Abstract
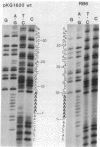
Mutations induced by (+/-)trans-benzo-[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide (BaP-diol epoxide-1) were selected by using a recombinant plasmid vector system designed for the study of transcription termination signals. The plasmid contains a transcription terminator positioned between a promotor signal and the Escherichia coli galactokinase structural gene (galK). By selections for the expression of galK (i.e., galK- to galK+), mutations are obtained in the terminator region that allow transcription from the promotor to read the galK gene. These mutations were characterized by direct DNA sequence of the terminator region. The DNA sequence changes caused by BaP-diol epoxide-1 were demonstrated for three different mutants. Two were found to be single-base-pair insertions of T.A into a cluster of consecutive T.A base pairs and the other change was a single-base-pair deletion of G.C from a cluster of consecutive G.C base pairs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiovanni J., Romson J. R., Linville D., Juchau M. R., Slaga T. J. Covalent binding of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to adenine correlates with tumorigenesis in mouse skin. Cancer Lett. 1979 Jun;7(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(79)80074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. Suppressible four-base glycine and proline codons in yeast. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):455–457. doi: 10.1126/science.7010605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. Benzo[alpha]pyrene metabolism, activation and carcinogenesis: role and regulation of mixed-function oxidases and related enzymes. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1107–1166. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., Szybalski W. Control of short leftward transcripts from the immunity and ori regions in induced coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 22;126(4):275–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00269438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., de Crombrugghe B., Rosenberg M. Transcription in vitro of bacteriophage lambda 4S RNA: studies on termination and rho protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):827–842. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. T., Lin E. J., Harvey R. G., Weiss S. B. Mechanism of phage phiX174 DNA inactivation by benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3335–3339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Sachs L., Yang S. K., Gelboin V. Identification of mutagenic metabolites of benzo(a)pyrene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono K., Yourno J. Chemical carcinogens as frameshift mutagens: Salmonella DNA sequence sensitive to mutagenesis by polycyclic carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1612–1617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovic V., Weinstein I. B. Genetic factors in Escherichia coli that affect cell killing and mutagenesis induced by benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol 9,10-oxide. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3508–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey A. M., Grzeskowiak K., Weinstein I. B., Nakanishi K., Roller P., Harvey R. G. Benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol 9,10-oxide adenosine and deoxyadenosine adducts: structure and stereochemistry. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.316186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakefuda T., Yamamoto H. Modification of DNA by the benzo[a]pyrene metabolite diol-epoxide r-7,t-8-dihydroxy-t-9,10-oxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaveille C., Kuroki T., Sims P., Grover P. L., Bartsch H. Mutagenicity of isomeric diol-epoxides of benzo[a]pyrene and benz[a]anthracene in S. typhimurium TA98 and TA100 and in V79 Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res. 1977 Sep;44(3):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(77)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Grover P. L., Sims P. In vitro malignant transformation of mouse fibroblasts by non-K-region dihydrodiols derived from 7-methylbenz(a)anthracene, 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene, and benzo(a)pyrene. Cancer Res. 1976 Jun;36(6):2059–2064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan T., Straub K., Calvin M. Benzo[alpha]pyrene diol epoxide covalently binds to deoxyguanosine and deoxyadenosine in DNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):725–727. doi: 10.1038/269725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H., Kakefuda T. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in vitro by binding of benzo(a) pyrene metabolite diol-epoxide I to DNA. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):75–78. doi: 10.1038/279075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H., Lee C. H., Kakefuda T. Alteration of plasmid DNA-mediated transformation and mutation induced by covalent binding of benzo[alpha]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-oxide in Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1981 Jun;82(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H., Tanaka S., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Alkali-labile colicinogenic factor E1 DNA molecules formed in the presence of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):570–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P., Strauss B. S. Sites of inhibition of in vitro DNA synthesis in carcinogen- and UV-treated phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):664–666. doi: 10.1038/278664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne M. R., Beland F. A., Harvey R. G., Brookes P. The reaction of (+/-)-7alpha, 8beta-dihydroxy-9beta, 10beta-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene with DNA. Int J Cancer. 1976 Sep 15;18(3):362–368. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B. DNA--benzo[a]pyrene adducts formed in a Salmonella typhimurium mutagenesis assay system. Mutat Res. 1979 Jul;61(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of cro, cII and part of the O gene in phage lambda DNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):410–414. doi: 10.1038/272410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L., Swaisland A., Pal K., Hewer A. Metabolic activation of benzo(a)pyrene proceeds by a diol-epoxide. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):326–328. doi: 10.1038/252326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B., Jeffrey A. M., Jennette K. W., Blobstein S. H., Harvey R. G., Harris C., Autrup H., Kasai H., Nakanishi K. Benzo(a)pyrene diol epoxides as intermediates in nucleic acid binding in vitro and in vivo. Science. 1976 Aug 13;193(4253):592–595. doi: 10.1126/science.959820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wislocki P. G., Wood A. W., Chang R. L., Levin W., Yagi H., Hernandez O., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. High mutagenicity and toxicity of a diol epoxide derived from benzo(a)pyrene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. K., McCourt D. W., Roller P. P., Gelboin H. V. Enzymatic conversion of benzo(a)pyrene leading predominantly to the diol-epoxide r-7,t-8-dihydroxy-t-9,10-oxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo(a)pyrene through a single enantiomer of r-7, t-8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo(a)pyrene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]