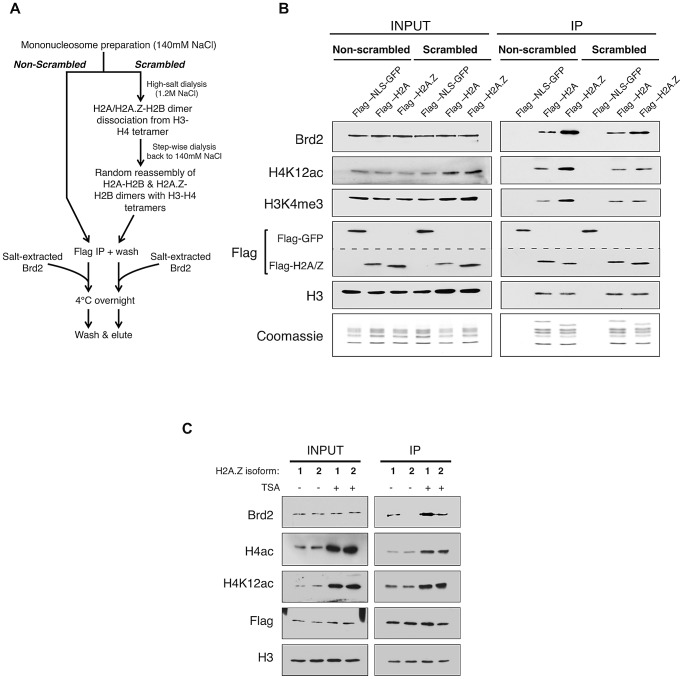
Figure 4. Additional elements of the H2A.Z nucleosome contribute to the interaction with Brd2.
A. Schematic workflow of nucleosome preparation used to randomly re-assemble H2A–H2B and H2A.Z-H2B dimers with H3–H4 tetramers, generating H2A- and H2A.Z-nucleosomes with comparable levels of H3 and H4 PTMs. B. Western blot comparison of “scrambled” versus “non-scrambled” nucleosomes for H3 and H4 PMTs and Brd2 binding. Immunoprecipitated nucleosomes subjected to re-assembly via high-salt/low-salt dialysis (scrambled) show comparable levels of H4 acetylation and H3 methylation compared to non-scrambled control nucleosomes, which show an enrichment of these marks on H2A.Z nucleosomes. Consistent with previous experiments, Brd2 shows preferential enrichment on H2A.Z nucleosomes in the non-scrambled control samples. Brd2 still shows a slight preference for H2A.Z nucleosomes, compared to H2A nucleosomes even when levels of H4 acetylation are comparable in the scrambled nucleosomes. The dashed lined between the two Flag blots is to indicate that a single membrane was cut and therefore Flag-NLS-GFP and Flag-H2A/H2A.Z blots are shown as separate panels. C. Comparison of Brd2 interaction with mononucleosomes containing the different isoforms of H2A.Z. Mononucleosomes IPs were performed as described in Materials and Methods, using cells expressing either Flag-H2A.Z-1 or Flag-H2A.Z-2. Although comparable levels of H4 acetylation are present on H2A.Z-1- and H2A.Z-2-nucleosomes, Brd2 is preferentially enriched on H2A.Z-1 nucleosomes, under both DMSO- and TSA-treated conditions.