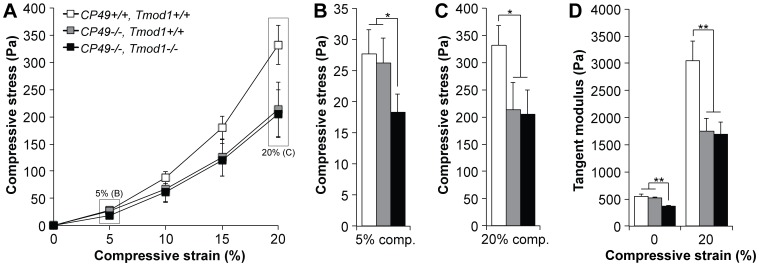
Figure 6. Tmod1 and CP49 synergistically regulate lens stiffness, as determined by a high-resolution Dynastat-based compression protocol.
(A) Compressive stress-strain curves of 2-mo-old wild-type, CP49−/−, and CP49−/−;Tmod1−/− mouse lenses reveal exponential stress-strain relationships. (B) At a low strain of 5%, CP49−/−;Tmod1−/− lenses bore less stress than wild-type or CP49−/− lenses. (C) At a high strain of 20%, CP49−/− and CP49−/−;Tmod1−/− lenses bore less stress than wild-type lenses. (D) At zero strain, the instantaneous (tangent) modulus of CP49−/−;Tmod1−/− lenses was lower than that of wild-type or CP49−/− lenses. By contrast, at 20% strain, the tangent moduli of both CP49−/− and CP49−/−;Tmod1−/− lenses were lower than that of wild-type lenses. Error bars reflect mean±SEM of n = 8−10 lenses/genotype. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.