Figure 6.
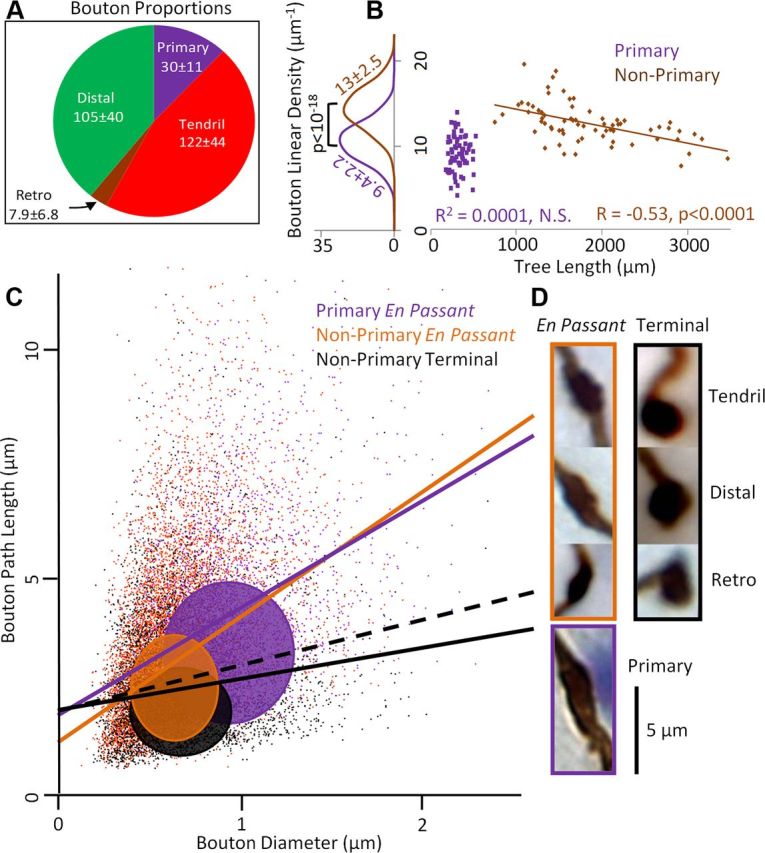
CF boutons differ by branch type and terminal versus en passant position. A, Bouton proportions (wedge sizes) and counts per CF (mean ± SD) by branch type. B, Relationship between linear bouton density (number of boutons per 100 μm) and tree length across CFs. Unlike in primary branches, nonprimary bouton density decreases with increased tree length. C, Scatter plot of bouton path length versus diameter for all boutons (N = 18,227) colored by type. En passant bouton path length strongly correlates with diameter (purple and orange lines). For terminal boutons the correlation is also positive (solid black line) but less than unitary (black dashed line, with Y intercept raised for visual comparison). Colored ovals are SDs for the three bouton types centered at the respective means. Primary boutons (purple) are larger than nonprimary (orange and black) in both diameter and path length. D, Gallery of representative boutons. En passant boutons are distinctly elongated along the path compared with the more spherical terminal boutons.
