Figure 4.
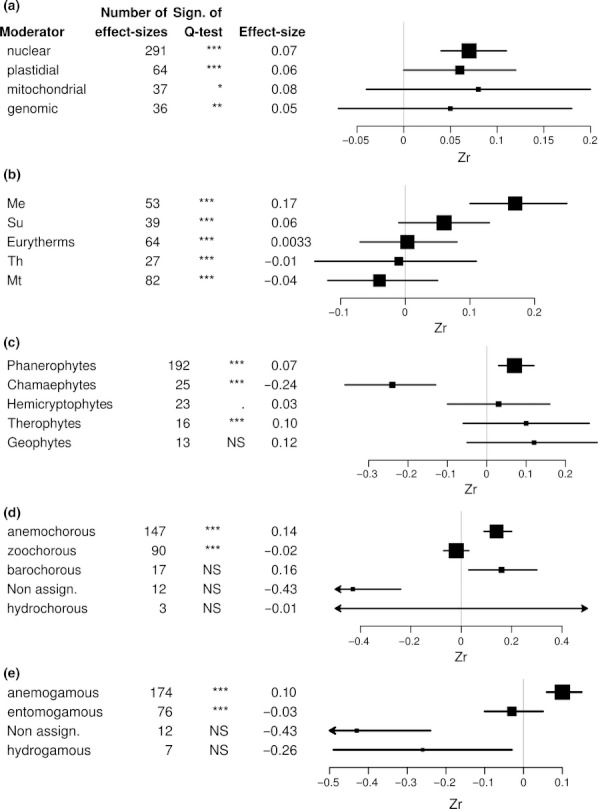
Square and error bars should be interpreted as indicated for Fig. 2a. (a) Mean effect-sizes across the Mediterranean basin for marker type. The category “genomic” refers to unassigned marker types. (b) Mean effect-sizes (ordered from most positive to most negative) of Mediterranean basin plants for ecological requirements. The categories refer to altitudinal belts where plant species are predominantly found: “Me” is meso-Mediterranean, “Su” is supra-Mediterranean, “Eurytherms” refers to plant species found across several altitudinal belts, “Th” is thermo-Mediterranean and “Mt” is mountain-Mediterranean (see Quézel and Médail 2003). Square and error bars should be interpreted as indicated for Fig. 2a. Nota bene: effect-sizes for ecological requirements do not add up to the total number of effect-sizes in plants because raw data communicated by some authors were pooled at the genus level or because data included species for which we were not able to retrieve their ecological requirement. (c) Mean plant effect-sizes (arranged in decreasing effect-size frequency per category) across the Mediterranean basin for Raunkiaer biological types. Phanerophytes are woody plants with over-wintering buds situated over 50 cm from the ground, chamaephytes are low-growing perennials (often woody plants) with wintering buds below 50 cm in height, hemicryptophytes are (often 2-year cycle) perennials with ground-level wintering buds, geophytes are plants with bulbs or rhizomes (wintering buds below ground level), and therophytes are annuals (wintering organs as seeds). Nota bene: Bryophytes were not assigned a Raunkiaer type (nine effect-sizes). (d) Mean plant effect-sizes (arranged in decreasing effect-size frequency per category) across the Mediterranean basin for seed dispersal types. Anemochorous plants have wind-dispersed seeds, zoochorous plants animal-dispersed seeds, barochorous plants gravity-dispersed seeds, and hydrochorous plants water-dispersed seeds. (e) Mean plant effect-sizes (arranged in decreasing effect-size frequency per category) across the Mediterranean basin for pollen dispersal types. Anemogamous plants have wind-dispersed pollen, entomogamous plants insect-dispersed pollen, and hydrogamous plants water-dispersed pollen.
