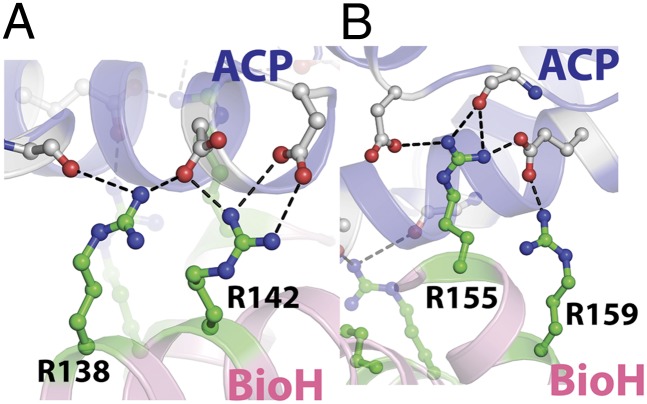
Fig. 3.
Ionic interactions between BioH and ACP are mediated by residues lying on the BioH capping helices and ACP helix2. Structural elements are represented and colored as in Fig. 2. (A) Ionic interaction at the amino terminus of ACP-α2 comprised of main-chain amide carbonyl oxygen and side-chain carboxylate oxygen atoms from ACP (carbon atoms colored gray), making salt bridge interactions (shown as black dashes) with BioH residues R138 and R142 (carbon atoms colored green). (B) Ionic interactions at the carboxyl terminus of ACP-α2 constitute the side-chain carboxylate oxygen atoms from aspartate and glutamate residues of ACP and the basic BioH residues R155 and R159.