Abstract
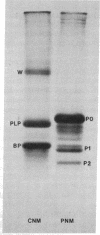
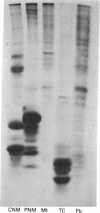
In some cases of polyneuropathy and plasma cell dyscrasia, the monclonal antibodies react with human peripheral nerve myelin. To identify the myelin antigens involved, we separated the proteins of human central and peripheral nerve myelin by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred the proteins onto nitrocellulose sheets, and used an immunoenzymatic technique to detect the reactive antigens. Serum IgM but not IgG from three patients with neuropathy and complement-fixing anti-human myelin IgM paraproteins immunostained a protein of approximately 100,000 daltons in human peripheral nerve myelin and a protein or closely migrating proteins of similar size in human central nervous system myelin. In a fourth patient, both IgM and IgG immunostained the antigen. Immunostaining was specific for the paraprotein light chain type, and absorption of the patients' sera with human peripheral nerve myelin eliminated the reaction with the central nervous system proteins. No reaction was seen with rabbit peripheral nerve myelin or with membranes prepared from human myotubes, human T cells, or human fibroblasts. Control sera from six patients with neuropathy and IgM paraproteins that did not react with myelin, from four patients with IgM paraproteins but no neuropathy, and from three normal subjects did not immunostain myelin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarli J. A., Aparicio S. R., Lumsden C. E., Tönder O. Binding of normal human IgG to myelin sheaths, glia and neurons. Immunology. 1975 Jan;28(1):171–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Eylar E. H. The proposed amino acid sequence of the P1 protein of rabbit sciatic nerve myelin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):590–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cream J. J., Hern J. E., Hughes R. A., MacKenzie I. C. Mixed or immune complex cryoglobulinaemia and neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jan;37(1):82–87. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C., Danon F. Cross-idiotypic antigens among monoclonal immunoglobulin M from patients with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia and polyneuropathy. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1530–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI109612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger H., Pruzanski W. Plasma cell neoplasia with peripheral polyneuropathy. A study of five cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 Jul;59(4):301–310. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198007000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Haren J. M., Kmiecik T. E. Evidence for shared idiotypy expressed by the IgM, IgG, and IgA serum proteins of a patient with a complex multiple paraprotein disorder. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):2000–2006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal A., Oger J. J., Arnason B. G. Cell-mediated immunity in idiopathic polyneuritis. Ann Neurol. 1981;9 (Suppl):65–69. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. N., Riches P. G., Kohn J. Paraproteinaemia in neurological disease: incidence, associations, and classification of monoclonal immunoglobulins. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):617–621. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latov N., Sherman W. H., Nemni R., Galassi G., Shyong J. S., Penn A. S., Chess L., Olarte M. R., Rowland L. P., Osserman E. F. Plasma-cell dyscrasia and peripheral neuropathy with a monoclonal antibody to peripheral-nerve myelin. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):618–621. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti G. V., Pettit D. The interaction of gamma-globulin with lipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1968 Feb;2(1):17–34. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(68)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T. Isolation of myelin from nerve tissue. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:435–444. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn G. M., Kunkel H. G., Grey H. M. Sharing of individual antigenic determinants between a gamma G and a gamma M protein in the same myeloma serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):660–665. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Myeloma proteins (M-components) with antibody-like activity. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):831–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D. J., Vanhegan R. I., Matthews W. B. Peripheral neuropathy and benign IgG paraproteinaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Mar;41(3):215–219. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida T., Saida K., Dorfman S. H., Silberberg D. H., Sumner A. J., Manning M. C., Lisak R. P., Brown M. J. Experimental allergic neuritis induced by sensitization with galactocerebroside. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1103–1106. doi: 10.1126/science.451555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki O., Kishimoto T., Kuritani T., Muraguchi A., Yamamura Y. In vitro induction of IgM secretion and switching to IgG production in human B leukemic cells with the help of T cells. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2609–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Brouet J. C. Antibody activity of human myeloma globulins. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Mihaesco E., Preud'homme J. L., Danon F., Brouet J. C. Heavy chain diseases: current findings and concepts. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:145–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Brostoff S. W., Carter H., Eylar E. H. Recurrent experimental allergic polyganglioradiculoneuritis. Multiple demyelinating episodes in rhesus monkey sensitized with rabbit sciatic nerve myelin. Arch Neurol. 1974 May;30(5):347–358. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490350005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Dawson R. M. Some properties of a major structural glycoprotein of sciatic nerve. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):627–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]