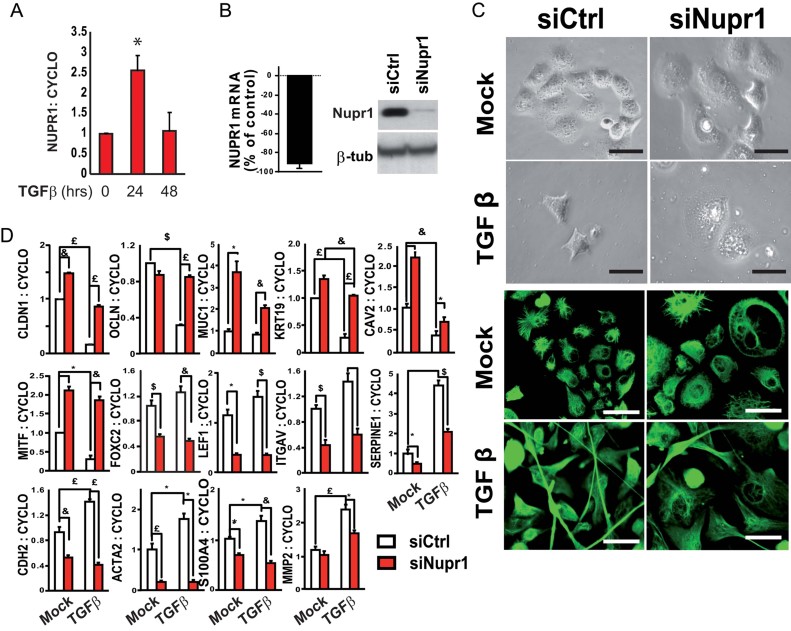
Figure 3. Nupr1-knockdown impairs acquirement of TGFβ-induced EMT features in Panc-1 cells.
Data are means of triplicates ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, $p ≤ 0.01, £p ≤ 0.005, &p ≤ 0.001.
- qRT-PCR showing Nupr1-expression in mock and TGFβ-treated Panc-1 cells.
- qRT-PCR (left) and immunoblot (right) showing reduced Nupr1 expression in Panc-1 cells transfected with a Nupr1-specific siRNA (siNupr1) compared to cells transfected with a control siRNA (siCtrl).
- (Top) Phase contrast microphotographs illustrating alterations in cell morphology and size upon Nupr1-knockdown, before and after 24 h of TGFβ1 stimulation (10 ng/ml). (Bottom) Immunofluorescent detection of vimentin, 72 h after TGFβ1 treatment of Nupr1-depleted or control cells. Note that Panc-1 cells present the particular feature of a strong vimentin expression previous to TGFβ stimulation, although they remain dependent on TGFβ for the induction of fibroblastic markers such as CDH2/N-cadherin (see D).
- qRT-PCR showing altered expression of epithelial and fibroblastic genes in Nupr1-depleted cells compared to controls, after 24 h of TGFβ1 treatment. Cyclophilin A mRNA expression was used for normalization.