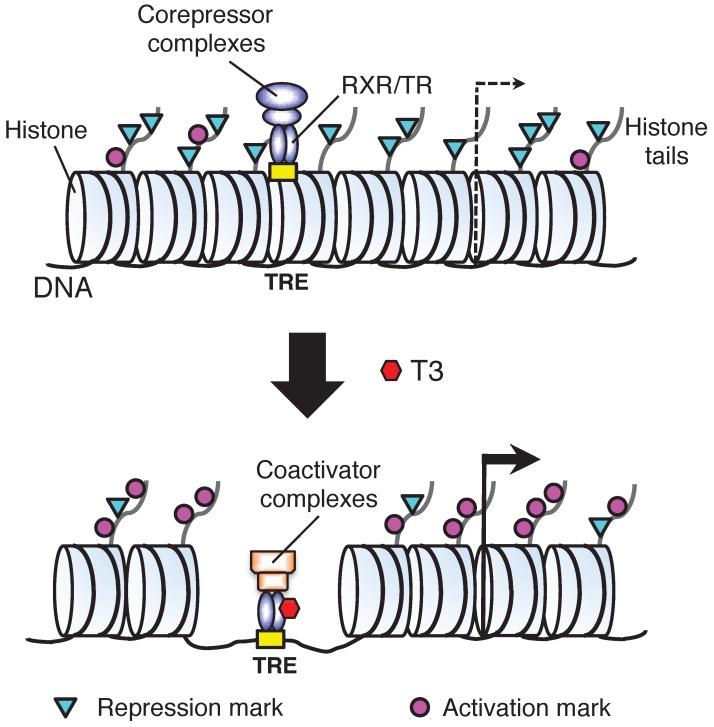
Fig 3.
A model for gene regulation by TR. T3 functions by regulating gene transcription through T3 receptors (TRs). In the absence of T3 (as in premetamorphic tadpole), TR forms heterodimers with RXR (9-cis retinoic acid receptor) and the heterodimer binds to the T3 response elements (TREs) in the target genes to repress their expression by recruiting corepressor complexes containing histone deacetylases. When T3 is present, the corepressor complexes are released and the liganded TR/RXR recruits coactivator complexes containing histone acetyltransferases and histone methyltransferases such as PRMT1 (protein arginine methyltransferase 1). The coactivator complexes will modify histones or cause the removal of nucleosomes, leading to the activation of gene expression. Based on 55.