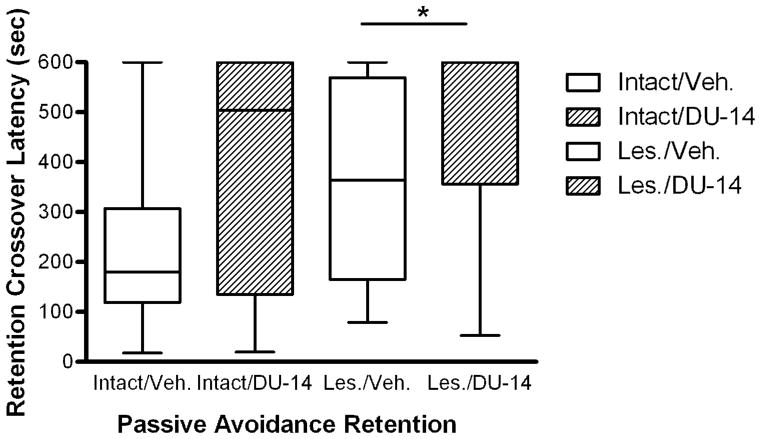
Figure 4.
The effect of DU-14 and vehicle treatment on retention crossover latency. Kruskal-Wallis analysis (p=0.05; h=7.92) shows that crossover latency was significantly longer in the lesioned DU-14 treatment group (n=6) compared to the lesioned vehicle group (n=8; * = p< 0.05 Dunn’s post-hoc test). There was a non-significant trend for an increase in retention crossover latency in the intact DU-14 treatment group (n=11) compared to intact vehicle (n=9).