Figure 5.
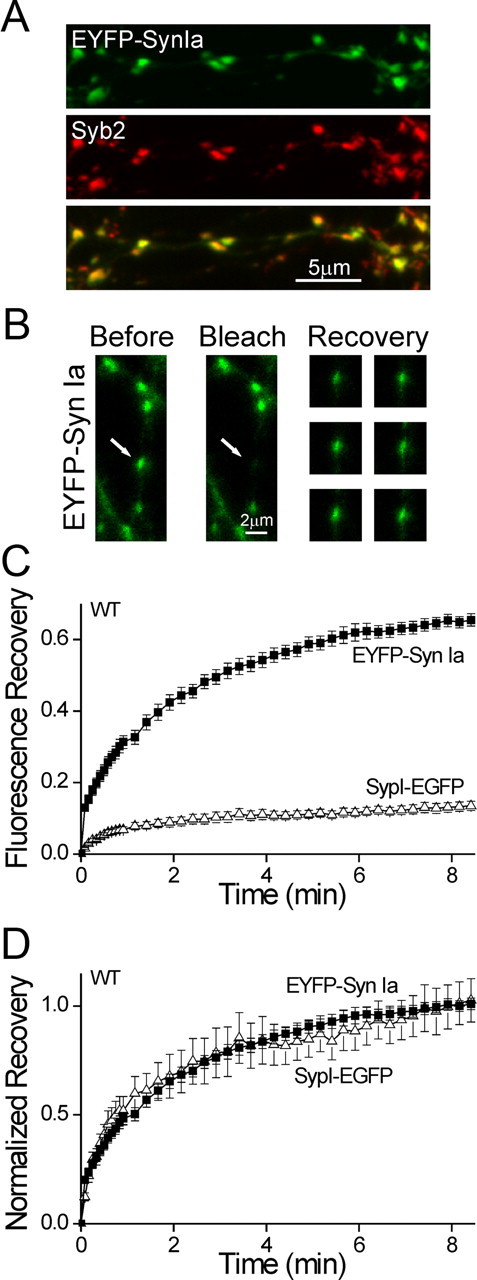
Intersynaptic transport of synapsin is faster than that of the vesicles. A, EYFP-Synapsin Ia (green) expressed in a WT neuron immunostained for Syb2 (red). Exogenous synapsin Ia localized to synapses, indicating that FRAP measures the intersynaptic transport of synapsin. B, Representative FRAP experiment in a WT neuron expressing EYFP-synapsin Ia. A single punctum (white arrow) is bleached, without affecting neighboring synapses. The recovery of fluorescence is shown at right 90, 165, 255, 330, 420, and 510 s after bleaching. The contrast of the recovery images was increased homogeneously to enhance visibility. C, Comparison of time course of FRAP of EYPF-synapsin Ia (EYPF-Syn Ia; solid squares) and SypI-EGFP (open triangles) in WT neurons (mean ± SEM). A shorter time period is shown than in Figure 4. Recovery of synapsin is markedly more extensive, indicating that synapsin Ia is transported independently of the vesicles. D, Same data as in C, normalized by the average of the three end points. Recovery proceeds with equal kinetics, indicating that the rate of movement of the mobile fractions of both labels is similar.
