwa K. (2007) The architecture of outer dynein arms in situ. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 1249–1258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42).Inaba K., Mohri H. (1989) Dynamic conformational changes of 21S dynein ATPase coupled with ATP hydrolysis revealed by proteolytic digestion. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8384–8388 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43).Inaba K., Mohri H. (1989) Two states of the conformation of 21S outer arm dynein coupled with ATP hydrolysis. J. Biochem. 106, 349–354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44).Inaba K. (2000) Conformational changes of dynein: mapping and sequence analysis of ATP/vanadate-dependent trypsin-sensitive sites on the outer arm dynein β heavy chain from sea urchin sperm flagella. J. Biochem. 127, 1115–1120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45).Movassagh T., Bui K.H., Sakakibara H., Oiwa K., Ishikawa T. (2010) Nucleotide-induced global conformational changes of flagellar dynein arms revealed by in situ analysis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 761–767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46).Ueno H., Yasunaga T., Shingyoji C., Hirose K. (2008) Dynein pulls microtubules without rotating its stalk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 205, 19702–19707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47).Yano-Toyoshima Y. (1985) Two heavy chains of 21S dynein from sea urchin sperm flagella. J. Biochem. 98, 767–779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48).Moss A.G., Sale W.S., Fox L.A., Witman G.B. (1992) The α subunit of sea urchin sperm outer arm dynein mediates structural and rigor binding to microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 118, 1189–1200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49).Toyoshima Y.Y. (1987) Chymotryptic digestion of Tetrahymena 22S dynein. I. Decomposition of three-headed 22S dynein to one- and two-headed particles. J. Cell Biol. 105, 887–895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50).Toyoshima Y.Y. (1987) Chymotryptic digestion of Tetrahymena ciliary dynein. II. Pathway of the degradation of 22S dynein heavy chains. J. Cell Biol. 105, 897–901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51).Ogawa K., Takai H., Ogiwara A., Yokota E., Shimizu T., Inaba K., Mohri H. (1996) Is outer arm dynein intermediate chain 1 multifunctional? Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 1895–1907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52).Takada S., Kamiya R. (1994) Functional reconstitution of Chlamydomonas outer dynein arms from α-β and γ subunits: requirement of a third factor. J. Cell Biol. 126, 737–745 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53).Koutoulis A., Pazour G.J., Wilkerson C.G., Inaba K., Sheng H., Takada S., Witman G.B. (1997) The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii ODA3 gene encodes a protein of the outer dynein arm docking complex. J. Cell Biol. 137, 1069–1080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54).Takada S., Wilkerson C.G., Wakabayashi K., Kamiya R., Witman G.B. (2002) The outer dynein arm-docking complex: composition and characterization of a subunit (oda1) necessary for outer arm assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 1015–1029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55).Casey D.M., Inaba K., Pazour G.J., Takada S., Wakabayashi K., Wilkerson C.G., Kamiya R., Witman G.B. (2003) DC3, the 21-kDa subunit of the outer dynein arm-docking complex (ODA-DC), is a novel EF-hand protein important for assembly of both the outer arm and the ODA-DC. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 3650–3663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56).Ushimaru Y., Konno A., Kaizu M., Ogawa K., Satoh N., Inaba K. (2006) Association of a 66 kDa homolog of Chlamydomonas DC2, a subunit of the outer arm docking complex, with outer arm dynein of sperm flagella in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Zool. Sci. 23, 679–687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57).Hozumi A., Satouh Y., Makino Y., Toda T., Ide H., Ogawa K., King S.M., Inaba K. (2006) Molecular characterization of Ciona sperm outer arm dynein reveals multiple components related to outer arm docking complex protein 2. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 63, 591–603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58).Kagami O., Gotoh M., Makino Y., Mohri H., Kamiya R., Ogawa K. (1998) A dynein light chain of sea urchin sperm flagella is a homolog of mouse Tctex 1, which is encoded by a gene of the t complex sterility locus. Gene 211, 383–386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59).Inaba K., Kagami O., Ogawa K. (1999) Tctex2-related outer arm dynein light chain is phosphorylated at activation of sperm motility. