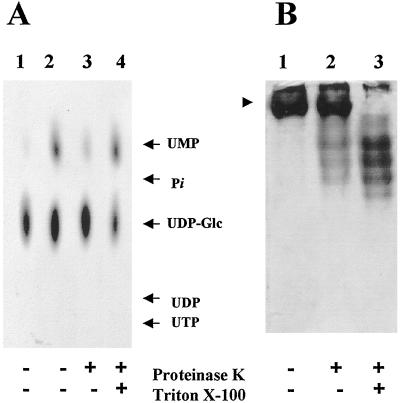
Figure 5.
Topology of UMP formation in Golgi vesicles. A, Golgi vesicles (100 μg of protein) were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of proteinase K (20 μg) for 30 min at 30°C. The reaction was stopped with 1 mm PMSF, and then the vesicles were incubated on ice for 10 min in the presence or in the absence of 0.1% Triton X-100. The vesicles were then incubated with 1 μm (1.0 μCi/nmol) [α-32P]UDP-Glc for 10 min. The products formed during the incubation were analyzed by TLC using PEI plates and exposed to autoradiography at −70°C with an enhancing screen. Lanes: 1, Heat-inactivated Golgi vesicles; 2, normal Golgi vesicles; 3, proteolyzed Golgi vesicles; and 4, Golgi vesicles subjected to proteolysis and further permeabilization. Migration of standards is shown by arrows. B, Topology of Golgi UDPase. Sealed or Triton X-100-permeabilized Golgi vesicles were incubated in the presence of proteinase K using the same conditions as described in A. The samples were then separated in native gels and the UDPase activity was determined in situ as described in Methods. Lanes: 1, Untreated Golgi vesicles; 2, sealed Golgi vesicles treated with proteinase K; and 3, permeabilized Golgi vesicles treated with proteinase K. The arrowhead indicates the migration of Golgi UDPase in the native gel.