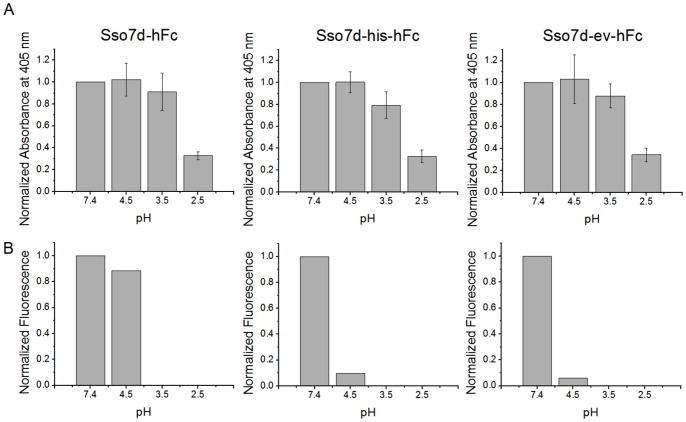
Figure 8. pH sensitivity hFc binding to Sso7d mutants immobilized on a surface.
(A) Sso7d-hFc, Sso7d-his-hFc and Sso7d-ev-hFc were recombinantly expressed with a C-terminal cysteine. 2 µg/ml of each mutant was chemically conjugated to wells of a maleimide-activated microtiter plate and incubated with 6 µM of hIgG-biotin. After a wash step, wells were incubated with buffers of pH 7.4, 4.5, 3.5 and 2.5 for 30 min with shaking, and the hIgG-biotin remaining undissociated was detected with alkaline phosphatase conjugated streptavidin and p-nitrophenyl-phosphate; absorbance measurements at 405 nm on a plate reader were obtained. Background-subtracted absorbance values were normalized by the absorbance value corresponding to dissociation in buffer at pH 7.4, and are reported. Error bars indicate standard deviation of measurements from six different wells. All three mutants show similar dissociation behavior in buffers at different pH. (B) Data from end-point assays for pH sensitivity of Sso7d mutants (see Figures 1A, 2A, 4A) are analyzed for comparison with (A). As in (A), Sso7d mutants immobilized on the surface of yeast are incubated with hFc-biotin and subsequently, the surface-bound hFc complexes are allowed to dissociate for 30 min in a buffer at pH 7.4 or pH 4.5; experiments with dissociation at pH 3.5 and pH 2.5 were not conducted. The fluorescence due to surface-bound hFc remaining undissociated was measured by flow cytometry, following labeling with strep-PE. Mean fluorescence values, normalized to the value for dissociation with pH 7.4 buffer, are plotted; data shown is the average from two separate experiments. A significantly greater fraction of hFc remains bound to Sso7d-hFc immobilized on the yeast cell surface.