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 256, 177–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60).Mizuno K., Padma P., Konno A., Satouh Y., Ogawa K., Inaba K. (2009) A novel neuronal calcium sensor family protein, calaxin, is a potential Ca2+-dependent regulator for the outer arm dynein of metazoan cilia and flagella. Biol. Cell 101, 91–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61).Kagami O., Takada S., Kamiya R. (1990) Microtubule translocation caused by three subspecies of inner-arm dynein from Chlamydomonas flagella. FEBS Lett. 264, 179–182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62).Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Smith E.F., Sale W.S. (1990) Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J. Cell Biol. 110, 379–389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63).Kamiya R. (2002) Functional diversity of axonemal dyneins as studied in Chlamydomonas mutants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 219, 115–155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64).Habermacher G., Sale W.S. (1997) Regulation of flagellar dynein by phosphorylation of a 138-kD inner arm dynein intermediate chain. J. Cell Biol. 136, 167–176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65).King S.J., Dutcher S.K. (1997) Phosphoregulation of an inner dynein arm complex in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is altered in phototactic mutant strains. J. Cell Biol. 136, 177–191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66).Hozumi A., Padma P., Toda T., Ide H., Inaba K. (2008) Molecular characterization of axonemal proteins and signaling molecules responsible for chemoattractant-induced sperm activation in Ciona intestinalis. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 65, 249–267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67).Tilney L.G., Bryan J., Bush D.J., Fujiwara K., Mooseker M.S., Murphy D.B., Snyder D.H. (1973) Microtubules: evidence for 13 protofilaments. J. Cell Biol. 59, 267–275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68).Linck R.W., Stephens R.E. (2007) Functional protofilament numbering of ciliary, flagellar, and centriolar microtubules. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 64, 489–495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69).Amos L.A. (2008) The tektin family of microtubule-stabilizing proteins. Genome Biol. 9, 229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70).Nicastro D., Fu X., Heuser T., Tso A., Porter M.E., Linck R.W. (2011) Cryo-electron tomography reveals conserved features of doublet microtubules in flagella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, E845–E853 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71).Hoops H.J., Witman G.B. (1983) Outer doublet heterogeneity reveals structural polarity related to beat direction in Chlamydomonas flagella. J. Cell Biol. 97, 902–908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72).Kobayashi Y., Mohri H. (1977) Microheterogeneity of alpha and beta subunit of tubulin from microtubules of starfish (Asterias amurensis) sperm flagella. J. Mol. Biol. 116, 613–617 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73).Sullivan K.F. (1988) Structure and utilization of tubulin isotypes. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 4, 687–716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74).Huitorel P., White D., Fouquet J.P., Kann M.L., Cosson J., Gagnon C. (2002) Differential distribution of glutamylated tubulin isoforms along the sea urchin sperm axoneme. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 62, 139–148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75).Wloga D., Gaertig J. (2010) Post-translational modifications of microtubules. J. Cell Sci. 123, 3447–3455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76).Janke C., Rogowski K., Wloga D., Regnard C., Kajava A.V., Strub J.M., Temurak N., van Dijk J., Boucher D., van Dorsselaer A., Suryavanshi S., Gaertig J., Eddé B. (2005) Tubulin polyglutamylase enzymes are members of the TTL domain protein family. Science 308, 1758–1762 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77).Wloga D., Webster D.M., Rogowski K., Bré M.H., Levilliers N., Jerka-Dziadosz M., Janke C., Dougan S.T., Gaertig J. (2009) TTLL3 is a tubulin glycine ligase that regulates the assembly of cilia. Dev. Cell 16, 867–876 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78).Ikegami K., Sato S., Nakamura K., Ostrowski L.E., Setou M. (2010) Tubulin polyglutamylation is essential for airway ciliary function through the regulation of beating asymmetry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 10490–10495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79).Smith E.F., Yang P. (2004) The radial spokes and central apparatus: mechano-chemical transducers that regulate flagellar motility. