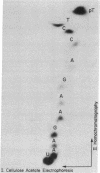
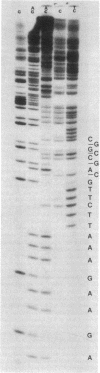
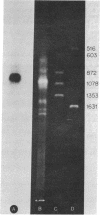
Abstract
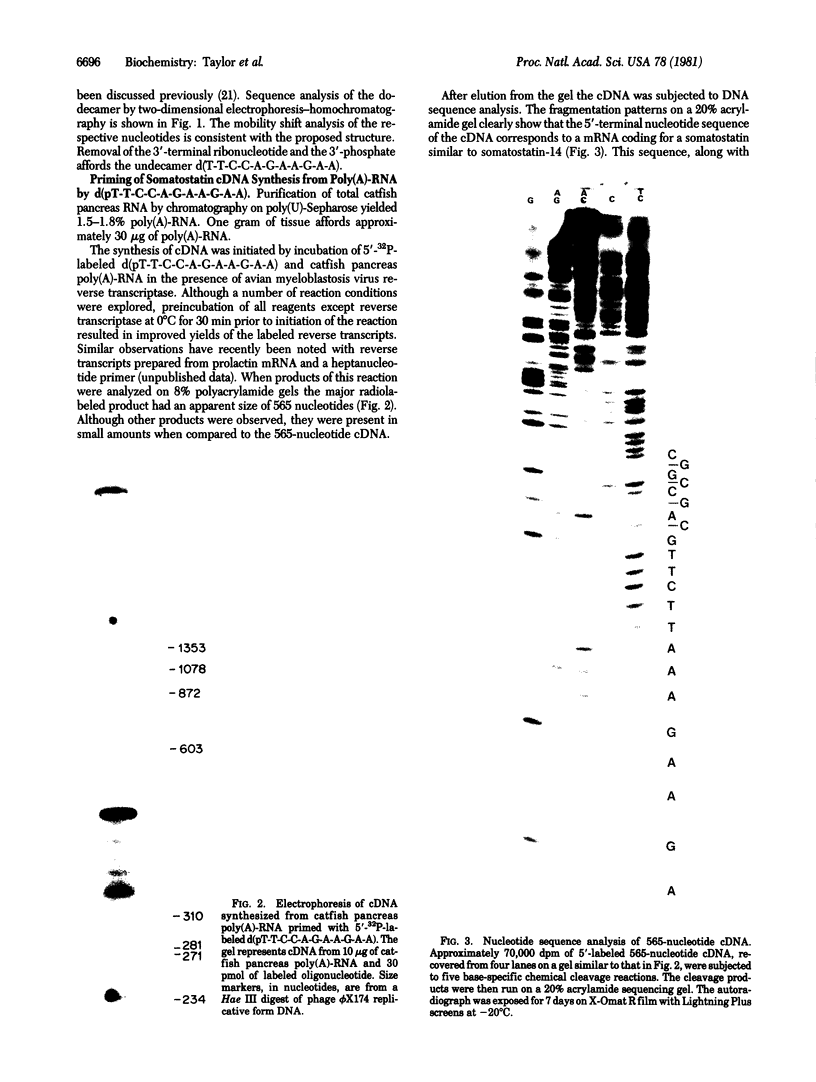
A synthetic oligonucleotide having the sequence d(T-T-C-C-A-G-A-A-G-A-A) deduced from the amino acid sequence Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys of somatostatin-14 was used to prime the synthesis of a cDNA from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) pancreatic poly(A)-RNA. The major product of this reaction was a cDNA fragment of 565 nucleotides. Chemical sequence analysis of the cDNA fragment revealed that it was complementary to a mRNA coding for somatostatin. The 565-nucleotide cDNA hybridizes strongly with a poly(A)-RNA estimated to be 1000 nucleotides in length. An amino acid sequence of the somatostatin precursor was predicted from the nucleotide sequence. Oyama et al. [Oyama, H., Bradshaw, R. A., Bates, O. J. & Permutt, A. (1980) J. Biol. Chem. 255, 2251-2254] have reported the isolation of a somatostatin from the catfish that is 22 residues in length (somatostatin-22). This peptide differs from somatostatin-14 in amino acid sequence. The cDNA sequence obtained by this laboratory codes for somatostatin-14 and predicts another somatostatin gene product from this species. Thus it would appear that there are at least two somatostatin gene products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. L., Brunstedt J., Noyes B. E. A general method for detection and characterization of an mRNA using an oligonucleotide probe. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1023–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. C., Dixon J. E. Isolation and structure of a peptide hormone predicted from a mRNA sequence. A second somatostatin from the catfish pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8267–8270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Mortimer C. H., Thorner M. O., Besser G. M., Hall R., Gomez-Pan A., Roy V. M., Russell R. C., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J. Inhibition of gastrin and gastric-acid secretion by growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone. Lancet. 1974 Nov 9;2(7889):1106–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90869-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Noyes B. E., Agarwal K. L., Steiner D. F. Construction and selection of recombinant plasmids containing full-length complementary DNAs corresponding to rat insulins I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M. L., Cohn M. 'Barrel rotation' induced by somatostatin in the non-lesioned rat. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 10;96(1):138–141. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Böhlen P., Ling N., Benoit R., Brazeau P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of ovine hypothalamic somatostatin-28 and somatostatin-25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6827–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. H., Jacobs J. W., Chin W. W., Lund P. K., Dee P. C., Habener J. F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned structural gene coding for a precursor of pancreatic somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5869–5873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. H., Lund P. K., Jacobs J. W., Habener J. F. Pre-prosomatostatins. Products of cell-free translations of messenger RNAs from anglerfish islets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6549–6552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough G. R., Collier K. J., Weith H. L., Gilham P. T. The use of barium salts of protected deoxyribonucleoside-3' p-chlorophenyl phosphates for construction of oligonucleotides by the phosphotriester method: high-yield synthesis of dinucleotide blocks. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1955–1964. