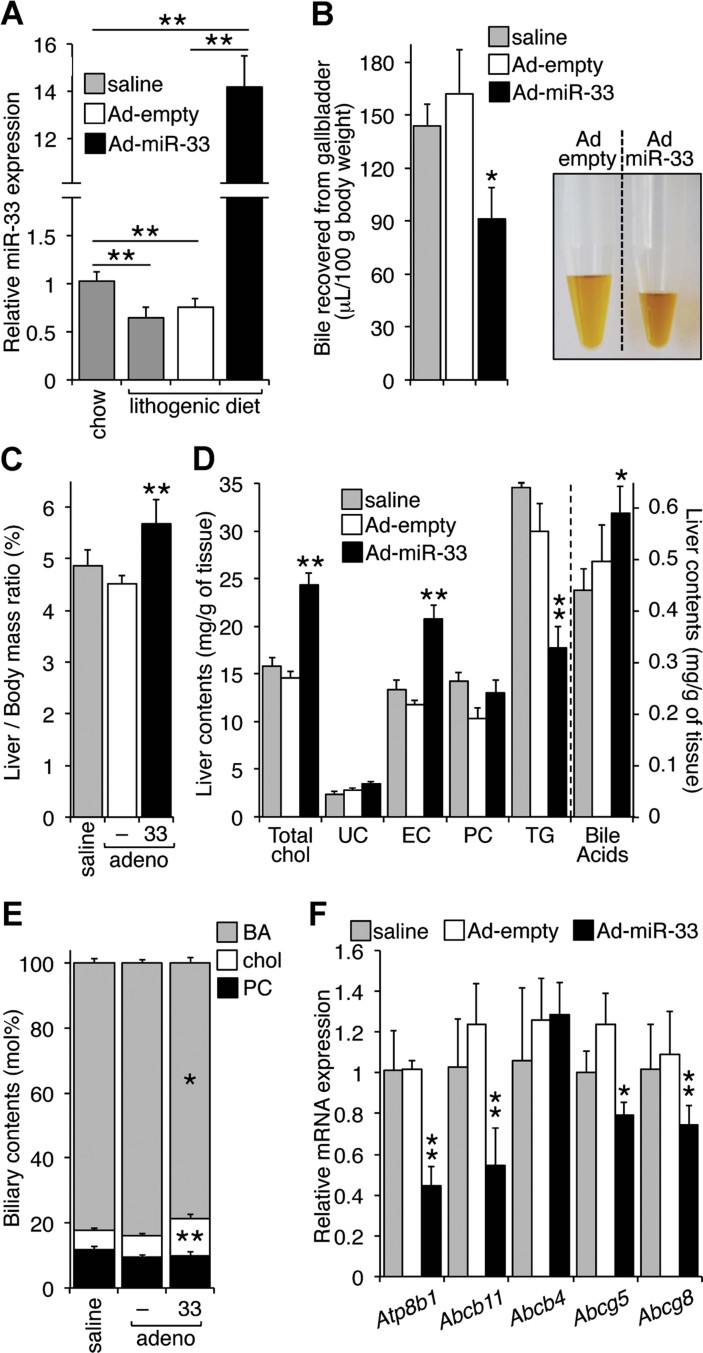
C57BL/6 mice (n = 5–7) were kept on chow diet or lithogenic diet for 7 days (lanes 1–2). A different group of animals were transduced i.v. with empty or miR-33 adenovirus (2 × 109 pfu/mouse), and then switched to the lithogenic diet (lanes 3–4). After 7 days, mice were fasted overnight and killed the following morning. Data show relative levels of hepatic miR-33.
The volume of bile recovered from the gallbladder is significantly reduced in mice transduced with miR-33. Picture shows pooled bile collected from five mice each in an independent experiment.
Liver to body mass ratios.
Hepatic levels of bile acids; total, unesterified (UC) and esterified (EC) cholesterol; phosphatidylcholine (PC) and triglycerides (TG).
The amounts of bile acids (BA), cholesterol (chol) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) were determined in bile, and expressed as mol% (mol per 100 mol). Compared to mice infused with saline or Adeno-empty, the bile from animals transduced with Adeno-miR-33 showed increased amounts of cholesterol (11.6 ± 1.1 vs. 6.6 ± 0.5 vs. 5.9 ± 0.6 mol%; miR vs. scrambled vs. saline; p = 0.009), and decreased amounts of bile acids (78.6 ± 1.7 vs. 83.7 ± 1.0 vs. 82.1 ± 1.4 mol%; miR vs. scrambled vs. saline; p = 0.03), but no change in PC contents (9.8 ± 1.3 vs. 9.7 ± 0.6 vs. 12.0 ± 0.9 mol%; miR vs. scrambled vs. saline).
Relative expression of hepatic canalicular transporters in the same mice. Data shown as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.