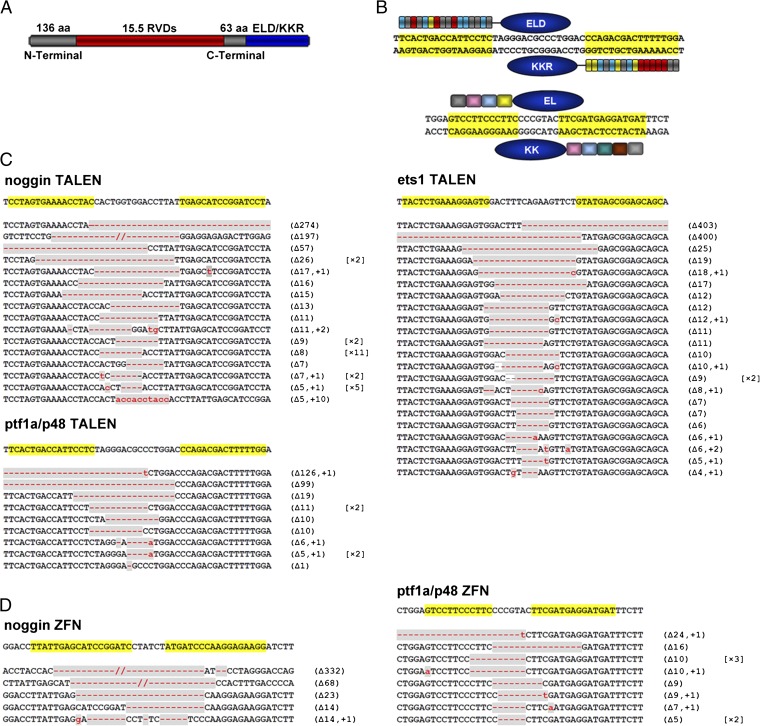
Fig. 1.
Schematic drawing of TALENs and ZFNs and sequences of somatic mutations induced in X. tropicalis G0 embryos. (A) Schematic drawing of TALEN with 15.5 RVDs located between 136-aa N-terminal and 63-aa C-terminal regions. The ELD and KKR Fok I nuclease domains are linked to the C terminus of the TALE monomer. RVDs are shown in red and Fok I domains in blue. (B) Schematic drawing of TALENs (Upper) and ZFNs (Lower) that target ptf1a/p48. Recognition sequences are highlighted in yellow. (C) DNA sequences targeted by noggin-, ptf1a/p48-, or ets1-TALENs, and somatic mutations induced in Xenopus embryos. Sequenced mutations are listed. The largest forward deletion (400 bp) and the largest backward deletion (403 bp) were found in ets1 of X. tropicalis. (D) noggin- and ptf1a/p48- ZFNs targeting sites and somatic mutations induced by these pairs of ZFNs. In C and D, mutated regions are marked in gray, with red dashes indicating deletions (Δ) and lowercase letters in red indicating insertions (+). The numbers in parentheses show the number of deleted or inserted base pairs, whereas numbers in square brackets show the frequencies of the mutation in the sequenced samples.