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 57, 8–17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80).Yang P., Diener D.R., Yang C., Kohno T., Pazour G.J., Dienes J.M., Agrin N.S., King S.M., Sale W.S., Kamiya R., Rosenbaum J.L., Witman G.B. (2006) Radial spoke proteins of Chlamydomonas flagella. J. Cell Sci. 119, 1165–1174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81).DiPetrillo C.G., Smith E.F. (2010) Pcdp1 is a central apparatus protein that binds Ca2+-calmodulin and regulates ciliary motility. J. Cell Biol. 189, 601–612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82).Gardner L.C., O’Toole E., Perrone C.A., Giddings T., Porter M.E. (1994) Components of a ‘dynein regulatory complex’ are located at the junction between the radial spokes and the dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1311–1325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83).Heuser T., Raytchev M., Krell J., Porter M.E., Nicastro D. (2009) The dynein regulatory complex is the nexin link and a major regulatory node in cilia and flagella. J. Cell Biol. 187, 921–933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84).Bui K.H., Sakakibara H., Movassagh T., Oiwa K., Ishikawa T. (2009) Asymmetry of inner dynein arms and inter-doublet links in Chlamydomonas flagella. J. Cell Biol. 186, 437–446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85).Satir P. (1968) Studies on cilia. III. Further studies on the cilium tip and a “sliding filament” model of ciliary motility. J. Cell Biol. 39, 77–94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86).Sale W.S., Satir P. (1977) Direction of active sliding of microtubules in Tetrahymena cilia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2045–2049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87).Ishijima S., Kubo-Irie M., Mohri H., Hamaguchi Y. (1996) Calcium-dependent bidirectional power stroke of the dynein arms in sea urchin sperm axonemes. J. Cell Sci. 109, 2833–2842 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88).Lorch D.P., Lindemann C.B., Hunt A.J. (2008) The motor activity of mammalian axonemal dynein studied in situ on doublet microtubules. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 65, 487–494 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89).Hata H., Yano Y., Mohri T., Mohri H., Miki-Noumura T. (1980) ATP-driven tubule extrusion from axonemes without outer dynein arms of sea-urchin sperm flagella. J. Cell Sci. 41, 331–340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90).Yano Y., Miki-Noumura T. (1980) Sliding velocity between outer doublet microtubules of sea-urchin sperm axonemes. J. Cell Sci. 44, 169–186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91).Wada S., Okuno M., Mohri H. (1991) Inner arm dynein ATPase fraction of sea urchin sperm flagella causes active sliding of axonemal outer doublet microtubule. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 175, 173–178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92).Kamimura S., Shingyoji C., Takahashi K. (1982) Microtubule sliding in reactivated flagella. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 35, 159–177 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93).Kamimura S., Takahashi K. (1981) Direct measurement of the force of microtubule sliding in flagella. Nature 293, 566–568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94).Oiwa K., Takahashi K. (1988) The force-velocity relationship for microtubule sliding in demembranated sperm flagella of the sea urchin. Cell Struct. Funct. 13, 193–205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95).Hiramoto, Y. (1974) Mechanics of ciliary movement. In Cilia and Flagella (ed. Sleigh, M.A.). Academic Press, London, pp. 177–196. [Google Scholar]
- 96).Kaneko T., Mōri T., Ishijima S. (2007) Digital image analysis of the flagellar beat of activated and hyperactivated Suncus spermatozoa. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 74, 478–485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97).Ishijima S. (2007) The velocity of microtubule sliding: its stability and load dependency. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 64, 809–813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98).Bannai H., Yoshimura M., Takahashi K., Shingyoji C. (2000) Calcium regulation of microtubule sliding in reactivated sea urchin sperm flagella. J. Cell Sci. 113, 831–839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99).Nakano I., Kobayashi T., Yoshimura M., Shingyoji C. (2003) Central-pair-linked regulation of microtubule sliding by calcium in flagellar axonemes. J. Cell Sci. 116, 1627–1636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100).Sale W.S. (1986) The axonemal axis and Ca2+-induced asymmetry of active microtubule sliding in sea urchin sperm tails. J. Cell Biol. 102, 2042–2052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101).Mogami Y., Takahashi K. (1983) Calcium and microtubule sliding in ciliary axonemes isolated from Paramecium caudatum. J. Cell Sci. 61, 107–121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102).Lindemann C.B., Orlando A., Kanous K.S. (1992) The flagellar beat of rat sperm is organized by the interaction of two functionally distinct populations of dynein bridges with a stable central axonemal partition. J. Cell Sci. 102, 249–260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103).Kanous K.S., Casey C., Lindemann C.B. (1993) Inhibition of microtubule sliding by Ni2+ and Cd2+: evidence for a differential response of certain microtubule pairs within the bovine sperm axoneme. