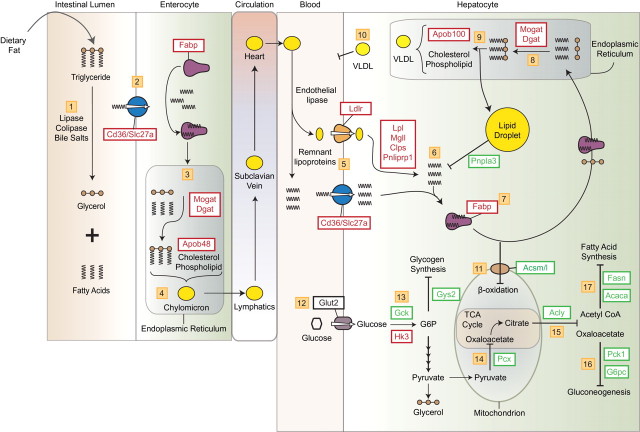
FIG. 3.
AhR-mediated increase in dietary lipid in TCDD-elicited hepatic steatosis. Steps 1–4: Fat absorption by the intestinal epithelium and export to the circulatory system. Steps 5–11: Enhanced hepatic fatty acid uptake and storage. Inhibition of efflux and β-oxidation-mediated degradation pathways. Steps 12–17: Hepatic glucose metabolism including glycogen synthesis, gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis are inhibited. Lines with arrowheads indicate reaction/pathway direction. Lines with blunted ends indicate reactions/pathways that are inhibited. Red boxes indicate induced gene expression. Green boxes indicate repressed gene expression. A more detailed description is provided in the Discussion section.