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough G. R., Singleton C. K., Weith H. L., Gilham P. T. Protected deoxyribonucleoside-3' aryl phosphodiesters as key intermediates in polynucleotide synthesis. Construction of an icosanucleotide analogous to the sequence at the ends of Rous sarcoma virus 35S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1557–1570. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobart P., Crawford R., Shen L., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding two distinct somatostatin precursors found in the endocrine pancreas of anglerfish. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):137–141. doi: 10.1038/288137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Ruch W., Chideckel E., Palmer J., Goodner C. J., Ensinck J., Gale C. C. Somatostatin: hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):482–484. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Tasler J., Obtulowicz W., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Effect of growth hormone-release inhibiting hormone on hormones stimulating exocrine pancreatic secretion. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber M., Camier M., Cohen P. Higher molecular weight forms of immunoreactive somatostatin in mouse hypothalamic extracts: evidence of processing in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):6004–6008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.6004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noe B. D., Fletcher D. J., Bauer G. E., Weir G. C., Patel Y. Somatostatin biosynthesis occurs in pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1675–1685. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noe B. D., Fletcher D. J., Spiess J. Evidence for the existence of a biosynthetic precursor for somatostatin. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):724–730. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noe B. D., Spiess J., Rivier J. E., Vale W. Isolation and characterization of somatostatin from anglerfish pancreatic islet. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1410–1415. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Mevarech M., Stein R., Agarwal K. L. Detection and partial sequence analysis of gastrin mRNA by using an oligodeoxynucleotide probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1770–1774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama H., Bradshaw R. A., Bates O. J., Permutt A. Amino acid sequence of catfish pancreatic somatostatin I. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2251–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt C., Tager H. S., Carroll R. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of prosomatostatin in pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradayrol L., Jörnvall H., Mutt V., Ribet A. N-terminally extended somatostatin: the primary structure of somatostatin-28. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Dupont A., Arimura A., Redding T. W., Nishi N., Linthicum G. L., Schlesinger D. H. Isolation and structure of somatostatin from porcine hypothalami. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):509–514. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Huang W. Y., Chang R. C., Arimura A., Redding T. W., Millar R. P., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Isolation and structure of pro-somatostatin: a putative somatostatin precursor from pig hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4489–4493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. In vitro biosynthesis of fish islet preprosomatostatin: evidence of processing and segregation of a high molecular weight precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4074–4078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess J., Rivier J. E., Rodkey J. A., Bennett C. D., Vale W. Isolation and characterization of somatostatin from pigeon pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]