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 26, 66–76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104).Kinukawa M., Oda S., Shirakura Y., Okabe M., Ohmuro J., Baba S.A., Nagata M., Aoki F. (2006) Roles of cAMP in regulating microtubule sliding and flagellar bending in demembranated hamster spermatozoa. FEBS Lett. 580, 1515–1520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105).Ishijima S., Mohri H. (1985) A quantitative description of flagellar movement in golden hamster spermatozoa. J. Exp. Biol. 114, 463–475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106).Woolley D.M. (1997) Evidence for “twisted plane” undulations in golden hamster sperm tails. J. Cell Biol. 75, 851–865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107).Mohri H., Mohri T., Okuno M. (1987) Topographical relationship between the axonemal arrangement and the bend direction in starfish sperm flagella. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 8, 76–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108).Fujimura M., Okuno M. (2006) Requirement of the fixed end for spontaneous beating in flagella. J. Exp. Biol. 209, 1336–1343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109).Sugino K., Naitoh Y. (1982) Simulated cross-bridge patterns corresponding to ciliary beating in Paramecium. Nature 295, 609–611 [Google Scholar]
- 110).Murase, M. (1992) The Dynamics of Cellular Motility. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. [Google Scholar]
- 111).Riedel-Kruse I.H., Hilfinger A., Howard J., Jülicher F. (2007) How molecular motors shape the flagellar beat. HFSP J. 1, 192–208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112).Woolley D.M. (2010) Flagellar oscillation: a commentary on proposed mechanisms. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 85, 453–470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113).Hiramoto Y., Baba S.A. (1978) A quantitative analysis of flagellar movement in echinoderm spermatozoa. J. Exp. Biol. 76, 85–104 [Google Scholar]
- 114).Ishijima S., Hamaguchi M.S., Naruse M., Ishijima S.A., Hamaguchi Y. (1992) Rotational movement of a spermatozoon around its long axis. J. Exp. Biol. 163, 15–31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115).Ishijima S., Hamaguchi Y. (1993) Calcium ion regulation of chirality of beating flagellum of reactivated sea urchin spermatozoa. Biophys. J. 65, 1445–1448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116).Woolley D.M., Vernon G.G. (2001) A study of helical and planar waves on sea urchin sperm flagella, with a theory of how they are generated. J. Exp. Biol. 204, 1333–1345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117).Ishijima S. (2012) Mechanical constraint converts planar waves into helices on tunicate and sea urchin sperm flagella. Cell Struct. Funct. 37, 13–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118).Ishijima S., Sekiguchi K., Hiramoto Y. (1988) Comparative study of the beat patterns of American and Asian horseshoe crab sperm: evidence for a role of the central pair complex in forming planar waveforms in flagella. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 9, 264–270 [Google Scholar]
- 119).Okuno M., Hiramoto Y. (1979) Direct measurements of the stiffness of echinoderm sperm flagella. J. Exp. Biol. 79, 235–243 [Google Scholar]
- 120).Ishijima S., Hiramoto Y. (1994) Flexural rigidity of echinoderm sperm flagella. Cell Struct. Funct. 19, 349–362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121).Ohmuro J., Mogami Y., Baba S.A. (2004) Progression of flagellar stages during artificially delayed motility initiation in sea urchin sperm. Zool. Sci. 21, 1099–1108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122).Kinukawa M., Ohmuro J., Baba S.A., Murashige S., Okuno M., Nagata M., Aoki F. (2005) Analysis of flagellar bending in hamster spermatozoa: characterization of an effective stroke. Biol. Reprod. 73, 1269–1274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123).Ohmuro J., Ishijima S. (2006) Hyperactivation is the mode conversion from constant-curvature beating to constant-frequency beating under a constant rate of microtubule sliding. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 73, 1412–1421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124).Morisawa M. (1994) Cell signaling mechanisms for sperm motility. Zool. Sci. 11, 647–662 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125).Inaba K. (2003) Molecular architecture of the sperm flagella: molecules for motility and signaling. Zool. Sci. 20, 1043–1056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126).Morisawa M., Yoshida M. (2005) Activation of motility and chemotaxis in the spermatozoa: from invertebrates to humans. Reprod. Med. Biol. 4, 101–114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127).Mohri H., Yasumasu I. (1963) Studies on the respiration of sea-urchin spermatozoa. V. The effect of Pco2. J. Exp. Biol. 40, 573–586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128).Johnson C.H., Clapper D.L., Winkler M.M., Lee H.C., Epel D. (1983) A volatile inhibitor immobilizes sea urchin sperm in semen by depressing the intracellular pH. Dev. Biol. 98, 493–501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129).Yanagisawa T. (1967) Studies on echinoderm phosphagens. III. Changes in the content of creatine phosphate after stimulation of sperm motility. Exp. Cell Res. 46, 348–354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130).Tombes R.M., Shapiro B.M. (1985) Metabolic channeling: a phosphortylcreatine shuttle to mediate high energy phosphate transport between sperm mitochondria and tail. Cell 41, 325–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131).Inaba K., Dréanno C., Cosson J. (2003) Control of flatfish sperm motility by CO2 and carbonic anhydrase. