Figure 1.
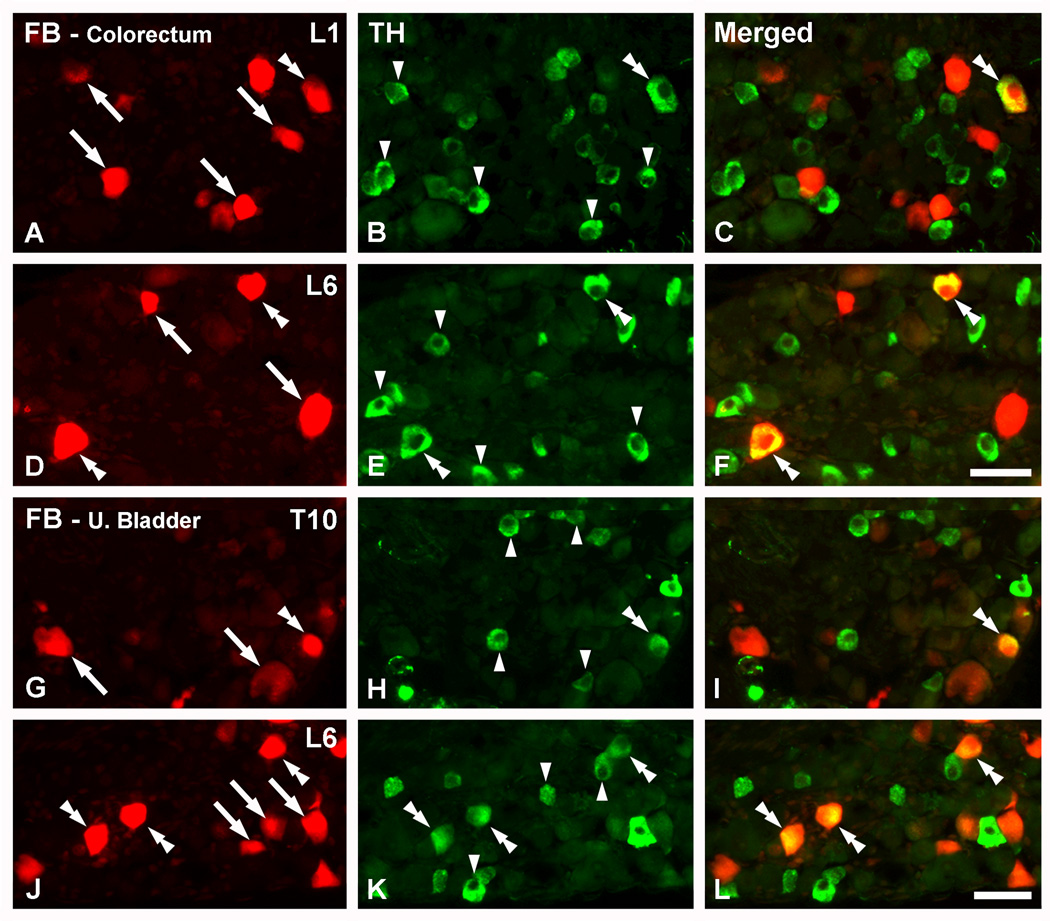
TH is expressed in colorectal and urinary bladder DRG neurons. Optical immunofluorescence photomicrographs of sections of L1 (A–C), L6 (D–F; J–L) or T10 (G–I) DRGs incubated with antiserum to TH. Retrogradely labeled colorectal (A–F) or urinary bladder (G–L) neurons containing FB (A, D, G, J) are shown in red. (C, F, I, L) show merged micrographs. (A–F) A number of colorectal NPs, as evidenced by the presence of FB, express TH in L1 and L6 DRGs (doble arrowheads in A–F). FB+ colorectal NPs lacking the enzyme are also present (arrows in A, D), as well as several TH-only NPs (arrowheads in B, E). (G–L) FB+TH+ urinary bladder NPs are seen in T10 (double arrowheads in G–I) and L6 (double arrrowheads in J–L) DRGs. Also here, FB+ urinary bladder (arrows in G, J) or TH-only (arrowheads in H, K) DRG NPs are detected. Scale bar: 50 µm (F=A–E; L=G–K).