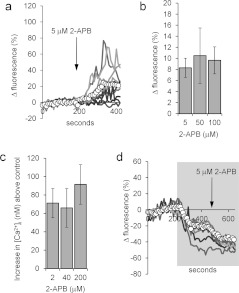
Figure 1. 2-APB elevates resting [Ca2+]i.
(a) 2-APB (5 μM; arrow) causes a sustained increase in the PHN [Ca2+]i of a subset of cells. The traces show ten individual cell responses and ΔFmean (○-○) for all 87 cells in the experiment. (b and c) 2-APB-induced [Ca2+]i elevation is dose-independent. (b) Increase in ΔFmean 3 min after application of 2-APB. Results are means±S.E.M. for sets of four experiments in each of which aliquots from the sample were tested with each of the three concentrations of 2-APB. (c) Dose-dependence of 2-APB-induced [Ca2+]i increment in fura-2-loaded cell populations (means±S.E.M. for 6–17 experiments). (d) 2-APB-induced rise in [Ca2+]i is reversed in low-Ca2+ saline. Cells were superfused with EGTA-buffered saline (shown by shading) then exposed to 5 μM 2-APB (arrow). 2-APB-induced [Ca2+]i increase was abolished and in many cells 2-APB induced a further fall in [Ca2+]i. Traces show six individual cell responses and ΔFmean (○-○) for all 85 cells in the experiment.