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 55, 174–187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132).Nishioka, D. and Cross, N. (1978) The role of external sodium in sea urchin fertilization. In Cell Reproduction (eds. Dirksen, E.R., Prescott, D.M. and Fox, C.F.). Academic Press, New York, pp. 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- 133).Ishiguro K., Murofushi H., Sakai H. (1982) Evidence that cAMP-dependent protein kinase and a protein factor are involved in reactivation of Triton X-100 models of sea urchin and starfish spermatozoa. J. Cell Biol. 92, 777–782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134).Morisawa M., Suzuki K. (1980) Osmolality and potassium ion: their roles in initiation of sperm motility in teleosts. Science 210, 1145–1147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135).Morisawa M., Okuno M. (1982) Cyclic AMP induces maturation of trout sperm axoneme to initiate motility. Nature 295, 703–704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136).Inaba K., Morisawa S., Morisawa M. (1998) Proteasomes regulate the motility of salmonid fish sperm through modulation of cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of an outer arm dynein light chain. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1105–1115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137).Itoh A., Inaba K., Ohtake H., Fujinoki M., Morisawa M. (2003) Characterization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from rainbow trout sperm. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 305, 855–861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138).Morisawa, M., Oda, S., Yoshida, M. and Takai, H. (1999) Transmembrane signal transduction for the regulation of sperm motility in fishes and ascidians. In The Male Gamete: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications (ed. Gagnon, C.). Cache River Press, Vienna, pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- 139).Morita M., Fujinoki M., Okuno M. (2005) K+-independent initiation of motility in chum salmon sperm treated with an organic alcohol, glycerol. J. Exp. Biol. 208, 4549–4556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140).Takei G.L., Mukai C., Okuno M. (2012) Transient mobilization caused by osmotic shock initiates salmonid fish sperm motility. J. Exp. Biol. 215, 630–641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141).Tash, J.S. (1990) Role of cAMP, calcium, and protein phosphorylation in sperm motility. In Controls of Sperm Motility: Biological and Clinical Aspects (ed. Gagnon, C.). CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- 142).Ishida K., Okuno M., Morisawa S., Mohri T., Mohri H., Waku M., Morisawa M. (1987) Initiation of sperm motility induced by cyclic AMP in hamster and boar. Dev. Growth Differ. 29, 47–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143).Si Y., Okuno M. (1995) Activation of mammalian sperm motility by regulation of microtubule sliding via cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate-dependent phosphorylation. Biol. Reprod. 53, 1081–1087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144).Okamura N., Tajima Y., Soejima A., Masuda H., Sugita Y. (1985) Sodium bicarbonate in seminal plasma stimulates the motility of mammalian spermatozoa through direct activation of adenylate cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 9699–9705 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145).Chen Y., Cann M.J., Litvin T.N., Iourgenko V., Sinclair M.L., Levin L.R., Buck J. (2000) Soluble adenylyl cyclase as an evolutionarily conserved bicarbonate sensor. Science 289, 625–628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146).Spehr M., Schwane K., Riffell J.A., Zimmerd R.K., Hatt H. (2006) Odorant receptors and olfactory-like signaling mechanisms in mammalian sperm. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 250, 128–136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147).Chilcote T.J., Johnson K.A. (1990) Phosphorylation of Tetrahymena 22 S dynein. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17257–17266 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148).Inaba K. (2002) Dephosphorylation of Tctex2-related dynein light chain by type 2A protein phosphatase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 297, 800–805 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149).Ficarro S., Chertihin O., Westbrook V.A., White F., Jayes F., Kalab P., Marto J.A., Shabanowitz J., Herr J.C., Hunt D.F., Visconti P.E. (2002) Phosphoproteome analysis of capacitated human sperm. Evidence of tyrosine phosphorylation of a kinase-anchoring protein 3 and valosin-containing protein/p97 during capacitation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11579–11589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150).Yoshida