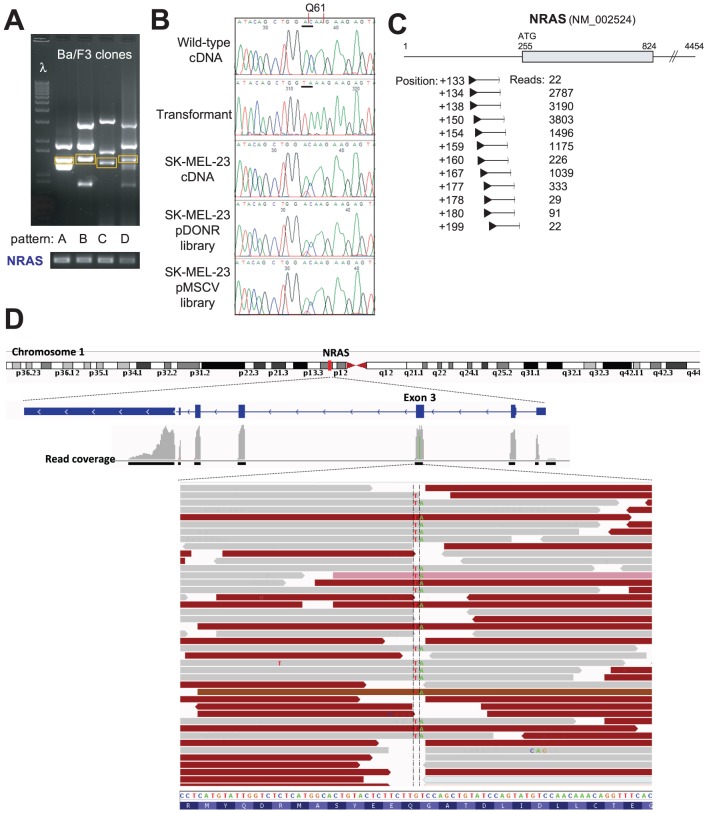
Figure 4. Deep sequencing deconvolution of multiple cDNA inserts.
A. Screening of the SK-MEL-23 melanoma cell line results in multiple clones with different patterns of cDNA inserts (upper) that all harbor NRAS based on an NRAS specific PCR (lower). B. The mutant NRAS allele harbors an A434T (G60G) and C435A (Q61K) dinucleotide substitution (underlined by thick black bar) that is present as 100% of sequence within a BaF3 transformant and as 50% or less in the SK-MEL-23 cDNA, plasmid acceptor library and retroviral library. C. Deep sequencing identified 12 distinct fusion sequences between the attB (black triangle) and 5′ UTR of NRAS from the SK-MEL-23 library. The number of individual reads for each of the sequences is provided. D. A subset of approximately 90,000 reads across the NRAS dinucleotide substitution are shown. The sequence is on the genomic negative strand and thus reversed from C. The C435A (G→T shown on the positive strand) substitution that results in Q61K is between the hashed marks. Gray reads have the paired-end on the same exon while brown reads have the paired-end on the next exon.