Figure 2.
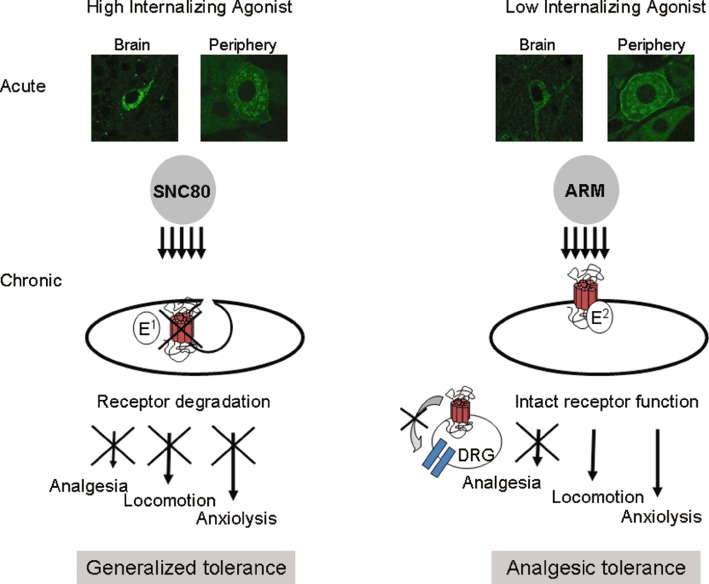
The behavioural consequences of functional selectivity at the δ opioid receptor. SNC80 and ARM390 (ARM) have comparable selectivity and potencies for the δ opioid receptor, but highly distinct internalization properties. Systemic SNC80, but not ARM390, produces clear receptor internalization in vivo as shown in slices from DOR-eGFP knock-in mice (representative images from the hippocampus and dorsal root ganglia) (Pradhan et al., 2009). Chronic administration of either agonist produces two distinct forms of tolerance. Repeated administration of SNC80 produces widespread receptor down-regulation, thus resulting in a generalized tolerance where all δ agonist-induced behaviours are affected. In contrast, chronic administration of the low-internalizing agonist, ARM390, appears to affect δ opioid receptors only at the level of the dorsal root ganglia, thus producing tolerance at the level of pain processing (Pradhan et al., 2010).