M., Murata M., Inaba K., Morisawa M. (2002) A chemoattractant for ascidian spermatozoa is a sulfated steroid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 14831–14836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151).Shiba K., Baba S.A., Inoue T., Yoshida M. (2008) Ca2+ bursts occur around a local minimal concentration of attractant and trigger sperm chemotactic response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 19312–19317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152).Brokaw C.J. (1979) Calcium-induced asymmetrical beating of triton-demembranated sea urchin sperm flagella. J. Cell Biol. 82, 401–411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153).Gibbons B.H., Gibbons I.R. (1980) Calcium-induced quiescence in reactivated sea urchin sperm. J. Cell Biol. 84, 13–27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154).Bessen M., Fay R.B., Witman G.B. (1980) Calcium control of waveform in isolated flagellar axonemes of Chlamydomonas. J. Cell Biol. 86, 446–455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155).Kamiya R., Okamoto M. (1985) A mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that lacks the flagellar outer dynein arm but can swim. J. Cell Sci. 74, 181–191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156).Wakabayashi K., Yagi T., Kamiya R. (1997) Ca2+-dependent waveform conversion in the flagellar axoneme of Chlamydomonas mutants lacking the central-pair/radial spoke system. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 38, 22–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157).Sakato M., King S.M. (2003) Calcium regulates ATP-sensitive microtubule binding by Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 43571–43579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158).Walt, H. and Hedinger, C. (l983) Loss of activity of motile components in rat spermatids during differentiation to virtually immotile testicular spermatozoa. In The Sperm Cell (ed. André, J.). Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, The Hague, pp. 376–379. [Google Scholar]
- 159).Si Y., Okuno M. (1993) Multiple activation of mouse sperm motility. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 36, 89–95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160).Yanagimachi R. (1970) The movement of golden hamster spermatozoa before and after capacitation. J. Reprod. Fertil. 23, 193–196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161).Yanagimachi, R. (1994) Mammalian fertilization. In The Physiology of Reproduction (eds. Knobil, E. and Neill, J.D.). Raven Press, New York, pp. 189–317. [Google Scholar]
- 162).Suarez S.S. (2008) Control of hyperactivation in sperm. Hum. Reprod. Update 14, 647–657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163).Ishijima S., Baba S.A., Mohri H., Suarez S.S. (2002) Quantitative analysis of flagellar movement in hyperactivated and acrosome-reacted golden hamster spermatozoa. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 61, 376–384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164).Drobnis E.Z., Yudin A.I., Cherr G.N., Katz D.F. (1988) Hamster sperm penetration of the zona pellucida: kinematic analysis and mechanical implications. Dev. Biol. 130, 311–323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165).Ishijima S. (2011) Dynamics of flagellar force generated by a hyperactivated spermatozoon. Reproduction 142, 1–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166).Mohri H., Yanagimachi R. (1980) Characteristics of motor apparatus in testicular, epididymal and ejaculated spermatozoa. Exp. Cell Res. 127, 191–196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167).Fujinoki M., Ohtake H., Okuno M. (2001) Serine phosphorylation of flagellar proteins associated with the motility activation of hamster spermatozoa. Biomed. Res. 22, 45–58 [Google Scholar]
- 168).Hoskins, D.D. and Vijayaraghavan, S. (1990) A new theory on the acquisition of sperm motility during epididymal transit. In Controls of Sperm Motility: Biological and Clinical Aspects (ed. Gagnon, C.). CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- 169).Morisawa S., Morisawa M. (1988) Induction of potential for sperm motility by bicarbonate and pH in rainbow trout and chum salmon. J. Exp. Biol. 136, 13–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170).Fujinoki M. (2009) Non-genomic regulation of mammalian sperm hyperactivation. Reprod. Med. Biol. 8, 47–52 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171).Ho H.C., Granish K.A., Suarez S.S. (2002) Hyperactivated motility of bull sperm is triggered at the axoneme by Ca2+ and not cAMP. Dev. Biol. 250, 208–217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172).Ishijima S., Mohri H., Overstreet J.W., Yudin A.I. (2006) Hyperactivation of monkey spermatozoa is triggered by Ca2+ and completed by cAMP. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 73, 1129–1139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173).Mohri H., Mohri T., Ernster L. (1965) Isolation and enzymic properties of the midpiece of bull spermatozoa. Exp. Cell Res. 38, 217–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174).Mukai C., Okuno M. (2004) Glycolysis plays a major role for adenosine triphosphate supplementation in mouse sperm flagellar movement. Biol. Reprod. 