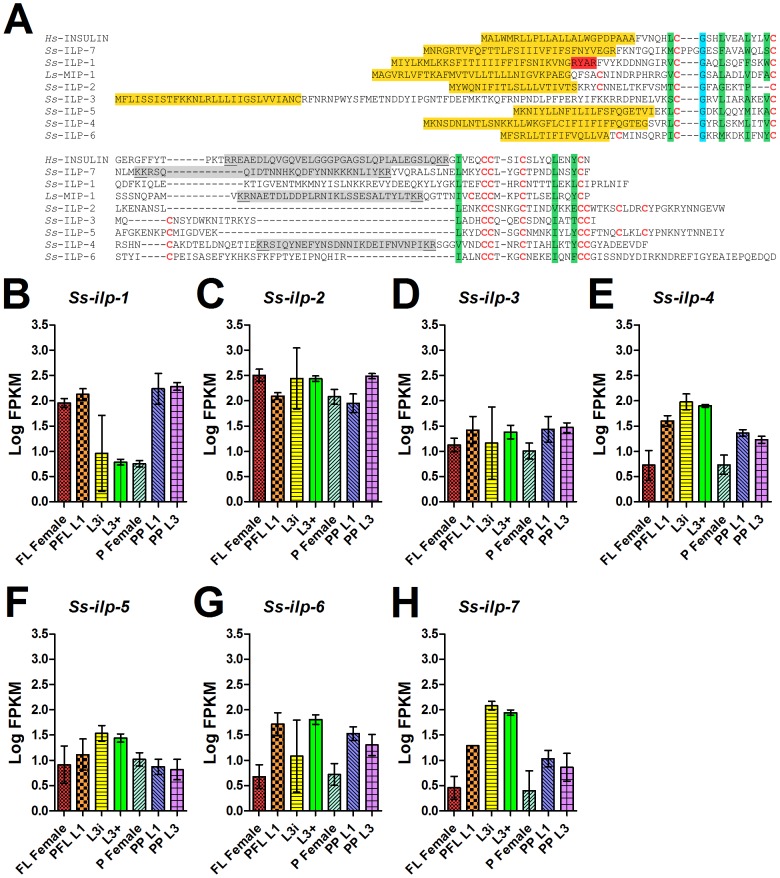
Figure 5. Protein sequence diversity and temporal regulation of S. stercoralis insulin-like peptides.
(A) A predicted protein sequence alignment of seven S. stercoralis insulin-like peptides (ILPs), Ss-ILP-1 through -7, was constructed using human insulin (Hs-INSULIN) and Lymnaea stagnalis molluscan insulin-related peptide I (Ls-MIP-1) as the references. Cysteine residues, which are predicted to form disulfide bonds, are in red letters. Predicted signal sequences are highlighted in yellow, predicted furin recognition motifs are highlighted in red, hydrophobic residues important for helix formation are highlighted in green, and a conserved glycine is highlighted in blue. Predicted C peptides are highlighted in gray with dibasic predicted cleavage sites underlined. The B peptide is N-terminal of the C peptide, while the A peptide is C-terminal of the C peptide. (B-H) Transcript abundances were determined for the coding region of seven S. stercoralis ILP-encoding genes (Ss-ilp-1 through -7) in seven developmental stages: free-living females (FL Female), post-free-living first-stage larvae (PFL L1), infectious third-stage larvae (L3i), in vivo activated third-stage larvae (L3+), parasitic females (P Female), post-parasitic first-stage larvae (PP L1), and post-parasitic third-stage larvae (PP L3). Transcript abundances were calculated as fragments per kilobase of coding exon per million mapped reads (FPKM) and log transformed. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. The y-axes were scaled from 0 to 3.5 to aid comparison between genes.