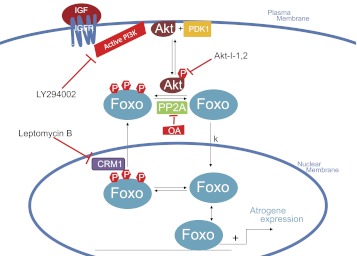
Fig. 11.
Schematic presentation of regulators of subcellular localization of Foxo. Nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking is regulated by phosphorylation of Foxo by active Akt. Binding of IGF to its membrane bound receptor IGF receptor (IGFR) activates the kinase PI3K, indirectly causing the phosphorylation of Akt, which directly phosphorylates Foxo. Inhibition of PI3K by LY294002 or inhibition of Akt by Akt-I-1,2 prevents phosphorylation of Foxo and thus induces nuclear import of Foxo. CRM1 facilitates of nuclear export of Foxo1 and inhibition of chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) by LMB prevents nuclear export of Foxo.