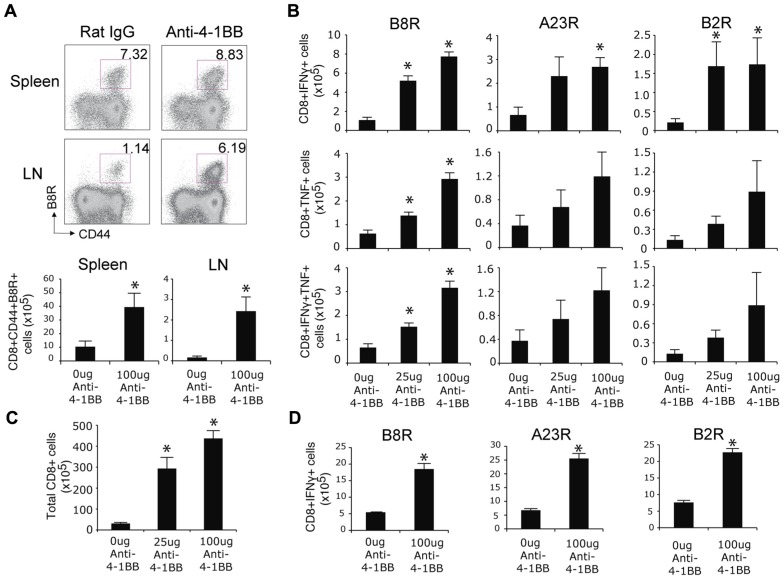
FIGURE 1.
Anti-4-1BB augments primary CD8 T cell responses to VACV-WR. WT mice were infected i.p. with VACV-WR (2 × 104 PFU/mouse) and treated with 0, 25, or 100 μg agonist anti-4-1BB or control antibody on day 1 post-infection. Seven days after infection, (A) Cells from spleen and peripheral lymph nodes (LN) were stained with anti-CD8, -CD44, and B8R-tetramer. Top: Representative dot plots of gated CD8+ cells. The numbers indicate the percentage of CD8+CD44+B8R-tetramer-positive cells. Bottom: Total number of CD8+CD44+B8R-tetramer-positive cells in the spleen and LN were calculated. (B) Splenocytes were stimulated with B8R, A23R, or B2R peptide, followed by staining for intracellular IFN-γ and TNF. Total numbers of CD8+IFN-γ+ (top), CD8+TNF+ (middle), and CD8+IFN-γ+TNF+ cells (bottom) were calculated. (C) Total splenic CD8 T cells numbers were determined. (D) Lung cells were stimulated with B8R, A23R, or B2R peptide, followed by staining for intracellular IFN-γ. Total numbers of CD8+IFN-γ+ cells were calculated. Data represent mean value ± SEM from n = 4 mice. Similar results were reproduced in two separate experiments. The Student’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. *p < 0.05.