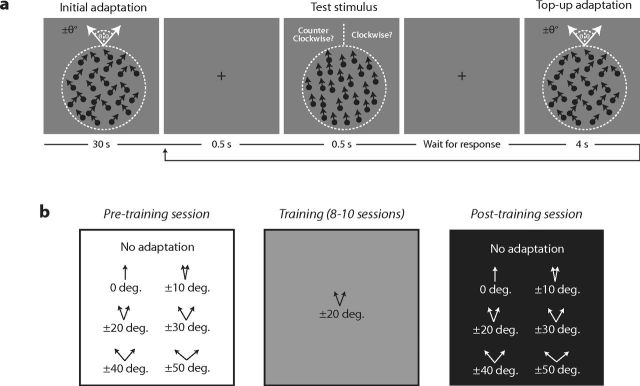
Figure 2.
Perceptual adaptation and training procedures. a, Adaptation procedure. Subjects judged whether a field of dots was moving in a direction clockwise or counterclockwise from upward. The change in discrimination performance caused by adapting to motion in an upward direction (0°) or two directions offset symmetrically (±10 to ±50°) from upward was measured. Adapting directions were presented initially for 30 s with 4 s top-ups between each trial. Test stimuli were presented for 0.5 s, separated by a 0.5 s interval containing a fixation cross on a uniform luminance background. b, Training procedure. Before and after training, we measured the change in baseline direction discrimination performance caused by adapting to motion in an upward direction (0°) or two directions offset symmetrically (±10 to ±50°) from upward. During training, the same group of subjects repeatedly practiced the direction discrimination task while adapted to directions ±20° from upward.