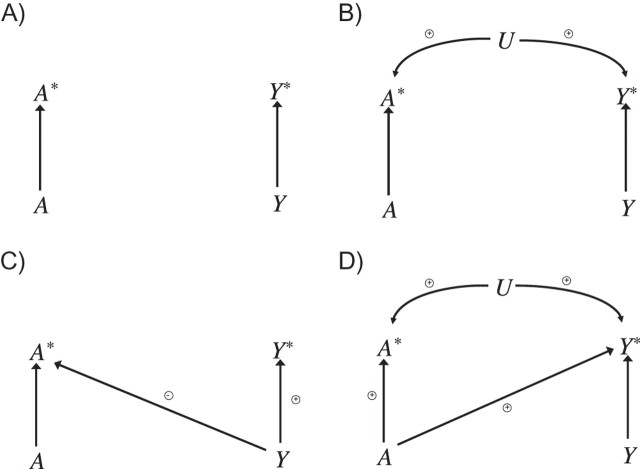
Figure 1.
Signed directed acyclic graphs illustrating tests for a causal effect in the presence of measurement error. A) Independent nondifferential measurement error; B) dependent nondifferential measurement error; C) independent differential measurement error; D) dependent differential measurement error. A represents true exposure; A*, measured exposure; Y, the true outcome; Y*, the measured outcome; and U, a variable leading to correlated/dependent measurement errors. Data are available only on A* and Y*. In part A, if there is any association between A* and Y*, there must be a causal effect of A on Y. In parts B and D, if there is a negative association between A* and Y*, there must be a causal effect of A on Y. In part C, if there is a positive association between A* and Y*, there must be a causal effect of A on Y.