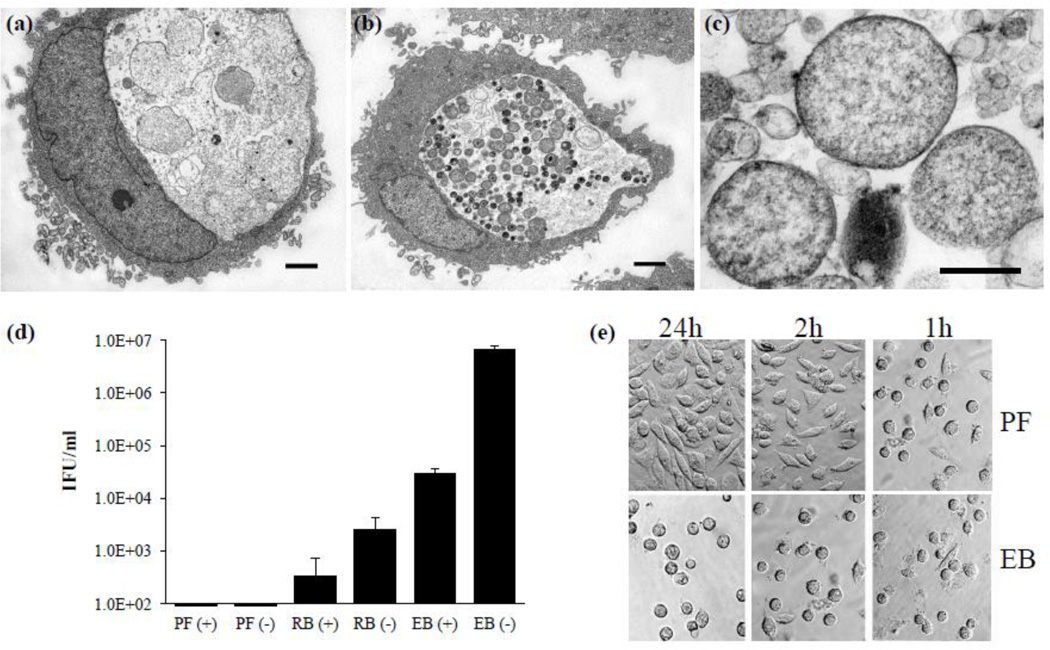
Figure 3.
The persistent form purification. Representative transmission electron micrographs of infected L929 cells (a) exposed or (b) unexposed to ampicillin and (c) the purified persistent form fraction containing aberrant RBs with a less electron dense appearance. Based on multiple cross-sections purified persistent form size is estimated at approximately 0.7–2.0 µm. Scale bars in (a) and (b) represent 2 µm and 0.5 µm in (c). (d) Endpoint infection assays determining IFUs on monolayers of L929 cells in each isolated density gradient fraction. Values represent mean IFU ± SD of three independent chlamydial preparations. (e) Representative images of the cell adherence assays demonstrating the inability of the persistent form to produce infection and inhibit cover slip adherence. Abbreviations: PF (+), persistent fraction purified from an infection exposed to ampicillin; PF (−) persistent fraction purified from an infection with no ampicillin exposure; RB (+), reticulate body fraction purified from an infection exposed to ampicillin; RB (−), reticulate body fraction purified from an infection with no ampicillin exposure; EB (+), elementary body fraction purified from an infection exposed to ampicillin; EB (−), elementary body fraction purified from an infection with no ampicillin exposure.