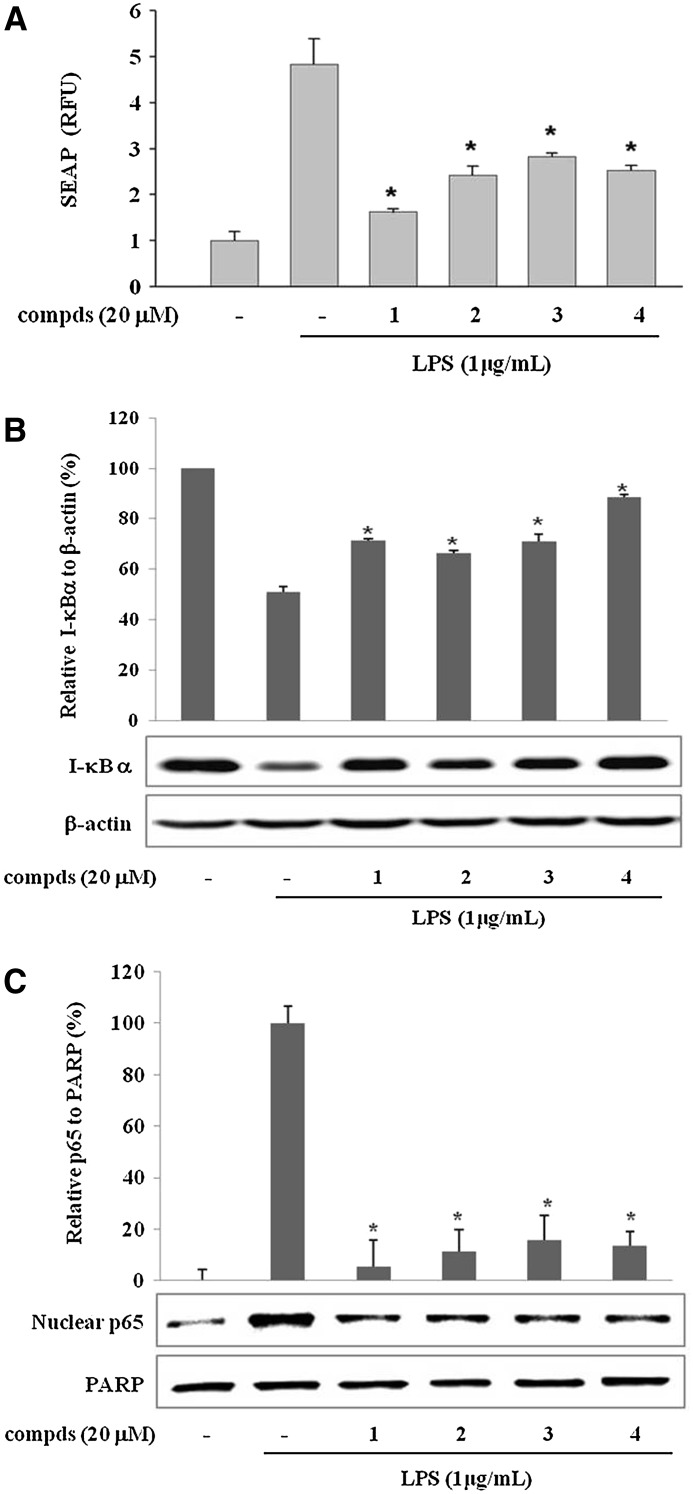
FIG. 4.
Sulfur compounds 1–4 from garlic suppress the activation of nuclear factor-κB in LPS-stimulated macrophages. (A) Effect of sulfur compounds on LPS-induced nuclear factor-κB transcriptional activation in T-RAW cells. T-RAW cells were treated with compds for 2 h prior to stimulation by LPS for 16 h. Data are mean±SD values of three individual experiments. *P<.01, significant difference from LPS alone. SEAP, secretory alkaline phosphatase. (B, C) Effect of sulfur compounds on (B) inhibitory-κBα (I-κBα) degradation and (C) p65 translocation to the nucleus in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Cells were pretreated with compds for 30 min prior to LPS treatment for 15 min. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared for the western blotting of I-κBα and p65, respectively. Images are representative of three independent experiments that showed similar results. The relative intensity of (B) I-κBα/β-actin bands and (C) p65/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) bands was measured by densitometry. Data are mean±SD values of three individual experiments. *P<.01, significant difference from LPS alone.