Fig 3.
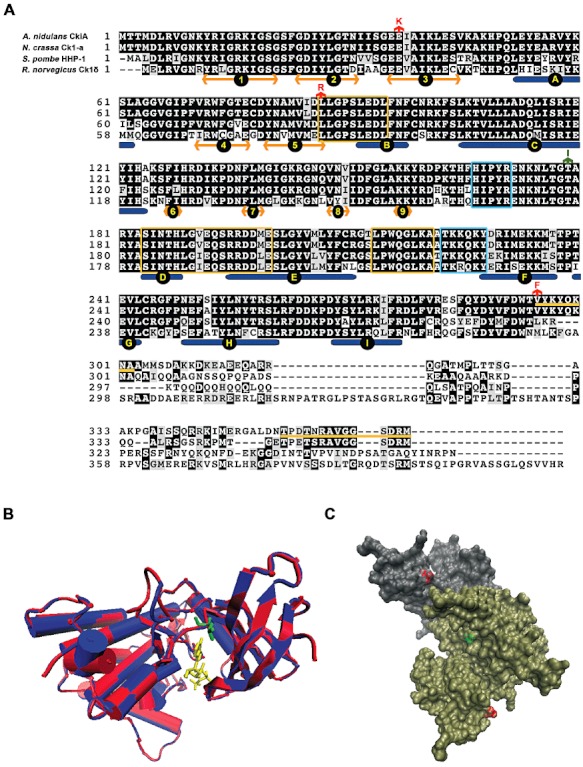
A. Alignment of A. nidulans CkiA with selected orthologues (see text). Alignment carried out with MUSCLE and visualized with box-shade. Under the alignment the succession of β-sheets and α-helices as deduced from known structures is shown (Longenecker et al., 1996). Double headed golden arrows, β-sheets (numbered from 1–9), rounded-ended blue rectangles, α-helixes (A to I). The sequences boxed in yellow represent the signature motifs of casein kinase I proteins (see text), the sequences boxed in cyan, the kinesin homology domain and downstream from it the SV40 T-antigen nuclear localization sequence (Gross and Anderson, 1998). The yellow lines between the sequences of the A. nidulans and N. crassa orthologues show sequences that are conserved in the Pezizomycotina but not among other ascomycetes (see text). The three amino acid substitutions described in this article are indicated by red arrows above the A. nidulans CkiA sequence. In green we indicate the position and mutant change of the hrr25-2 (rst2-1) suppressor of S. cerevisiæ (Murakami et al., 1999; see Discussion). B. Model of the CkiA protein. In red, CkiA, Val8-Thr294, in blue S. pombe Cki1 Asn6-Leu298 (PDB 1cnsA). In yellow ATP molecule. The substrate lies in a groove between the β-sheet lobe and α-helix lobe of the molecule. Leucine 87 is shown in green. We show the comparison with the S. pombeγ-like homologue, rather than the closer rat δ-homologue (Longenecker et al., 1996; see Fig. 4) as only the former has been crystallized with the bound ATP (Xu et al., 1995). C. Surface representation of the rat casein kinase I δ dimer (Longenecker et al., 1996) showing the surface residues discussed in this article. Subunit A in grey, subunit B in tan. In red Glu 34, corresponding to Glu 37 of CkiA, in green Thr 176, corresponding to Thr 176 of Hrr25. Modelling with I-Tasser, images made with VMD/NAMD/BioCoRE/JMV/other software support. VMD/NAMD/BioCoRE/JMV/ is developed with NIH support by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics group at the Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
