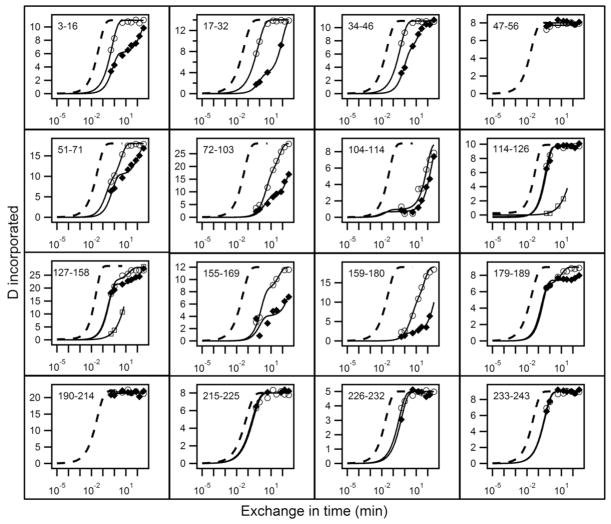
Figure 1.
HX analysis of lipid-free apoA-IWT (◆) and apoA-IIowa (○) at pD 7.3, 5°C. HX kinetics for 16 peptides covering the apoA-I sequence are shown out of a total of 51 listed in Table S1. Each panel compares the measured H to D exchange time-course for the indicated peptide to its reference curve (dotted line) computed for the case of a dynamically disordered random coil with Pf = 1. Exposed but rigidly held segments tend to have Pf ~10 (37–38), as is seen for the C-terminal 180 to 243 residues in both proteins and for some inter-helical segments in the N-terminal domain. Mono-exponential HX behavior indicates a single cooperatively unfolding segment of secondary structure. A bi-exponential fit indicates a peptide that spans a helix terminus (21). Two time-courses (○, □) are shown for apoA-IIowa peptides between residues 114 to 158 because the HX MS envelopes measured these peptides exhibit bimodal HX behavior (see Fig. S1 for examples).