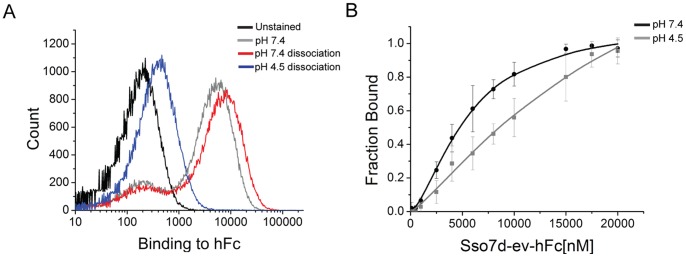
Figure 4. Characterization of pH sensitivity for Sso7d-ev-hFc.
(A) End-point assay to determine pH sensitivity for Sso7d-ev-hFc. Yeast cells displaying Sso7d-his-hFc were incubated with 2 µM hFc-biotin and the yeast-hFc complexes were dissociated in buffers at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5. Undissociated hFc remaining on yeast surface was detected using strep-PE. A cell sample where no dissociation step was carried out after hFc labeling at pH 7.4, and unstained cells were used as controls. (C) ELISA for determination of the apparent KD of binding between hFc and Sso7d-ev-hFc, at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5. hIgG (2 µg/ml) was immobilized on a microtiter plate and incubated with twelve different concentrations of soluble Sso7d-ev-hFc. hIgG-bound Sso7d-ev-hFc was detected using an anti-his-alkaline phosphatase conjugated antibody, and p-nitrophenyl phosphate as the substrate. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of absorbance measurements at 405 nm.