71, 540–547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175).Miki, K. (2007) Energy metabolism and sperm function. In Spermatology (eds. Roldan, E.R.S. and Gomendio, M.). Nottingham Univ. Press, Nottingham, pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- 176).Hang P., Miller M.G., Meyers S.A., VandeVoort C.A. (2008) Sperm mitochondrial integrity is not required for hyperactivated motility, zona binding, or acrosome reaction in the rhesus macaque. Biol. Reprod. 79, 367–375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177).Krisfalusi M., Miki K., Magyar P.L., O’Brien D.A. (2006) Multiple glycolytic enzymes are tightly bound to the fibrous sheath of mouse spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 75, 270–278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178).Si Y., Okuno M. (1999) Role of tyrosine phosphorylation of flagellar proteins in hamster sperm hyperactivation. Biol. Reprod. 61, 240–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179).Visconti P.E., Kopf G.S. (1998) Regulation of protein phosphorylation during sperm capacitation. Biol. Reprod. 59, 1–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180).Turner R.M.O., Eriksson R.M.L., Geerton G.L., Moss S.B. (1999) Relationship between sperm motility and the processing and tyrosine phosphorylation of two human sperm fibrous sheath proteins, pro-hAKAP82 and hAKAP82. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 5, 816–824 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181).Kota V., Dhople V.M., Shivaji S. (2009) Tyrosine phosphoproteome of hamster spermatozoa: role of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 in sperm capacitation. Proteomics 9, 1809–1826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182).Almog T., Naor Z. (2010) The role of mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) in sperm functions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 314, 239–243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183).Publicover S., Barratt C. (2011) Progesteron’s gateway into sperm. Nature 471, 313–314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184).Fujinoki M. (2010) Suppression of progesterone-enhanced hyperactivation in hamster spermatozoa by estrogen. Reproduction 140, 453–464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185).de Lamirande E., O’Flaherty C. (2008) Sperm activation: role of reactive oxygen species and kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1784, 106–115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186).Erickson H.P. (1997) FtsZ, a tubulin homolog, in prokaryote cell division. Trends Cell Biol. 7, 362–367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187).Wada S., Okuno M., Nakamura K.-I., Mohri H. (1992) Dynein of sperm flagella of oyster belonging to Protostomia also has a two-headed structure. Biol. Cell 76, 311–317 [Google Scholar]
- 188).Sakakibara H., Mitchell D.R., Kamiya R. (1991) A Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein mutant missing the α heavy chain. J. Cell Biol. 113, 615–622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189).Mohri, H., Kubo-Irie and Irie, M. (1995) Outer arm dynein of sperm flagella and cilia in the animal kingdom. Mém. Mus. natn. Hist. nat. Paris 166, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- 190).Wickstead, B. and Gull, K. (2012) Evolutionary biology of dyneins. In Dyneins. Structure, Biology and Disease (ed. King, S.M.). Academic Press, New York, and Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 89–121. [Google Scholar]
- 191).Mohri, H., Kubo-Irie, M., Udagawa, K., Irie, M. and Yagi, T. (2005) Outer arm dynein in living organisms. A morphological approach. Abstracts of International Workshop Dynein 2005, S4-4. [Google Scholar]
- 192).Li Y., Wang F.H., Knox R.B. (1989) Ultrastructural analysis of the flagellar apparatus in sperm cells of Ginkgo biloba. Protoplasma 149, 57–63 [Google Scholar]
- 193).Hodges M.E., Wickstead B., Gull K., Langdale J.A. (2011) Conservation of ciliary proteins in plants with no cilia. BMC Plant Biol. 11, 185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194).Davis E.E., Brueckner M., Katsanis N. (2006) The emerging complexity of the vertebrate cilium: new functional roles for an ancient organelle. Dev. Cell 11, 9–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195).Garstang W. (1928) The morphology of the Tunicata. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 72, 51–189 [Google Scholar]
- 196).Mitchell D.R. (2004) Speculations on the evolution of 9+2 organelles and the role of central pair microtubules. Biol. Cell 96, 691–696 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197).Margulis L., Bermudes D. (1985) Symbiosis as a mechanism of evolution: status of cell symbiosis theory. Symbiosis 1, 101–124 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198).Cavalier-Smith T. (2002) The phagotrophic origin of eukaryotes and phylogenetic classification of Protozoa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 297–354 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]