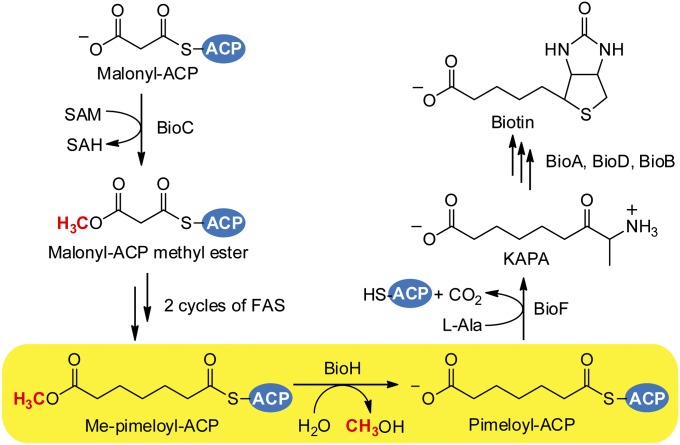
Fig. 1.
Proposed E. coli biotin synthetic pathway showing the catalytic role of BioH. Biotin biosynthesis is initiated by BioC methylation of ACP (or malonyl-CoA) to give malonyl-ACP methyl ester, which, after two successive cycles of fatty acid synthesis (FAS), becomes pimeloyl-ACP methyl ester. Once pimelate is synthesized, BioH hydrolyzes the methyl ester bond to expose the ω-carboxyl group and terminate chain elongation. The ACP moiety is subsequently released in the BioF reaction, the first step of biotin ring assembly.